
Exercises 13 through 16 refer to the construction of the quadratic Koch island. The quadratic Koch island is defined by the following recursive replacement rule.
Quadratic Koch Island
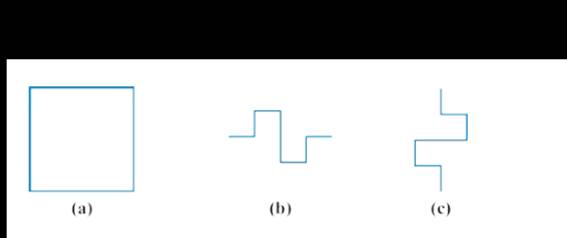
• Start: Start with a seed square [Fig. 12-37(a)]. (Notice that here we
are only dealing with the boundary of the square.)
• Replacement rule: In each step replace any horizontal boundary
segment with the “sawtooth” version shown in Fig. 12-37(b) and
any vertical line segment with the “sawtooth” version shown in Fig.
12-37(c)
This exercise is a continuation of Exercise 13.
a. Find the area of the figure obtained in Step
b. Find the area of the figure obtained in Step
c. Explain why the area of the quadratic Koch Island is the same as the area of the seed square.
13. Assume that the seed square of the quadratic Koch Island has sides of length
a. Carefully draw the figures obtained in Steps
b. Find the perimeter of the figure obtained in Step
c. Find the perimeter of the figure obtained in Step
d. Explain why the quadratic Koch island has infinite perimeter.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
EXCURSIONS IN MODERN MATH. >ANNOT.<
- Suppose we used our failing perfect shuffling of digits to mix the digits of the numbers (x,y) that describe a point on the square to get a one-to-one correspondence with the points on a line segment. What point in the square would be paired with the point 0.12000100010001000100010001...?arrow_forwardUse the Simplex algorithm to solve the following LP models:arrow_forwardfind the dimensions of the desired canarrow_forward
- a. Draw any two segments, AC and BD, that bisect each other at O. Whatappears to be true of quad. ABCD?b. This exercise investigates the converse of what theorem?arrow_forward13. A point lies on the bisector of LABC if and only if it is equidistant fromA and C.arrow_forwardLet A and B be congruent nonintersecting cubes, with B a translated copy of A. What is the most faces conv(A U B) can have? What is the fewest?arrow_forward
- You are given the cyclic quadrilateral ABCD. Show that if the diagonals AC and BD have the same length, then a pair of opposite sides of the quadrilateral have the same length (although a different length to the diagonals).arrow_forwardI need help with all parts of this questiion 16arrow_forwardThe upper line as shown is described by N = (2.233 × 109) × 10(Year-2014)/10.1. Based upon a straight-line projection, estimate the number of transistors in a complex IC chip in the year 2021.arrow_forward
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra for College StudentsAlgebraISBN:9781285195780Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra for College StudentsAlgebraISBN:9781285195780Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. SchwittersPublisher:Cengage Learning


