
Concept explainers
(a)
To Calculate: The force that exerted by the ladder against the wall.
(a)
Answer to Problem 67P
Explanation of Solution
Given information :
Mass of the ladder
Tension of the wire
Breaking point tension of the wire
Mass of the person
Formula used:
Torque can be obtained:
Where,
Calculation:
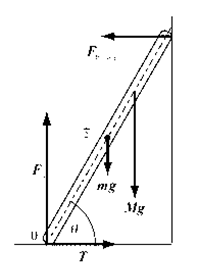
The free-body diagram of the forces acting on the ladder.
Here,
Apply
Solve for
From the figure given above determine
Conclusion:
The force that exerted by the ladder against the wall.
(b)
To Calculate: The distance thatfrom the bottom end of the ladder that can an
(b)
Answer to Problem 67P
Explanation of Solution
Given information :
Mass of the ladder
Tension of the wire
Breaking point tension of the wire
Mass of the person
Formula used :
From Newton’s second law of motion:
Where, m is the mass and a is the acceleration.
Calculation:
Apply
Apply
Here,
Conclusion:
The distance thatfrom the bottom end of the ladder that can an
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Physics For Scientists And Engineers Student Solutions Manual, Vol. 1
- A uniform ladder 10.0 m long and weighing 50.0 N rests against a smooth vertical wall. (a) If the ladder is just on the verge of slipping when it makes a 50.0° with the ground, find the coefficient of static friction between the ladder and ground. (b) If the coefficient of static friction is 0.360, and the same ladder makes a angle with respect to the horizontal, how far along the length of 60.0° the ladder can a 65-kg painter climb before the ladder begins to slip?arrow_forwardTwo ladders, 4.00 m and 3.00 m long, are hinged at point A and tied together by a horizontal rope 0.90 m above the floor. The ladders weigh 480 N and 360 N, respectively, and the center of gravity of each is at its center. Assume that the floor is freshly waxed and frictionless. (a) Find the upward force at the bottom of each ladder. (b) Find the tension in the rope. (c) Find the magnitude of the force one ladder exerts on the other at point A. (d) If an 800-N painter stands at point A, find the tension in the horizontal rope.arrow_forwardOne end of a 2.00 m uniform meter stick is placed against a vertical wall. The other end is held by a lightweight cord that makes an angle θ with the stick. The coefficient of static friction between the end of the meter stick and the wall is 0.530. What is the maximum value that θ can have if the stick is to remainin equilibrium?arrow_forward
- A uniform horizontal board of mass 34 kg and length 4.7 m is supported at each end by vertical posts. A 62 kg man stands on the board 1.3 m from the left end. What are the forces applied to the board by the posts?arrow_forwardThe figure shows three boards clamped together. The center board weighs 93.5 N, and the coefficient of static friction between the boards is 0.490. What is the minimum magnitude of the horizontal compression forces (in N) acting on either side of the center board so it does not slip?arrow_forwardA horizontal plank 4.00 m long and having mass 20.0 kg rests on two pivots, one at the left end and a second 1.00 m from the right end. Find the magnitude of the force exerted on the plank by the second pivot.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
