
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
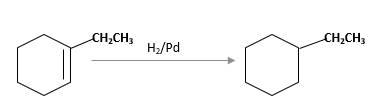
The product should be identified when 1-ethylcyclohexene treated with
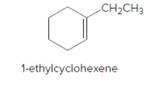
Concept Introduction:
Cyclic
Reaction of an alkene with
Answer to Problem 13.63P
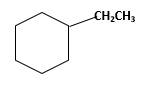
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated 1-ethylcyclohexene,alkene molecule reacts with
(b)
Interpretation:
The product should be identified when 1-ethylcyclohexene treated with
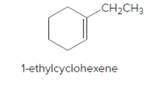
Concept Introduction:
Cyclic alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of an alkene with
Answer to Problem 13.63P
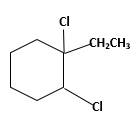
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated 1-ethylcyclohexene, alkene molecule reacts with
(c)
Interpretation:
The product should be identified when 1-ethylcyclohexene treated with
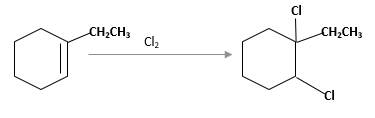
Concept Introduction:
Cyclic alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of an alkene with
Answer to Problem 13.63P
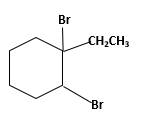
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated 1-ethylcyclohexene, alkene molecule reacts with
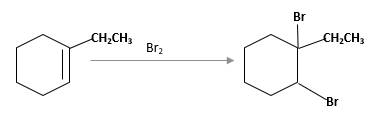
(d)
Interpretation:
The product should be identified when 1-ethylcyclohexane treated with
Concept Introduction:
Cyclic alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of an alkene with
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 13.63P
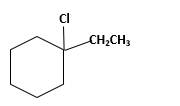
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated 1-ethylcyclohexene, alkene molecule reacts with
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule. When
Refer to the below reaction:
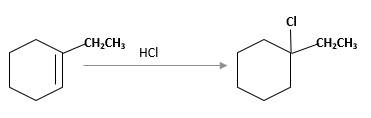
(e)
Interpretation:
The product should be identified when 1-ethylcyclohexene treated with
Concept Introduction:
Cyclic alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of an alkene with
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 13.63P
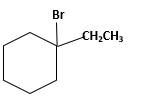
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated 1-ethylcyclohexene, alkene molecule reacts with
Hydro halogenation reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule. When
Refer to the below reaction;
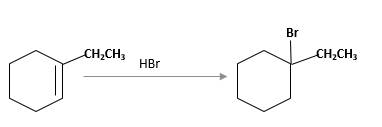
(f)
Interpretation:
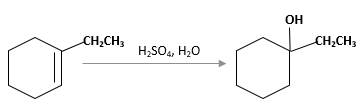
The product should be identified when 1-ethylcyclohexene treated with
Concept Introduction:
Cyclic alkenes are hydrocarbon molecules that consist of a carbon-carbon double bond which has the general formula of
Reaction of an alkene with
Hydration reaction of alkenes follows the Markovnikov's rule.
Answer to Problem 13.63P
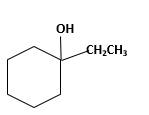
Explanation of Solution
Unsaturated 1-ethylcyclohexene, alkene molecule reacts with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
GENERAL ORGANIC+BIOCHEM (LL)W/CONNECT
- Draw the structure corresponding to 1-bromopent-2-ynearrow_forwardDraw the organic products formed when cyclopentene is treated withfollowing reagent. KMnO4, H2O, HO−arrow_forwardDraw a structure for each compound (includes old and new names).(a) 3-methylpent-1-ene (b) cis-3-methyl-3-hexene (c) 3,4-dibromobut-1-ene(d) 1,3-cyclohexadienearrow_forward
- Draw the organic products formed when attached alkyne is treated with two equivalents of HBr.arrow_forwardDraw the organic products formed when cyclopentene is treated withfollowing reagent. mCPBAarrow_forwardDraw the structure corresponding to each IUPAC name. a.3-ethyl-2-methylhexane b. sec-butylcyclopentane c.4-isopropyl-2,4,5-trimethylundecane d.cyclobutylcycloheptane e.3-ethyl-1,1-dimethylcyclohexane f. 4-butyl-1,1-diethylcyclooctane g.6-isopropyl-2,3-dimethyldodecane h. 2,2,6,6,7-pentamethyloctane i. cis-1-ethyl-3-methylcyclopentane j. trans-1-tert-butyl-4-ethylcyclohexanearrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
