
Subpart (a):
Effect on Aggregate Demand and Supply.
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
When consumers fear of an impending economic depression, their spending decline and they tend to save more. This leads to a decrease in AD curve. This can be explained by using figure 1.
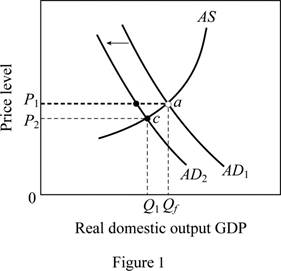
In figure 1, horizontal axis represents the real GDP(
Concept Introduction:
Aggregate demand (AD): Aggregate demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in a given period of time.
Subpart (b):
Effect on Aggregate Demand and Supply.
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
When a new tax is imposed on producers, cost of production comes up and there is no incentive to produce more. This leads to a decline in
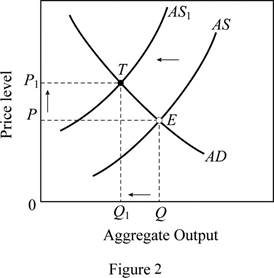
In figure 2, horizontal axis represents the real GDP and vertical axis represents price level. In this case, the AS curve shifts left (from AS to AS1), this moves the equilibrium position from E to T, thus there is a decline in the output (from Q to Q1) and a rise in the price level (from P to P1).
Concept Introduction:
Aggregate demand (AD): Aggregate demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in a given period of time.
Aggregate supply (AS): Aggregate supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in a given period of time.
Subpart (c):
Effect on Aggregate Demand and Supply.
Subpart (c):
Explanation of Solution
Figure 3 can explain the shift in AD curve due to reduction in interest rates at each price level. In figure 3, horizontal axis measures the real GDP and vertical axis measures the price level.
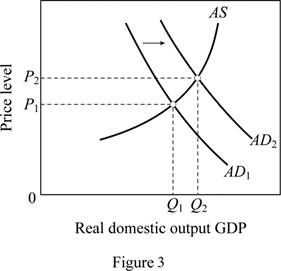
A reduction in interest rates decreases the borrowing cost increases the spending.
This leads to a rightward shift of AD curve from AD1 to AD2. Thus, it brings the output and price level up. The output increases from Q1 to Q2 and price level increases from P1 to P2.
Concept Introduction:
Aggregate demand (AD): Aggregate demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in a given period of time.
Aggregate supply (AS): Aggregate supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in a given period of time.
Subpart (d):
Effect on Aggregate Demand and Supply.
Subpart (d):
Explanation of Solution
A major increase in spending shifts the AD curve to right. Figure 4 is used to explain this situation. In figure 4, horizontal axis measures the real GDP and vertical axis measures the price level.
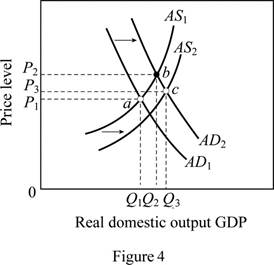
Government expenditure is a key determinant of changes in the aggregate demand. The increase in government spending (spending for health care) increases the aggregate demand leading to a shift of AD curve from AD1 to AD2. Any real improvements in healthcare resulting from the spending would ultimately increase the productivity, thereby shifting the AS curve to the right (from AS1 to AS2). The equilibrium moves from a to c leading to an increase in output (from Q1 to Q3) . It will also move the price level up from P1 to P3.
Concept Introduction:
Aggregate demand (AD): Aggregate demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in a given period of time.
Aggregate supply (AS): Aggregate supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in a given period of time.
Subpart (e):
Effect on Aggregate Demand and Supply.
Subpart (e):
Explanation of Solution
The general expectation of surging inflation in the near future will increase the aggregate demand today because the consumers will want to buy products before their prices escalate. This can be illustrated using figure 3. As a result, there will be a rightward shift of AD curve from AD1 to AD2 which brings the output and price level up. In figure 3, the output increases from Q1 to Q2 and price level increases from P1 to P2.
Concept Introduction:
Aggregate demand (AD): Aggregate demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in a given period of time.
Aggregate supply (AS): Aggregate supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in a given period of time.
Subpart (f):
Effect on Aggregate Demand and Supply.
Subpart (f):
Explanation of Solution
Figure 5 is used to explain this case. In figure 5, horizontal axis measures the real GDP and vertical axis measures the price level.
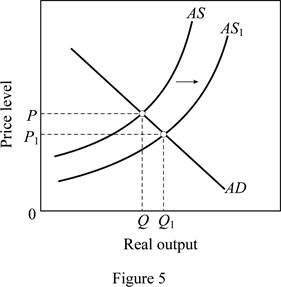
As oil prices fall (oil is an imported resource) due to the disintegration of OPEC, it increases the U.S. aggregate supply. As a result, there will be a rightward shift of AS curve from AS to AS1. This brings the output level up from Q to Q1 and price level down from P to P1.
Concept Introduction:
Aggregate demand (AD): Aggregate demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in a given period of time.
Aggregate supply (AS): Aggregate supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in a given period of time.
Subpart (g):
Effect on Aggregate Demand and Supply.
Subpart (g):
Explanation of Solution
A reduction in the personal income tax rates raises take-home income increases consumer purchases at each possible price level. This is illustrated in figure 3. Tax cuts shift the aggregate demand curve to the right from AD1 to AD2 which brings the output and price level up. In figure 3, the output increases from Q1 to Q2 and price level increases from P1 to P2.
Concept Introduction:
Aggregate demand (AD): Aggregate demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in a given period of time.
Aggregate supply (AS): Aggregate supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in a given period of time.
Subpart (h):
Effect on Aggregate Demand and Supply.
Subpart (h):
Explanation of Solution
The sizable increase the labor productivity with no change in nominal wages will increase the overall productivity as more output is available for the given input. This increases the aggregate supply thereby shifting the AS curve to the right from AS to AS1 (Refer Figure 5). This leads to an increase in output (from Q to Q1) and a decrease in price level from P to P1.
Concept Introduction:
Aggregate demand (AD): Aggregate demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in a given period of time.
Aggregate supply (AS): Aggregate supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in a given period of time.
Subpart (i):
Effect on Aggregate Demand and Supply.
Subpart (i):
Explanation of Solution
This case can be explained using Figure 2. When there is an increase in nominal wages with no change in productivity, it increases per unit cost of production. This force the AS curve to shift left (from AS to AS1). The equilibrium position moves from E to T, thus there are a decline in the output (from Q to Q1) and a rise in the price level (from P to P1).
Concept Introduction:
Aggregate demand (AD): Aggregate demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in a given period of time.
Aggregate supply (AS): Aggregate supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in a given period of time.
Subpart (j):
Effect on Aggregate Demand and Supply.
Subpart (j):
Explanation of Solution
Figure 6 shows the impact of increasing demand and decreasing supply.
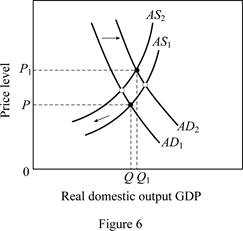
Figure 6 is used to explain this condition. The horizontal axis in Figure 6 measures the real domestic output whereas price level is measured by the vertical axis. A rise in net exports (higher exports relative to imports) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right (from AD1 to AD2). But, due to the higher input prices, per unit cost is more, leading to a shift of the aggregate supply curve to the left from AS1 to AS2. This leads to an increase in output from Q to Q1 along with an increase in price level from P to P1.
Concept Introduction:
Aggregate demand (AD): Aggregate demand refers to the total value of the goods and services that are demanded at a particular price in a given period of time.
Aggregate supply (AS): Aggregate supply refers to the total value of the goods and services that are available for purchase at a particular price in a given period of time.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
MACROECONOMICS (LL)
- Suppose that the aggregate demand and aggregate supply schedules for a hypothetical economy are as shown below: a. Use these sets of data to graph the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves. What is the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real output in this hypothetical economy? Is the equilibrium real output also necessarily the full-employment real output? Explain.b. Why will a price level of 150 not be an equilibrium price level in this economy? Why not 250?c. Suppose that buyers desire to purchase $200 billion of extra real output at each price level. Sketch in the new aggregate demand curve as AD1. What factors might cause this change in aggregate demand? What is the new equilibrium price level and level of real output?arrow_forward7 Suppose that the government increases its expenditure on goods and services by $100 billion and pays for these goods and services by raising autonomous taxes by $100 billion. What is the effect on aggregate demand and real GDP of each change individually and of the two combinedarrow_forward9. Suppose Amal calculates her permanent income by adaptive expectations . Year 2020 Amal's permanent income was 38,000 , and year 2021 actual income is 41,000 . Assume that , long - run marginal to consume is 0.90 and short - run marginal propensity to consume is 0.28 . What is her consumption expenditure year 2021 ? O 36.774 O 35,040 O 40.226 O 33.454 O 34.740 O None of the above is correctarrow_forward
- Suppose that consumer spending initially rises by $5 billion for every 1 percent rise in household wealth and that investment spending initially rises by $20 billion for every 1 percentage point fall in the real interest rate. Also assume that the economy’s multiplier is 4. a. If household wealth falls by 5 percent because of declining house values, and the real interest rate falls by 3 percentage points, in what direction and by how much will the aggregate demand curve initially shift at each price level?arrow_forwardGiven the following information about each economy , either calculate the missing variable or determine that it cannot be calculated . [LO 7.2,7.3] a. If C=\$20.1 billion, I=\$3.5 billion G=\$5.2 billion, and NX=-\$1 billion, what is total income ? b. If total income is $1 trillion G=\$0.3 tr trillion , and C=\$0.5 trillion , what is I? c. If total expenditure is $675 billion, C=\$433 billion , I = $105 billion , and G=\$75 billion , what is NX ? How much are exports ? How much are imports?arrow_forwardSuppose that a hypothetical economy has the following relationship between its real output and the input quantities necessary for producing that output: a. What is productivity in this economy?b. What is the per-unit cost of production if the price of each input unit is $2?c. Assume that the input price increases from $2 to $3 with no accompanying change in productivity. What is the new per-unit cost of production? In what direction would the $1 increase in input price push the economy’s aggregate supply curve? What effect would this shift of aggregate supply have on the price level and the level of real output?d. Suppose that the increase in input price does not occur but, instead, that productivity increases by 100 percent. What would be the new per-unit cost of production? What effect would this change in per-unit production cost have on the economy’s aggregate supply curve? What effect would this shift of aggregate supply have on the price level and the level of real output?arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





