
a)
To Draw: the graph for demand, marginal cost, and marginal revenue curves.
a)
Answer to Problem 12.2P
Explanation of Solution
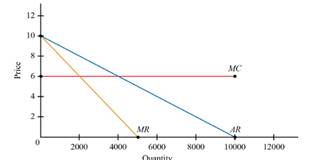
Given Figure
Given demand is
Marginal cost is constant at
Marginal revenue curve=
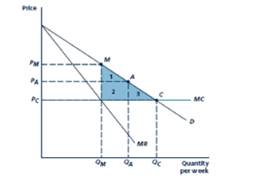
The above figure shows that demand curve, marginal cost curve and marginal revenue.
One of the negatively sloped curve is demand Curve. Also the marginal revenue curve is negatively sloped and twice vertically than the demand curve. The marginal cost is fixed and finally marginal cost is horizontal.
Introduction:
When the produced quantity is added by one whenever changes occur in the whole cost is called marginal cost. Suppose many number of goods are produced that time the marginal cost will be increased unit by unit.
One of another revenue that would be generated by product sales when increasing with one unit is called market revenue. It’s defined by divide the changes in total revenue and changes in output quantity.
b)
To Calculate: the price and quantity associated with Point C, the
b)
Answer to Problem 12.2P
Industry Profit is
Consumer Surplus is
Social Welfare is
Explanation of Solution
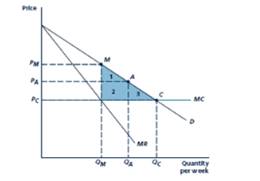
Given Figure
Given demand is
Marginal cost is constant at
Marginal revenue curve=
When the Price equals marginal cost, i.e.)
The price level of
Thus, when the competitive equilibrium C, the quantity level is
The total revenue
The marginal cost is constant at
The total cost
Thus, the total revenue and total cost are equal, the industry profit is
The consumer surplus equals to the area of triangle BCD.
Area of triangle
Consumer Surplus
Social welfare= Consumer surplus +Industry Profit
Introduction:
c)
To Calculate: the price and quantity associated with point M, the
c)
Answer to Problem 12.2P
Industry Profit is
Consumer Surplus is
Social Welfare is
Deadweight loss is
Explanation of Solution
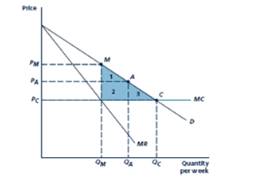
Given Figure
Given demand is
Marginal cost is constant at
Marginal revenue curve=
The monopoly outcome M, the quantity level is
The total revenue
The marginal cost is constant at
The total cost
Thus, the total revenue and total cost are
The industry profit is

The consumer surplus equals to the area of triangle BME.
Area of triangle
Consumer Surplus
Social welfare= Consumer surplus +Industry Profit
Deadweight Loss=Social welfare at competitive equilibrium - social welfare at the monopoly outcome
Introduction: One kind of firms are having formal agreement for collusion to produce the trademark output and sell in the trademark price is generally known as cartel. Extreme type of perfect collusion is called Perfect cartel. Through this, firms producing a different homogeneous product to make the centralized product.
d)
To Calculate: the price and quantity associated with point A, a hypothetical imperfectly competitive outcome, it lies at a price halfway between C and M and also compute industry profit, consumer surplus, social welfare and deadweight loss.
d)
Answer to Problem 12.2P
Industry Profit is
Consumer Surplus is
Social Welfare is
Deadweight loss is
Explanation of Solution
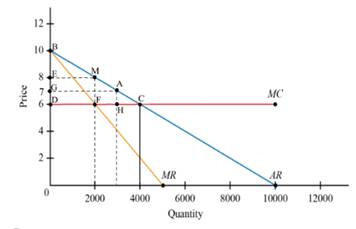
Given Figure

Given demand is
Marginal cost is constant at
Marginal revenue curve=
When the Price equals marginal cost, i.e.)
The price level of
The outcome A, the quantity level is
The total revenue
The marginal cost is constant at
The total cost
Thus, the total revenue and total cost are
The industry profit is

The consumer surplus equals to the area of triangle BAG.
Area of triangle
Consumer Surplus
Social welfare= Consumer surplus +Industry Profit
Deadweight Loss=Social welfare at competitive equilibrium - social welfare at the outcome A
Introduction: imperfectly competition occurs in a market suppose one of the conditions are left or unmet with perfectly competition. This kind of market is generally very common. Here products and services and prices are not set by supply and demand.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK INTERMEDIATE MICROECONOMICS AND ITS
- Discuss the economic efficiency comparisons between a perfectly competitive market and a monopoly. Consumer surplus Producer surplus Deadweight surplusarrow_forwardTwo curves that remain parallel as the quantity of output increases are:. Single choice. Total fixed cost and total variable cost. Total cost and total variable cost. Average fixed cost and average variable cost. Average total cost and average fixed cost. Which of the following is necessary for a natural monopoly?. Single choice. economies of scale copy rights government regulations all of the above Price discrimination involves. Single choice. firms selling different products at different prices to different consumers. firms selling the same product at different prices to different consumers. consumers discriminating between different sellers on the basis of the different prices they quote for different products. consumers discriminating between different sellers on the basis of the different prices they quote for the same product. A profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market is currently producing 100 units of output. It has average revenue…arrow_forwardThese are statements comparing monopoly with perfect competition. Which of the following statements is/are false? Select all that apply. A. A a perfectly competitive industry faces a horizontal straight line demand curve whereas a monopoly faces a downward sloping demand curve. B. A perfectly competitive firm faces a small fraction of the industry demand curve whereas a monopoly faces the entire market demand curve. C. A perfectly competitive firm can only set quantities; a monopoly can set both price and quantity, although once it chooses a price (quantity), the other variable, quantity (price), is determined by the demand curve it faces. D. A perfectly competitive equilibrium is efficient; a monopoly equilibrium is inefficient. E. A perfectly competitive firm necessarily earns zero economic profit in a long run equilibrium; a monopoly typically earns a super-normal profit in a long run equilibrium.arrow_forward
- Consider a market with demand function P = 12 - 0.04Q and marginal cost function P = 6 + 0.12Q. (a) If this market is perfectly competitive, compute the equilibrium price, the equilibrium quantity, the consumer surplus and the producer surplus in the market. (b) If this market is a monopoly, compute the equilibrium price, the equilibrium quantity, the consumer surplus, the producer surplus and the deadweight loss (if any) in the market. Support your answers for (a) and (b) with one suitable market diagramarrow_forwardA firm sells some output in a perfectly competitive market, where the price is $60 per unit, and some on a market in which it has a monopoly, with a demand function p2= 100 - q2, where q2 is output in the monopoly market. Its total-cost function is C= (q1+q2)^2, where q1 is output in the competitive market. Find the profit maximizing outputs in the two markets and discuss the nature of the equilibrium. Suppose now that the price in the competitive market falls to $10. Find the new profit-maximizing solution, and discuss how it compares with the original.arrow_forwardIf occupational safety laws were changed so that firms no longer had to take expensive steps to meet regulatory requirements, we would expect a.competition to force producers to pass the lower production costs on to consumers in the long run. b.the firms in the industry to make long-run economic profit. c.the market price of the products of this industry to decrease in the short run but not in the long run. d.the demand for the products of this industry to increase.arrow_forward
- Intel is the world’s largest manufacture of semiconductor chips by revenue. During the 1990s, Intel became the dominant supplier of microprocessors for PCs and was known for aggressive and anti-competitive tactics in defense of its market position. Consider the market for Intel’s Pentium II processor, released in May 1997. Assume Pentium II enjoyed a monopoly in computer processors. Intel’s cost of production is characterized by function C = 10Q2, marginal cost MC = 20Q, while the market demand for the product is P = 400 − 10Q. Calculate Intel’s profit-maximizing quantity for its Pentium II processor. How much would Intel price its Pentium IIs?arrow_forwardSuppose that the average cost to one firm to supply an entire market is less than the average cost at which two or more firms could supply the same market, what is this industry called? a natural monopoly a resource industry a government monopoly an exclusive industry.arrow_forwardA natural monopoly is most likely to occur in which of the following industries? Group of answer choices a. the pharmaceutical industry because the development and approval of new drugs through the Food and Drug Administration can take more than 10 years b. the diamond mining and marketing industry because one firm can control a key resource c. the software industry because of the importance of network externalities d. an industry where fixed costs are very large relative to variable costsarrow_forward



 Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning





