
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Risk which causes greater threat to operation.
Concept Introduction:Control charts are the graphical representation to check or monitor the variations of the process and length of deviations from average.
Explanation of Solution
In the given scenario, sample is
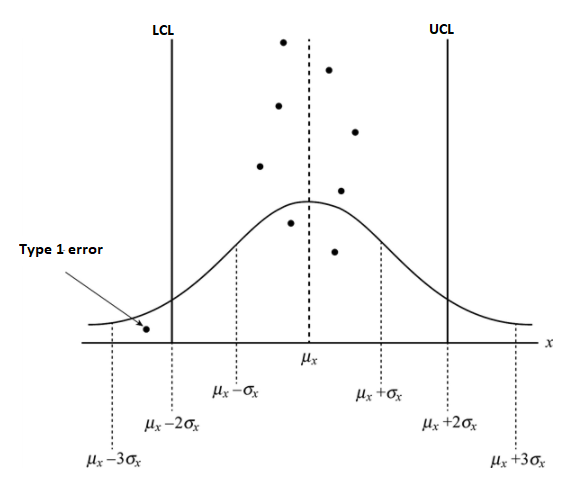
Apart from producer’s risk, there is also a possibility when sample value is lying under the control limits but it is a cause of interference in production process. The causes of interference may be assigned. It can be shown below:
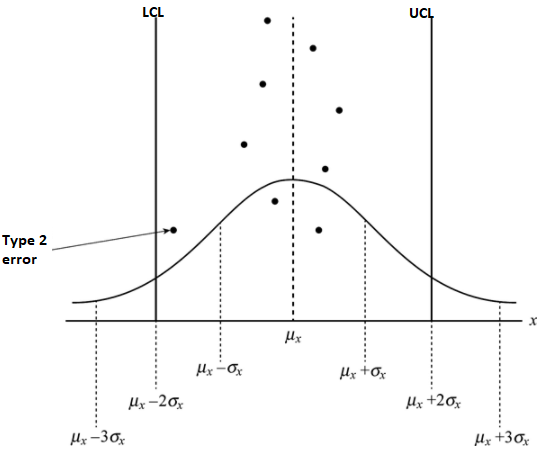
Despite assignable causes, which would make the products coming out of the production process non-confirming to desired specifications, the sample mean is falling within the control limits. This type of error is called a Type 2 error. This is a consumer’s risk, as the defective products in that batch would reach the consumer, undetected by the producer.
A producers’ risk is a minor problem of loss of production, whereas consumers’ risk is a greater threat as the consumer may ask for warranty replacement, may take the company to court, there could be claims, loss of company’s image and so on.
Therefore, consumer’s risk is the greatest threat to the success of an operation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Practical Operations Management
- A manufacturing company has been inspecting units of output from a process. Each prod uct inspected is evaluated on five criteria. If the unit does not meet standards for the criteria it counts as a defect for the unit. Each unit could have as few as zero defects, and as many as five. After inspecting 2,000 units, they discovered 33 defects. What is the DPMO measure for this process?arrow_forwardA machine produces parts that are either good (90%), slightly defective (2%), or obviously defective (8%). Produced parts get passed through an automatic inspection machine, which is able to detect any part that is obviously defective and discard it. What is the quality of the parts that make it through the inspection machine and get shipped?arrow_forwardA production operation is making 150 units of a product by engaging five workers for 300 hours. However, 40% of the units appear to have various quality problems, and the company decides to sell them as seconds at a price of £50 each when a normal unit is sold for £150. To improve the situation, several initiatives are proposed, including a scheme where, for every improvement, 50% will be given to workers and the other 50% will be held by the company. This results in a significant drop in defects as now only 10 units are faulty out of an output of 130 units.- Compare the productivity after Bonus with the initial productivity. - Determine the appropriate bonus per hour for the workers under the bonus scheme if the cost per piece is £70 both before and after the scheme.arrow_forward
- As part of an insurance company’s training program, participants learn how to conduct an analysis of clients’ insurability. The goal is to have participants achieve a time in the range of 30 to 45 minutes. Test results for three participants were the following: Armand, a mean of 36.0 minutes and a standard deviation of 2.0 minutes; Jerry, a mean of 37.0 minutes and a standard deviation of 2.0 minutes; and Melissa, a mean of 37.5 minutes and a standard deviation of 2.6 minutes. a.Compute process capability for the participants and determine whether each is capable, given 4-sigma quality standards. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardAs part of an insurance company’s training program, participants learn how to conduct an analysis of clients’ insurability. The goal is to have participants achieve a time in the range of 30 to 45 minutes. Test results for three participants were the following: Armand, a mean of 36.0 minutes and a standard deviation of 3.0 minutes; Jerry, a mean of 34.0 minutes and a standard deviation of 2.0 minutes; and Melissa, a mean of 37.5 minutes and a standard deviation of 1.7 minutes. a.Compute process capability for the participants and determine whether each is capable. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Melissa ? Cp what is itarrow_forwardA manufacturing company has been inspecting units of output from a process. Each product inspected is evaluated on five criteria’s. If the unit does not meet standards for the criteria it counts as a defect for the unit. Each unit could have a few as zero defects, and as many as five. After inspecting 2,000 units, they discover 33 defects. What is the DPMO measure for this process? (Round to nearest whole number)arrow_forward
- The output from a process contains a 0.02 defective unit. Defective units that go undetected into final assemblies cost $25 each to replace. An inspection process, which would detect and remove all defectives, can be established to test these units. However, the inspector, who can test 20 units per hour, is paid $8 per hour, including fringe benefits. Should an inspection station be established to test all units?a. What is the cost to inspect each unit?b. What is the benefit (or loss) from the inspection process?arrow_forwardBurger Doodle is a fast-food restaurant that processes anaverage of 680 food orders each day. The average cost of each order is $6.15. Four percent of the orders are incor-rect, and only 10% of the defective orders can be corrected with additional food items at an average cost of $1.75. Theremaining defective orders have to be thrown out.a. Compute the average product cost.b. In order to reduce the number of wrong orders,Burger Doodle is going to invest in a computerizedordering and cash register system. The cost of thesystem will increase the average order cost by $0.05and will reduce defective orders to 1%. What is theannual net cost effect of this quality-improvementinitiative?c. What other indirect effects on quality might be realizedby the new computerized order system?arrow_forwardhow does unethical business practices degrade the quality of the experience a customer has with a service or product. How is the International Organization for Standardization trying to encourage ethical business behavior?arrow_forward
- If you were the Vice-President of Quality Assurance, how would you evaluate the appropriate measure for process capability and then assess the capability of the in-control process to meet specifications? Why is this important?arrow_forwardWhat are typical performance testing errors?arrow_forwardManagement is trying to decide whether Part A, which is produced with a consistent 3 percent defective rate, should be inspected. If it is not inspected, the 3 percent defectives will go through a product assembly phase and have to be replaced later. If all Part A’s are inspected, one-third of the defectives will be found, thus raising the quality to 2 percent defectives.a. Should the inspection be done if the cost of inspecting is $0.01 per unit and the cost of replacing a defective in the final assembly is $4.00?b. Suppose the cost of inspecting is $0.05 per unit rather than $0.01. Would this change your answer in (a)?arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.





