
(a)
The IS and the LM equilibrium of the economy.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The investment function of the economy is given by
The values of the C, T, I and G can be plugged into the IS equation as follows:
The money demand function of the economy is given as
The supply of real money balances can be calculated by dividing the money supply with the price level in the economy. Since the values of the two are given, the value of the supply of the real money balances can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the supply of real money balance is 3,000. The LM curve can be calculated by setting the demand equation equal to the supply equation as follows:
The IS - LM equilibrium can be calculated by equating the IS equation equal to the LM equation. Thus, the IS-LM equilibrium can be calculated as follows:
By substituting the value of r in any equation, it can provide the value of Y as follows:
Thus, the rate of interest and the Y is 10 and 5,000, respectively. These values can be illustrated at point A through the graph as follows:
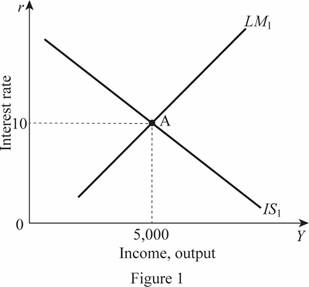
In Figure 1, horizontal axis measures the income or output and vertical axis measures the interest rate.
Fiscal policy: The fiscal policy is the policy of the government regarding the government expenditures and taxes of the economy.
(b)
The impact of tax cuts of 20 percent on the IS-LM equilibrium and the tax multiplier.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
When the tax rate decreases by 20 percent, the tax will be 800 in the economy. The IS curve will be then as follows:
The IS - LM equilibrium can be calculated by equating the IS equation equal to the LM equation. Thus, the IS-LM equilibrium can be calculated as follows:
By substituting the value of r in any equation, it can provide the value of Y as follows:
Thus, the rate of interest and the Y is 11.5 and 5,300, respectively. These values can be illustrated through the graph as follows:
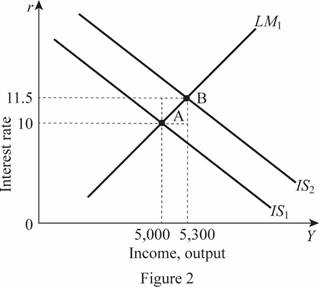
In Figure 2, horizontal axis measures the income or output and vertical axis measures the interest rate. Thus, the decrease in the tax rate by 20 percent leads to a shift in the IS curve toward the right by 300 forming a new equilibrium point B. The tax multiplier can be calculated by subtracting the change in the total output by the negative change in the taxes as follows:
Thus, the tax multiplier is -1.5.
(c)
The impact of holding the interest rate constant by Fed on Equilibrium.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The supply of real money balances can be calculated by dividing the money supply with the price level in the economy. Since the values of the two are given, the value of the supply of the real money balances can be calculated as follows:
The LM curve can be calculated by setting the demand equation equal to the supply equation as follows:
The IS - LM equilibrium can be calculated by equating the IS equation equal to the LM equation. Thus, the rate of interest is held constant which is equal to 10 and this value can be substituted in the equilibrium equation in order to calculate the money supply as follows:
By substituting the value of r in any equation, it can provide the value of Y as follows:
Thus, the rate of interest is held constant by the fed and adjusted the money supply to 7,600. Then, the Y is calculated as 5,600. These values can be illustrated through the graph as follows:
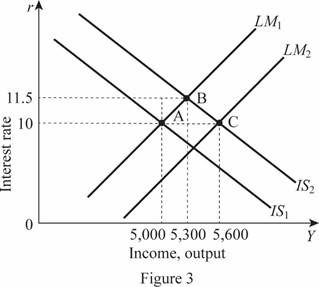
In Figure 3, horizontal axis measures the income or output and vertical axis measures the interest rate. Thus, the change leads to a shift in the LM curve toward the right by 600 by forming a new equilibrium point C. The tax multiplier can be calculated by subtracting the change in the total output by the negative change in the taxes as follows:
Thus, the tax multiplier is -3.
(d)
The impact keeping income constant through money supply on equilibrium and the tax multiplier.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
When the Fed gives importance to keep the income of the economy constant at 5,000 after the tax deduction, the value of the rate of interest can be calculated by plugging the value of the Y into the equation as follows:
Thus, the rate of interest in the economy will be then 13, which can be substituted in the LM curve to calculate the value of M as follows:
Thus, the value of M is 4,800. Thus, M decreases to 4,800 from 7,600 which means the LM curve will shift toward the left reducing the equilibrium to point D. Therefore, it can be illustrated as follows:
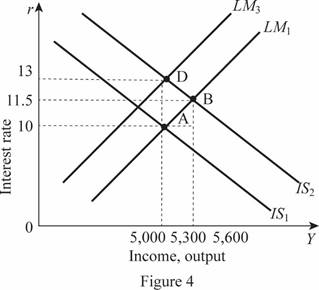
In Figure 4, horizontal axis measures the income or output and vertical axis measures the interest rate. Since the output is not changing and maintaining the same level of 5,000, there will be zero tax multiplier in the economy.
(d)
The illustration of all the equilibrium points of all the changes.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The various IS-LM equilibrium points can be illustrated on the single graph as A, B, C, and D as follows:
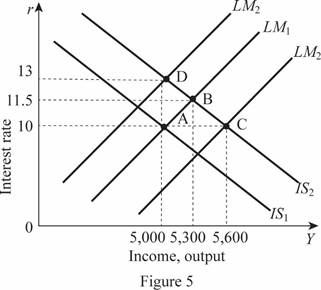
In Figure 5, horizontal axis measures the income or output and vertical axis measures the interest rate.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
MACROECONOMICS+SAPLING+6 M REEF HC>IC<
- Determine whether each of the following statements is true or false, and explain why it is true or false. Use the graph to clarify your answer. [2 x 3 marks] If the investment does not depend on the interest rate, IS curve is vertical. If there is an increase in Government expenditure IS curve will shift to the left.arrow_forwardConsider an economy described by the following equations:Y = C + I + GY = 5,000G = 1,000T = 1,000C = 250 + 0.75(Y −T )I = 1,000 − 50 r. a) find the equilibrium interest ratearrow_forwardConsider an economy described by the following equations. Y=C+I+G C=100+.75(Y−T) I=500−50r G=125 T=100 Where: Y is GDP, C is consumption, I is investment, G is government spending, T is taxes and r is the rate of interest. Question: In this case, explain the policy that was used by the policymaker to target the aggregate demand.arrow_forward
- Consider an economy described by the following equations:Y = C + I + GY = 5,000G = 1,000T = 1,000C = 250 + 0.75(Y −T )I = 1,000 − 50 r. a)Find the new equilibrium interest ratearrow_forwardConsider an economy described by the following equations: Y=C+I+G C=100+.75(Y−T)C=100+.75(Y−T) I=500−50rI=500−50r G=125G=125 T=100T=100 Where: Y is GDP, C is consumption, I is investment, G is government spending, T is taxes and r is the rate of interest. Questions: a. What is the value of the multiplier? b. What is the equilibrium equation for Y? Show solution. c. Suppose the Central Bank policy is to adjust the money supply to maintain the interest rate at 4 percent,so r=4. What is the value of output? d. Assuming that no change in fiscal policy, what is the effect of a reduction in interest rate from 4 percent to 3 percent on equilibrium output. e. In this case, explain the policy that was used by the policymaker to target the aggregate demand.arrow_forwardThe following equations describe an economy. Y=C+I+G C=120+0.6(Y-T) I=100-10r, G=60 T=40 M/P=Y-20r. M=600 P=20 a. Derive the equations for IS and LM curves. b. Find the equilibrium level of income and the equilibrium interest rate. c. Suppose government expenditure increases by 50%. Find the equilibrium interest rate and income.arrow_forward
- The following equations describe an economy. Y = C + I + G. C = 120 + 0.5( Y - T ). I = 100 - 10r. G = 50. T = 40. ( M/ P) d = Y - 20r. M = 600. P = 2. What are the equilibrium level of income and the equilibrium interest rate? If the government increases government spending by 45, what will be the new equilibrium level of income and equilibrium interest rate?arrow_forwardDraw a well labeled diagram of the LM Curve. Determine the equilibrium level of income and equilibrium interest ratearrow_forwardGeneral Equilibrium is a situation in which all market in an economy are simultaneously in equilibrium (both the good market and the money market in equilibrium, as shown below). Now suppose the U.S. economy is now shown at the intersection of the IS and LM curves. Now President Joe Biden passed his Infrastructure bill. Please use graph to explain how such a bill may affect the economy in the long run and short run, in terms of price level, P, output Y and interest rate r. Please also add the AD-AS analysis with your argument.arrow_forward
- Consider the following IS–LM model: C = 100 + .25YD I = 50 + .25Y - 1000i G = 150 T = 100 (M/P) d = 2Y - 8000i (M/P)s = 1000 a. Derive the IS relation b. Derive the LM relation c. Solve for equilibrium real output. d. Solve for the equilibrium interest rate e. Solve for the equilibrium values of C and I f. now suppose that the money supply increases to M/P = 1010. Solve for T, f. suppose that government spending increases to G = 155 What is the value of money supply? g. From what we studied, which policy, expansionary fiscal policy or expansionary monetary policy will undoubtedly increase investment.arrow_forwardConsider an economy with the following information: Y = C + I + G, C=180+0.7( Y-T), I= 100-18i + 0.1 Y, T =400, G=400, P=1, M=5400, L=6Y -120i, M/P=L Derive the IS equation. Derive the LM equation. Solve the IS-LM to obtain the equilibrium output and the interest ratearrow_forwardQUESTION TWOConsider a hypothetical economy with the following model.Goods Market Money MarketC = 200 + 0.75(Y − T) (M/P)d = Y − 100rI = 200 − 25? Ms = 1000G = 100 P = 2T = 100A. Derive an expression for the IS curve and an expression for the LM curve. B. On the same set of axes, draw the IS and LM curve. C. Find the level of interest and income that ensures a simultaneous equilibrium in the goods and money market.arrow_forward


