
Concept explainers
To Find:The tension in the backstay and the normal force that the deck exerts on the mast.
Answer to Problem 17P
The tension in thee backstay is
The normal force exerted by the deck on the mast is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Free body diagram for the given situation is as follows:
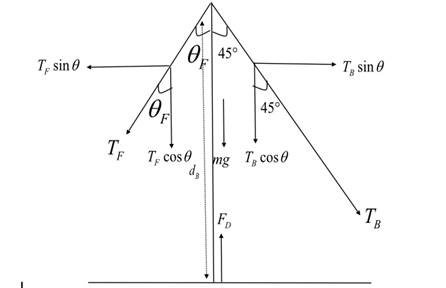
Formula used:
Apply the condition of translational and
Calculation:
Apply the condition of rotational equilibrium to the mast. The net torque due to tension by the wires is equal to zero and is represented as:
Torque due to the left side of the pole is given as
Torque due to right side of the pole is given as
Since the torque due to right side of the wire is in clock wise direction, it is negative.
Thus, the torque of horizontal components according to the condition of rotational equilibrium is given as
Here,
Substitute
From the figure, angle of forestay is obtained as follows:
Here,
Substitute
Determine the tension in the backstay as below.
Substitute the
Therefore, the tension in the backstay is
Torque due to the left side of the pole is given as,
Torque due to right side of the pole is given as,
Since the torque due to right side of the wire is in clock wise direction, it is negative.
Thus, the net torque of vertical components according to the condition of rotational equilibrium is given as,
Here,
Re-arrange the above equation for
Substitute
Conclusion:
The normal force exerted by the deck on the mast is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- A uniform steel plate 18 in. square weighing 68 lb is suspended in the horizontal plane by the three ver- tical wires as shown. Calculate the tension in each wire.arrow_forwardEnd A of the bar AB inFig. rests on a frictionlesshorizontal surface, and end Bis hinged. A horizontal force F S ofmagnitude 220 N is exerted on endA. Ignore the weight of the bar. Whatare the horizontal and vertical componentsof the force exerted by thebar on the hinge at B?arrow_forwardAn electric post is supported by a guy wire which exerts a pull of 100N on the top of the post. If the angle between the guy wire and the ground is 60 degrees, determine the vertical component of the force supporting the polearrow_forward
- The total mass of cable ACB is 20 kg. Assuming that the mass of the cable is distributed uniformly along the horizontal, determine (a) the sag h, (b) the slope of the cable at A.arrow_forwardA 500-kg load is suspended from the end of a horizontal boom, as in the figure. The angle between the boomand the cable supporting its end is 450Assuming that the boom’s mass can be neglected compared with thatof the load, find (a) the tension in the cable and, (b) the inward force the boom exerts on the wall.arrow_forward(2) Draw the free body diagram of the bar below Uniform horizontal bar of mass m suspended by vertical cable at A and supported by rough inclined surface at B. B.arrow_forward
- A uniform drawbridge must be held at a 38o angle above the horizontal to allow ships to pass underneath. The drawbridge weights 55000 N and is 15.0 m long. A cable is connected 3.5 m from the hinge where the bridge pivots (measured along the bridge) and pulls horizontally on the bridge to hold it in place. What is the tension in the cable? Find the magnitude and direction of the force the hinge exerts on the bridge. If the cable suddenly breaks, what is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the drawbridge just after the cable breaks? What is the angular speed of the drawbridge as it becomes horizontal? What is the velocity of the drawbridge, just before it “hits” (i.e. goes horizontal)?arrow_forwardinoge The Fink truss is supported by a hinge at A and by rollers on a 1 to 2 slope at B. The bracing bars are normal to the inclined members at their midpoints. The wind loads are perpendicular to AC. Determine the resultant of the forces. 1580 Ib 3160 Ib 1580 Ib 12' В 8400 Ib 18.000 lb 72'arrow_forwardA 1260 N uniform beam is attached to a vertical wall at one end and supported by a cable on th other end. A 1960 N crate hangs from the far end of the beam. Using the info on the diagram find the following: a) Magnitude of the tensiossnj on the cable b) the horizontal components of the varce that the wallexerts on the beam c) the vertical components of the force that the wall exerts on th eleft end of the beanarrow_forward
- a 1001 N uniform beam is attached to a vertical wall at one end and js supported by a cable at the other end 1550 N crate hangs from the far end of the beam find the magnitude if the tension in the wire the angle theta is 21 degrees and phi is 32 degrees length of beam is Larrow_forwardA 9.00-m-long uniformbeam is hinged to a vertical walland held horizontally by a 5.00-mlongcable attached to the wall 4.00m above the hinge (Fig. ).The metal of this cable has a teststrength of 1.00 kN, which meansthat it will break if the tension init exceeds that amount. (a) Drawa free-body diagram of the beam.(b) What is the heaviest beam thatthe cable can support in this configuration?(c) Find the horizontaland vertical components of theforce the hinge exerts on the beam. Is the vertical component upwardor downward?arrow_forwardThe 50-kg pot is supported from A by the three cables. Calculate the force acting in each cable for equilibrium. Take d = 2.5 marrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
