
(a)
Interpretation:
What is an ion has to be found and two examples have to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Ionizing radiation:
Ionizing radiation carries energetic electrons from atoms or molecules and thus converts those atoms and molecules as ions. Apart from electrons, ionizing radiation is made up of other energetic sub-atomic particles, ions or atoms that are moving at high-speeds.
(b)
Interpretation:
The examples for species having unpaired electrons have to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Generation of free-radicals:
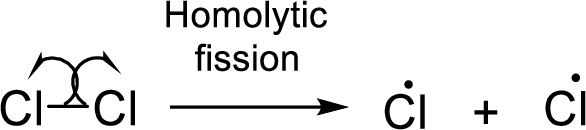
The free radicals are usually initiated by homolytic fission which is the
Example:
(c)
Interpretation:
How do radiation produces ions with unpaired electrons has to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Ionizing radiation:
Ionizing radiation carries energetic electrons from atoms or molecules and thus converts those atoms and molecules as ions. Apart from electrons, ionizing radiation is made up of other energetic sub-atomic particles, ions or atoms that are moving at high-speeds.
Free radicals: Free radicals are fragments that are resulted from homolytic cleavage of a chemical bond and thus hold an unshared electron which is always represented by a dot. These species are highly unstable species and thus being highly reactive species.
(d)
Interpretation:
How free radicals cause random mutation in DNA has to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
Ionizing radiation:
Ionizing radiation carries energetic electrons from atoms or molecules and thus converts those atoms and molecules as ions. Apart from electrons, ionizing radiation is made up of other energetic sub-atomic particles, ions or atoms that are moving at high-speeds.
- • The advantage of using ionizing radiation:
Under controlled circumstances, the use of selective ionizing radiation targets to promote the death of cancerous cells.
- • The disadvantage of using ionizing radiation:
The treatment of ionizing radiation involves the risk of causing damage to DNA and reproductive cells.
DNA:
DNA is a self-replicating genetic material that is present in all living organisms. It carries genetic information from one generation to the several successive generations. Basically it is a biopolymer of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Chemistry in Context
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





