
Concept explainers
The right end of the tube is now scaled with a stopper. The water on both sides remain the same. There is no air between the stopper and the water surface.
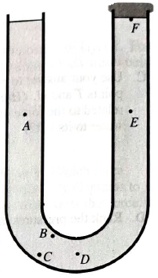
1. Does the pressure at points A and Dincrease, decrease,orremain the same? Explain.
2. Is the pressure al point E greater than, less than, or equal to the pressure at point D?
Does the difference in pressure
3. Is the pressure at pointF greater than, less than, or equal toatmospheric pressure?
Is the force exerted by the rubber stopper on the water surfaceon the right greater than, less than, or equal to the forceexerted by the atmosphere on the water surface on the left?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
Conceptual Integrated Science
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
College Physics
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
- The gauge pressure of the air-water interface in the tank shown in the figure to the right is 65 kPa. (a) Determine the absolute pressure at the interface between water and mercury. (b) What is the gauge pressure at the oil-mercury interface? (c) Determine the differential height h of the mercury column.arrow_forwardA 1-centimeter diameter cylindrical tube is open at the top. Oil is poured into the container followed by water. If the oil has a height of 2 cm and the water has a height of 3 cm, what is the absolute pressure at the bottom of the container in Pascal? The density of water is 1000 kg/m^3 while oil is 820 kg/m^3 solve with full solutions, figure&fbdarrow_forwardAir at 20∘C flows through the tube shown in (Figure 1). Assume that air is an ideal fluid. The density of air is 1.20 kg/m3, the density of mercury is 13600 kg/m3. Suppose that d1 = 3.00 mm and d2 = 1.20 cm . a) What is the air speed v1at point 1? Express your answer with the appropriate units. b)What is the air speed v2 at point 2? c) What is the volume flow rate?arrow_forward
- A car of mass 1500 kg is placed on a large piston with a radius of 4m. (i) What is the minimum upward force that the large piston must exert to lift the car? (ii) If the mechanical advantage of the lift is 20, what is the minimum downward force that must be given? (iii) Calculate the radius of the small piston? (iv) Determine the pressure exerted by the large piston? (v) How much the small piston should descend in order to lift the car by 2m? Discuss on any four applications of Surface tension in real life. How upward force and weight of the displaced fluid are related in fluid mechanics? Explain their related concepts with necessary sketches.arrow_forward1. What will happen to the calculated buoyant force if the object had internal cavities? What will happen to the calculated density? Will you get the correct density of the material? 2. From the previous item, what if the object instead had external cavities?arrow_forwardA) Without calculations, is the speed of the water greater at point 1 or point 2, or can you not tell? B) find the speed of water at point 1 and at point 2 C) without doing any calculations, is the pressure greater at point 1 or point 2, or can you not tell? D) find the pressure at point 1arrow_forward
- A hydraulic lift is used to jack a 960 kg car 42 cm off the floor. The diameter of the output piston is 18 cm, and the input force is 380 N.(a) What is the area of the input piston?(b) What is the work done in lifting the car 42 cm?arrow_forwardQ) Explain pressure in the fluid? And what is Pascal's principle?arrow_forwardWater flows from the pipe shown in (Figure 1) with a speed of 4.0 m/s . a)What is the water pressure as it exits into the air? b)What is the height h of the standing column of water?arrow_forward
- (II) A fish tank has dimensions 36 cm wide by 1.0 m long by 0.60 m high. If the filter should process all the water in the tank once every 3.0 h, what should the flow speed be in the 3.0-cm-diameter input tube for the filter?arrow_forwardA non-viscous fluid with density ρ = 0.810 g/cm3 is flowing in a horizontal direction as shown in the image below. At point 1, the speed of the fluid is v1 = 1.2 m/s. The cross-sectional areas at point 1 and 2 are A1 = 21 cm2 and A2 = 18 cm2, respectively. What is the gauge pressure at point 2 if the gauge pressure at point 1 is 413 Pa?arrow_forwardA hydraulic lift consists of an enclosed fluid with two pistons with circular cross sections - piston A with radius 1 m, and piston B with radius 6 m. a. If a 1000 N force is applied to piston A, what pressure does the fluid underneath it feel due to this force? b. What pressure will piston B feel due to this force? c. How much force will the fluid apply to piston B?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





