
Concept explainers
(a) How many
signals does each of the following compounds exhibit?

(a)
Interpretation: The number of
Concept introduction: The number of NMR signal in a compound is equal to the number of chemically non-equivalent protons present in that compound. In
Answer to Problem 36P
The given compound A gives four signals and compound B gives five signals in
Explanation of Solution
The given compound A is the ball and stick model of
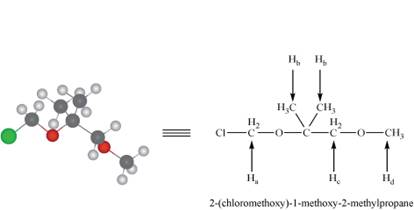
Figure 1
There are four non-equivalent protons
The given compound B is the ball and stick model of propyl butyrate. The bond-line representation of the compound B with all chemically non-equivalent protons is shown below.
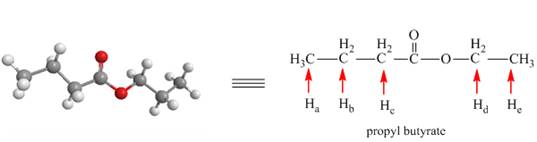
Figure 2
There are five non-equivalent protons
The given compound A gives four signals and compound B gives five signals in
(b)
Interpretation: The number of
Concept introduction: The number of NMR signal in a compound is equal to the number of carbon atoms present in that compound. In
Answer to Problem 36P
The given compound A gives five signals and compound B gives six signals in
Explanation of Solution
The given compound A is the ball and stick model of
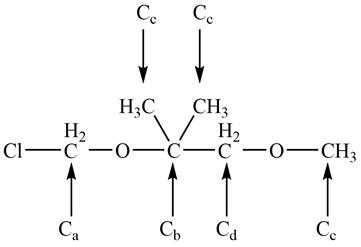
Figure 3
There are five non-equivalent carbon atoms
The given compound B is the ball and stick model of propyl butyrate. The bond-line representation of the compound B with all chemically non-equivalent carbon atoms is shown below.
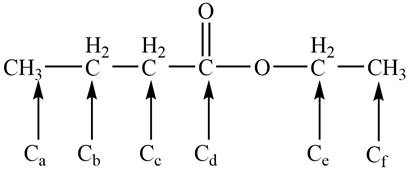
Figure 4
There are six non-equivalent carbon atoms
The given compound A gives five signals and compound B gives six signals in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12C Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL+SM+ACCESS)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (13th Edition)
The Organic Chem Lab Survival Manual: A Student's Guide to Techniques
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
- How many 1H NMR signals would you expect for each compound?arrow_forwardAnswer the following questions for each compound: a. How many signals are in its 13C NMR spectrum? b. Which signal is at the lowest frequency?arrow_forwardDraw all constitutional isomers of molecular formula C3H6Cl2.a. How many signals does each isomer exhibit in its 1H NMR spectrum?b. How many lines does each isomer exhibit in its 13C NMR spectrum?c. When only the number of signals in both 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy is considered, is it possible to distinguish all of these constitutional isomers?arrow_forward
- Draw all constitutional isomers of molecular formula C3H6Cl2. a. How many signals does each isomer exhibit in its 1H NMR spectrum? b. How many lines does each isomer exhibit in its 13C NMR spectrum? c.When only the number of signals in both 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy is considered, is it possible to distinguish all of these constitutional isomers?arrow_forwardHow many H-NMR signals would you expect to see for this compound?arrow_forwardDraw all constitutional isomers of molecular formula C3H6Cl2.a.) How many signals does each isomer exhibit in its 1H NMR spectrum?b.) How many lines does each isomer exhibit in its 13C NMR spectrum?c.) When only the number of signals in both 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy is considered,d.) is it possible to distinguish all of these constitutional isomers?arrow_forward
- A compound with a molecular formula C12H24 exhibits an H+ NMR spectrum with only one signal and a 13 C NMR spectrum with two signals. Draw the structure of the compound.arrow_forwardCompound A exhibits two signals in its 1H NMR spectrum at 2.64 and 3.69 ppm, and the ratio of the absorbing signals is 2:3. Compound B exhibits two signals in its 1H NMR spectrum at 2.09 and 4.27 ppm, and the ratio of the absorbing signals is 3:2. Which compound corresponds to dimethyl succinate, and which compound corresponds to ethylene diacetate?arrow_forwardHow many 1H NMR signals does each compound give?arrow_forward
- Consider geraniol, the principal constituent of rose oil.a.How many 1H NMR signals does geraniol exhibit? b.How many 13C NMR signals does geraniol exhibit? c.Into how many peaks will the protons on each C=C be split?arrow_forwardConsider geraniol, the principal constituent of rose oil. a.) How many 1H NMR signals does geraniol exhibit? b.) How many 13C NMR signals does geraniol exhibit?c.) Into how many peaks will the protons on each C=C be split?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





