
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product formed should be determined on the reaction of following

Concept Introduction:
A
In a chemical reaction, the substance which is involved in conversion is said to be reactant, whereas, the newly formed substance is known as a product. Both reactants and products must be separated by an arrow.
Hydration reaction is an addition reaction in which the hydrogen and hydroxyl group (-OH) are bonded on un-statured carbon atoms of alkene to form alcohol.
Answer to Problem 13.62P
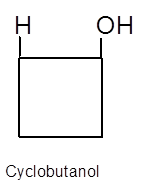
Explanation of Solution
To get the hydration product of any alkene, three steps must be followed:
- Locate the position of C=C in the molecule.
- Break the H-OH bond of the reagent.
- Add the -OH group atom to double-bonded C atom to form new C−OH single bonds in the molecule.
- Add one H atom to another double-bonded C atom to form new C−H single bonds in the molecule.
- The reaction follows the Markovnikov rule which states that the H atom of H-OH will bond to that double-bonded C atom which has more number of H atoms.
Hence, the hydration product is:
. 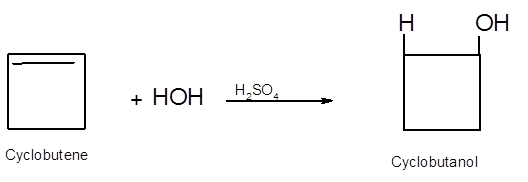
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed should be determined on the reaction of following alkene with
(CH3)3 -C =C -(CH3)2
Concept Introduction:
A chemical reaction is the symbolic representation of the conversion of substances to new substances.
In a chemical reaction, the substance which is involved in conversion is said to be reactant, whereas, the newly formed substance is known as a product. Both reactants and products must be separated by an arrow.
Hydration reaction is an addition reaction in which the hydrogen and hydroxyl group (-OH) are bonded on un-statured carbon atoms of alkene to form alcohol.
Answer to Problem 13.62P
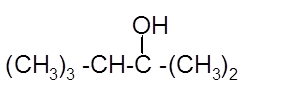
Explanation of Solution
To get the hydration product of any alkene, three steps must be followed;
- Locate the position of C=C in the molecule.
- Break the H-OH bond of the reagent.
- Add the -OH group atom to double-bonded C atom to form new C−OH single bonds in the molecule.
- Add one H atom to another double-bonded C atom to form new C−H single bonds in the molecule.
- The reaction follows the Markovnikov rule which states that the H atom of H-OH will bond to that double-bonded C atom which has more number of H atoms.
Hence, the hydration product is:
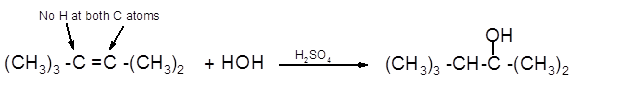
(c)
Interpretation:
The product formed should be determined on the reaction of following alkene with
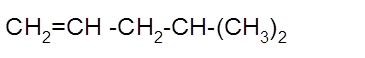
Concept Introduction:
A chemical reaction is the symbolic representation of the conversion of substances to new substances.
In a chemical reaction, the substance which is involved in conversion is said to be reactant, whereas, the newly formed substance is known as a product. Both reactants and products must be separated by an arrow.
Hydration reaction is an addition reaction in which the hydrogen and hydroxyl group (-OH) are bonded on un-statured carbon atoms of alkene to form alcohol.
Answer to Problem 13.62P
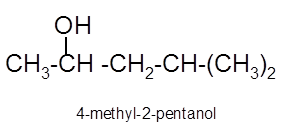
Explanation of Solution
To get the hydration product of any alkene, three steps must be followed;
- Locate the position of C=C in the molecule.
- Break the H-OH bond of the reagent.
- Add the -OH group atom to double-bonded C atom to form new C−OH single bonds in the molecule.
- Add one H atom to another double-bonded C atom to form new C−H single bonds in the molecule.
- The reaction follows the Markovnikov rule which states that the H atom of H-OH will bond to that double-bonded C atom which has more number of H atoms.
Hence, the hydration product is:
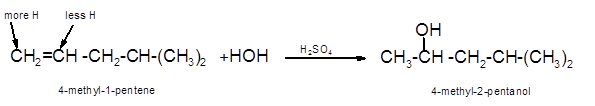
(d)
Interpretation:
The product formed should be determined on the reaction of following alkene with
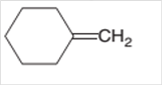
Concept Introduction:
A chemical reaction is the symbolic representation of the conversion of substances to new substances.
In a chemical reaction, the substance which is involved in conversion is said to be reactant, whereas, the newly formed substance is known as a product. Both reactants and products must be separated by an arrow.
Hydration reaction is an addition reaction in which the hydrogen and hydroxyl group (-OH) are bonded on un-statured carbon atoms of alkene to form alcohol.
Answer to Problem 13.62P
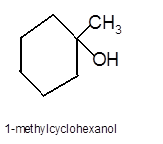
Explanation of Solution
To get the hydration product of any alkene, three steps must be followed;
- Locate the position of C=C in the molecule.
- Break the H-OH bond of the reagent.
- Add the -OH group atom to double-bonded C atom to form new C−OH single bonds in the molecule.
- Add one H atom to another double-bonded C atom to form new C−H single bonds in the molecule.
- The reaction follows the Markovnikov rule which states that the H atom of H-OH will bond to that double-bonded C atom which has more number of H atoms.
Hence the hydration product is:
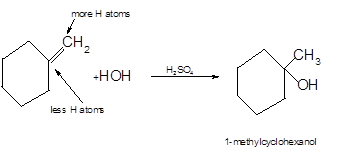
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
GENERAL ORGANIC+BIOCHEM (LL)W/CONNECT
- What alcohol is formed when each compound is treated with NaBH4 in CH3OH?arrow_forwardWhat alcohol is formed when the following compound is treated with H2 and a Pd catalyst?arrow_forwardWhat alkenes are formed when each alcohol is treated with H 2SO 4? Use the Zaitsev rule to predict the major product.arrow_forward
- What alcohol is formed when attached compound is treated with NaBH4 in CH3OH?arrow_forward14-60 Write a balanced equation for the complete combustion of ethanol, the alcohol blended with gasoline to produce E85.arrow_forwardGive the IUPAC name of the alcohol that fits each of the following descriptions. a. Moistening agent in many cosmetics b. Major ingredient in environmentally friendly antifreeze formulations c. Industrially produced from CO and H2 d. Often produced via a fermentation processarrow_forward
- Give both the IUPAC name and the common name for each alcohol.(a) CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3arrow_forwardDraw the products formed when each alcohol is oxidized with K 2Cr 2O 7. In some cases, no reaction occurs.arrow_forwardWhat products are formed when each alcohol is oxidized with K 2Cr 2O 7? In some cases, no reaction occurs.arrow_forward
- Give the structure corresponding to each IUPAC name. a. 3-methyl-3-pentanold. 1,3-propanediol b. 4-methyl-2-pentanole. 3,5-dimethylcyclohexanol c. 2,4-dimethyl-2-hexanolf. 6,6-diethyl-4-nonanolarrow_forwardWhat product is formed when the alcohol is oxidized with K2Cr2O7? In some cases, no reaction occurs (if so, draw the given alcohol).arrow_forwardGive the structure corresponding to each IUPAC name. 2,4 dimethyl- 2 hexanolarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



