
To evaluate: The intersection of best-response functions between firms.
Answer to Problem 1RQ
The intersection between firm’s responses proves to be graphical representation of Nash equilibrium.
Explanation of Solution
The following diagram shows the best-response functions of Firm-A and Firm-B.
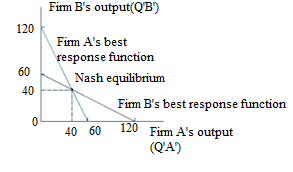
From the above diagram, it is clear that Firm A’s best-response function depicts the profit- maximizing quantity by the quantity chosen by Firm ‘B’. Similarly, the Firm ‘B’ best-response function depicts the profit-maximizing quantity chosen by Firm ’A’. To get the Nash equilibrium, both firms have to contribute their best-responses. The point of intersection of both the responses Q’A’ and Q’B’ is at 40.
The diagram given in 12.2 depicts the intersection between the firm’s best response stating the Cournot model and similarly the diagram given in 12.3 depicts the intersection between the firm’s best response stating the Bertrand model of Nash equilibrium. This is because the intersection depicts the situation where both the firms are stable. There won’t be any incentives if any changes occur in the quantity in case of Cournot model and no incentives are entertained if there is change in prices in case of Bertrand model.
In case of any deviation from the intersection point, it will lead to responses related to the other firm. This situation can be settled only if the intersection point is reached again.
Introduction:
Nash equilibrium: It is a situation where a stable state is created. At this stage, different participants interact with other and does not involve any gain or profit by change in strategy by one participant while other participants strategies remain constant.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application, 12th edition with CD-ROM (Exclude Access Card)
- 4)The result with unspecified N firms can be applied to N approaching infinity. Q2) Which of the following statements about the classic Cournot duopoly model is incorrect? 1)The products of the two firms are homogeneous. 2)It is a static game with complete information. 3)The two firms decide on their prices and let their quantities be dictated demand conditions. 4)There exist examples that have unique Nash equilibrium pointsarrow_forwardConsider a Duopoly model, in which two firms decide a quantity sequentially. For the convenience, let's say Firm 1 is a dominant firm and Firm 2 is a follower. The market demand is given by P=110 - 5Q, where Q is the total output (i.e., Q=Q1+Q2). Each firm has an identical cost function, TCi=7Qi, i=1, 2. Each firm maximizes its profit by choosing the quantity. In this Stackelberg equilibrium, Firm 1 will sell __________ units.arrow_forwardConsider a Duopoly model, in which two firms decide a quantity sequentially. For the convenience, let's say Firm 1 is a dominant firm and Firm 2 is a follower. The market demand is given by P=110 - 5Q, where Q is the total output (i.e., Q=Q1+Q2). Each firm has an identical cost function, TCi=7Qi, i=1, 2. Each firm maximizes its profit by choosing the quantity. In this Stackelberg equilibrium, Firm 1 will sell how many units.arrow_forward
- Assuming Cournot-Nash market, fill in the table below when firm one has MC, = 10, firm two has MC2 = 20 and firm three has MC3 = 20. Additionally, there is no Fixed cost for none of the firms.Using data from the table below, explain the merger paradox when firms 2 and 3 merge. How the merged firm (firm 2 and 3) will be worse off?How would this outcome differ if all three firms merged?arrow_forwardAnswer the given question with a proper explanation and step-by-step solution. Three firms produce identical products and compete in a market where the inverse demand function is P(q1, q2, q3) = 78 − q1− q2− q3. Each has a per-unit cost of 14 and zero fixed cost. They simultaneously choose quantities. In scenario (a), find the Nash equilibrium of this game and let A = firm 2's profit in the Nash equilibrium. In scenario (b), assume that the firms form a cartel, i.e., they act as a monopoly and split the profit evenly. If the total quantity produced by the cartel is Q, then the inverse demand is P(Q) = 78 - Q. Let B = firm 2's profit in the cartel. Calculate the value of A - B and enter your answer in the box below. Please round your answer to 3 decimal places (e.g., write 4/3 as 1.333).arrow_forwardThree oligopolistic firms ("1", "2" and "3") conduct quantity competition in a certain market. The interactions between them take place as follows: firm 1 defines its production quantity, which is immediately observed by firms 2 and 3; then, firm 2 makes its decision on how much it will produce, and only after observing the decisions of firms 1 and 2 does firm 3 finally make its respective choice. Furthermore, the total costs of firms 1, 2 and 3 correspond respectively to c₁(q₁) = 10q₁, c₂(q₂) = 8q₂ and c₃(q₃) = 2q₃, and the firms face a (inverse) demand given by p(Q) = 110 - Q (where Q = q₁ + q₂ + q₃). Based on this information, determine what will be the total amount produced by the firms in the (single) ENPS for that game. (Note: the correct answer is an integer.)arrow_forward
- Three firms produce identical products and compete in a market where the inverse demand function is P(q1, q2, q3) = 78 − q1− q2− q3. Each has a per-unit cost of 14 and zero fixed cost. They simultaneously choose quantities. In scenario (a), find the Nash equilibrium of this game and let A = firm 2's profit in the Nash equilibrium. In scenario (b), assume that the firms form a cartel, i.e., they act as a monopoly and split the profit evenly. If the total quantity produced by the cartel is Q, then the inverse demand is P(Q) = 78 - Q. Let B = firm 2's profit in the cartel. Calculate the value of A - B and enter your answer in the box below. Please round your answer to 3 decimal places (e.g., write 4/3 as 1.333).arrow_forwardThe figure below shows the market conditions facing two firms, Brooks, Inc., and Spring, Inc., in the domestic market for large utility pumps. Each firm has constant long-run costs, so that MC0 = AC0. As competitors in a duopoly, there are a number of models to determine output and prices. Assume that the Bertrand duopoly model applies, so that they both set price equal to their marginal cost. Initial output in this market will be 16,000 per year (this is split between the two firms), at a price of $300. (a) At the initial equilibrium, what is total surplus (consumer surplus plus producer surplus)? Suppose that Brooks, Inc. and Spring, Inc. form a joint venture, River Company, whose utility pumps replace the output sold by the parent companies in the domestic market. Assuming that River Company operates as a monopolist and that its costs equal MC0 = AC0, what is: (b) The price? (c) The output? (d) Total profit? (e) The resulting deadweight loss from River Company operating as a…arrow_forwardThe figure below shows the market conditions facing two firms, Brooks, Inc., and Spring, Inc., in the domestic market for large utility pumps. Each firm has constant long-run costs, so that MC0 = AC0. As competitors in a duopoly, there are a number of models to determine output and prices. Assume that the Bertrand duopoly model applies, so that they both set price equal to their marginal cost. Initial output in this market will be 16,000 per year (this is split between the two firms), at a price of $300. Suppose that Brooks, Inc. and Spring, Inc. form a joint venture, River Company, whose utility pumps replace the output sold by the parent companies in the domestic market. Assuming that River Company operates as a monopolist and that its costs equal MC0 = AC0, what is: (b) The price?arrow_forward
- The figure below shows the market conditions facing two firms, Brooks, Inc., and Spring, Inc., in the domestic market for large utility pumps. Each firm has constant long-run costs, so that MC0 = AC0. As competitors in a duopoly, there are a number of models to determine output and prices. Assume that the Bertrand duopoly model applies, so that they both set price equal to their marginal cost. Initial output in this market will be 16,000 per year (this is split between the two firms), at a price of $300. Suppose that Brooks, Inc. and Spring, Inc. form a joint venture, River Company, whose utility pumps replace the output sold by the parent companies in the domestic market. Assuming that River Company operates as a monopolist and that its costs equal MC0 = AC0, what is: (e) The resulting deadweight loss from River Company operating as a monopoly?arrow_forwardThe figure below shows the market conditions facing two firms, Brooks, Inc., and Spring, Inc., in the domestic market for large utility pumps. Each firm has constant long-run costs, so that MC0 = AC0. As competitors in a duopoly, there are a number of models to determine output and prices. Assume that the Bertrand duopoly model applies, so that they both set price equal to their marginal cost. Initial output in this market will be 16,000 per year (this is split between the two firms), at a price of $300. Suppose that Brooks, Inc. and Spring, Inc. form a joint venture, River Company, whose utility pumps replace the output sold by the parent companies in the domestic market. Assuming that River Company operates as a monopolist and that its costs equal MC0 = AC0, what is: (c) The output? (d) Total profit?arrow_forwardDan Murphy's (DM) and BWS are the only two liquor chains in Australia that hold the rights to sell a popular new beer named Victoria Sweeter (VS). Both Dan Murphy's and BWS are contemplating between charging a high price ($60 per case) or a low price ($40 per case). The payoff matrix below shows all possible scenarios and outcomes for the two firms. BWS Charge $60 per case Charge $40 per case Dan Murphy's (DM) Charge $60 per case DM: $30,000 profitBWS: $25,000 profit DM: $13,000 profitBWS: $38,000 profit Charge $40 per case DM: $45,000 profitBWS: $12,000 profit DM: $19,000 profitBWS: $20,000 profit * Profits reported in the above table are monthly figures on the Victoria Sweeter (VS) beer only. Required: (a) Identify the dominant strategy for Dan Murphy's in this game. Show a detailed analysis to prove why it is the dominant strategy (b) Identify the non-cooperative* Nash equilibrium for this game. (* Non-cooperative means that each firm makes their…arrow_forward
 Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc



