
Concept explainers
Project Evaluation This is a comprehensive project evaluation problem bringing together much of what you have learned in this and previous chapters. Suppose you have been hired as a financial consultant to Defense Electronics, Inc. (DEI), a large, publicly traded firm that is the market share leader in radar detection systems (RDSs). The company is looking at setting up a manufacturing plant overseas 10 produce a new tine of RDSs. This will be a five-year project. The company bought some land three years ago for $7 5 million in anticipation of using it as a toxic dump site for waste chemicals, but it built a piping system to safely discard the chemicals instead. The land was appraised last week for $7.1 million. In five years, the aftertax value of the land will be $7.4 million, but the company expects to keep the land for a future project. The company wants to build its new manufacturing plant on this land; the plant and equipment will cost $40 million 10 build. The following market data on DEI’s securities is current:
| Debt: | 260,000 6.8 percent coupon bonds outstanding, 25 years to maturity, selling for 103 percent of par; the bonds have a$1,000 par value each and make semiannual payments. |
| Common stock: | 9,500,000 shares outstanding, selling for $67 per share; the beta is 1.25. |
| 450,000 shares of 5.25 percent preferred stock outstanding, selling for $84 per share and having a par value of $100. | |
| Market: | 7 percent expected market risk premium; 3.6 percent risk-free rate. |
DEI use G.M. Wharton as its lead underwriter. Wharton charges DEI spreads of 6.5 percent on new common stock issues, 4.5 percent on new preferred stock issues, and 3 percent on new debit issues. Wharton has included all direct and indirect issuance costs (along with its profit) in setting these spreads. Wharton has recommended to DEI that it raise the funds needed to build the plant by issuing new shares of common stock. DEI’s tax rate is 35 percent. The project requires $1,400,000 in initial net working capital investment to get operational. Assume Wharton raises all equity for new projects externally.
- a. Calculate the project's initial Time 0 cash now, taking into account all side effects.
- b. The new RDS project is somewhat riskier than a typical project for DEI, primarily because the plant i~ being located overseas. Management has told you to use an adjustment factor of + 2 percent to account for this increased riskiness. Calculate the appropriate discount rate to use when evaluating DEI’s project.
- c. The manufacturing plant has an eight-year tax life, and DEI uses straight-line
depreciation. At the end of the project (i.e., the end of Year 5), the plant and equipment can be scrapped for $8.5 million. What is the aftertax salvage value of this plant and equipment? - d. The company will incur $7,900,000 in annual fixed costs. The plan is to manufacture 18,000 RDSs per year and sell them at $10,900 per machine; the variable production costs are $9,450 per RDS. What is the annual operating cash now (OCF) from this project?
- e. DEI’s comptroller is primarily interested in the impact of DEI’s investments on the bottom line of reported accounting Statement. What will you tell her is the accounting break-even quantity of ROSs sold for this project?
- f. Finally, DEI’s president wants you to throw all your calculations, assumptions, and everything else into the report for the chief financial officer all he want he to know is what the RDS project’s
internal rate of return (IRR) andnet present value (NPV) are. What will you report?
a.
To determine: The Initial Time 0 Cash Flow.
Introduction:
The cost of equity is the yield than an investor anticipates from the security as returns for the risk they accept by spend in the specific security. Additionally it is the return an investor needs before they prefer for an alternative investment which pays higher than the correct.
The cost of debt is the effective interest rate of cost which a business earns on their current debts. Debt involves in the formation of capital structure. As the debt is considered as an deduction expenditure, the cost of debt is usually determined as after-tax cost in order to formulate similar to the cost of equity.
Answer to Problem 24QP
The Initial Time 0 Cash Flow is -$50,794,407.64
Explanation of Solution
Determine the Value of Debt
Therefore the Value of Debt is $267,800,000
Determine the Value of Common Stock
Therefore the Value of Common Stock is $636,500,000
Determine the Value of Preferred Stock
Therefore the Value of Preferred Stock is $37,800,000
Determine the Total Market Value
Therefore the Total Market Value is $942,100,000
Determine the Weight of Debt
Therefore the Weight of Debt is 28.43%
Determine the Weight of Common Stock
Therefore the Weight of Common Stock is 67.56%
Determine the Weight of Preferred Stock
Therefore the Weight of Preferred Stock is 4.01%
Determine the Weighted Average Floatation Costs
Therefore the Weighted Average Floatation Costs is 5.42%
Determine the Amount Raised
Therefore the Amount Raised is $42,294,407.64
Determine the Initial Time 0 Cash Flow
Therefore the Initial Time 0 Cash Flow is -$50,794,407.64
b.
To determine: The Discount Rate of the Project.
Answer to Problem 24QP
The Discount Rate of the Project is 11.81%
Explanation of Solution
Determine the Cost of Equity using CAPM
Therefore the Cost of Equity is 12.35%
Determine the After-tax Cost of Debt
Using excel function =rate we find the pre-tax and after-tax cost of debt as,
Excel Spreadsheet:
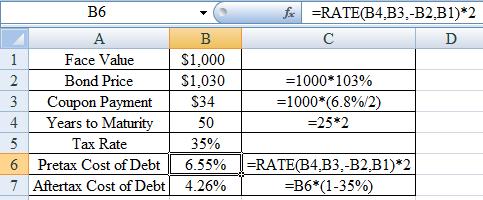
Therefore the After-tax Cost of Debt is 4.26%
Determine the Cost of Preferred Stock
Therefore the Cost of Preferred Stock is 6.25%
Determine the WACC
Therefore the WACC is 9.81%
Determine the Discount Rate of Project
Therefore the Discount Rate of Project is 11.81%
c.
To determine: The After-Tax Salvage Value.
Answer to Problem 24QP
The After-Tax Salvage Value is $10,775,000
Explanation of Solution
Determine the Annual Depreciation
Therefore the Annual Depreciation is $5,000,000
Determine the Book Value at the end of Year 5
Therefore Book Value at the end of Year 5 is $15,000,000
Determine the After-Tax Salvage Value
Therefore After-Tax Salvage Value is $10,775,000
d.
To determine: The Annual Operating Cash Flows.
Answer to Problem 24QP
The Annual Operating Cash Flows is $13,580,000
Explanation of Solution
Determine the Annual Operating Cash Flows
Therefore the Annual Operating Cash Flows is $13,580,000
e.
To determine: The Accounting Break-Even Sales Figure.
Answer to Problem 24QP
The Accounting Break-Even Sales Figure is 8,897 units
Explanation of Solution
Determine the Accounting Break Even Sales Figure
Therefore the Accounting Break Even Sales Figure is 8,897 units
f.
To determine: The Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR).
Answer to Problem 24QP
The Net Present Value (NPV) is $9,591,825.14 and Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is 18.17%
Explanation of Solution
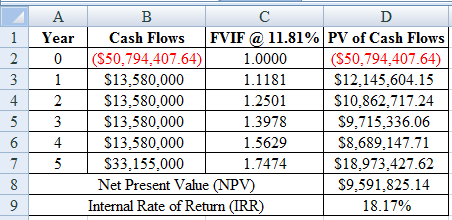
Determine the Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return
Using excel spreadsheet we calculate the Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return as,
Excel Spreadsheet:
Excel Workings:
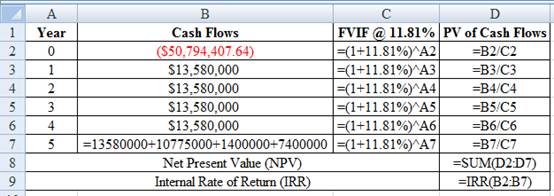
Therefore the Net Present Value (NPV) is $9,591,825.14 and Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is 18.17%
Since the net present value (NPV) is positive the project should be accepted.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
CORPORATE FINANCE CUSTOM W/CONNECT >BI
- Analyze CSR initiatives at Green Manufacturing Green Manufacturing is a traditional manufacturing company located in the midwestern United States. The companys operations manager is developing a strategy to become more CSR-oriented. In an effort to evaluate possible areas where CSR initiatives can be implemented, the manager has gathered the following data regarding three potential CSR activities: The recycling activity would carry on indefinitely. The solar panels would have a useful life of 30 years. The replacement of assembly room light fixtures with natural light is assumed to have an 80-year effect. A. Identify which CSR activities Green Manufacturing should implement. B. For each CSR activity you recommend, identify an appropriate related performance metric.arrow_forwardSuppose you have been hired as a financial consultant to Defense Electronics, Incorporated (DEI), a large, publicly traded firm that is the market share leader in radar detection systems (RDSs). The company is looking at setting up a manufacturing plant overseas to produce a new line of RDSs. This will be a five-year project. The company bought some land three years ago for $3.8 million in anticipation of using it as a toxic dump site for waste chemicals, but it built a piping system to safely discard the chemicals instead. The land was appraised last week for $6.9 million on an aftertax basis. In five years, the aftertax value of the land will be $7.3 million, but the company expects to keep the land for a future project. The company wants to build its new manufacturing plant on this land; the plant and equipment will cost $33.5 million to build. The following market data on DEI’s securities are current: Debt: 145,000 bonds with a coupon rate of 6.9 percent outstanding, 22…arrow_forwardSuppose you have been hired as a financial consultant to Defense Electronics, Incorporated (DEI), a large, publicly traded firm that is the market share leader in radar detection systems (RDSs). The company is looking at setting up a manufacturing plant overseas to produce a new line of RDSs. This will be a five-year project. The company bought some land three years ago for $3.8 million in anticipation of using it as a toxic dump site for waste chemicals, but it built a piping system to safely discard the chemicals instead. The land was appraised last week for $6.9 million on an aftertax basis. In five years, the aftertax value of the land will be $7.3 million, but the company expects to keep the land for a future project. The company wants to build its new manufacturing plant on this land; the plant and equipment will cost $33.5 million to build. The following market data on DEI’s securities are current: Debt: 145,000 bonds with a coupon rate of 6.9 percent outstanding, 22…arrow_forward
- Suppose you have been hired as a financial consultant to Defense Electronics, Incorporated (DEI), a large, publicly traded firm that is the market share leader in radar detection systems (RDSs). The company is looking at setting up a manufacturing plant overseas to produce a new line of RDSs. This will be a five-year project. The company bought some land three years ago for $3.8 million in anticipation of using it as a toxic dump site for waste chemicals, but it built a piping system to safely discard the chemicals instead. The land was appraised last week for $6.9 million on an aftertax basis. In five years, the aftertax value of the land will be $7.3 million, but the company expects to keep the land for a future project. The company wants to build its new manufacturing plant on this land; the plant and equipment will cost $33.5 million to build. The following market data on DEI’s securities are current: Debt: 145,000 bonds with a coupon rate of 6.9 percent outstanding, 22…arrow_forwardThe Chief Operations Officer (COO) of a manufacturing firm recommends one of the manufacturing sites to undergo a process improvement initiative. He claims that this project will enable the company to realize a net savings of at least $3.25 Mln. The Chief Financial Officer (CFO) of the company tasked you to conduct a financial analysis to verify the claims of the COO. After performing cost analysis, you estimated that the project will require an initial investment of $2 Mln today and $1 Mln in Year 1. Afterwards, the initiative will yield an annual cost savings of $850k from Year 2 to Year 10. You assume that these cost savings are realized at the end of each year. (a) Suppose that you use a discount rate of 5%. Will the resulting net savings support the claim of the COO? (b) Determine the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) of the process improvement initiative. (c) Show the NPV profile of the project.arrow_forwardSuppose you have been hired as a financial consultant to Defense Electronics, Incorporated (DEI), a large, publicly traded firm that is the market share leader in radar detection systems (RDSs). The company is looking at setting up a manufacturing plant overseas to produce a new line of RDSs. This will be a five-year project. The company bought some land three years ago for $4.6 million in anticipation of using it as a toxic dump site for waste chemicals, but it built a piping system to safely discard the chemicals instead. The land was appraised last week for $7.7 million on an aftertax basis. In five years, the aftertax value of the land will be $8.1 million, but the company expects to keep the land for a future project. The company wants to build its new manufacturing plant on this land; the plant and equipment will cost $29.8 million to build. The following market data on DEI’s securities are current: Debt: 185,000 bonds with a coupon rate of 7.7 percent outstanding, 25…arrow_forward
- Suppose you have been hired as a financial consultant to Defense Electronics, Inc. (DEI), a large, publicly traded firm that is the market share leader in radar detection systems (RDSs). The company is looking at setting up a manufacturing plant overseas to produce a new line of RDSs. This will be a five-year project. The company bought some land three years ago for $7.3 million in anticipation of using it as a toxic dump site for waste chemicals, but it built a piping system to safely discard the chemicals instead. If the land were sold today, the net proceeds would be $7.79 million after taxes. In five years, the land will be worth $8.09 million after taxes. The company wants to build its new manufacturing plant on this land; the plant will cost $13.76 million to build. The following market data on DEI’s securities are current: Debt: 93,800 7.2 percent coupon bonds outstanding, 26 years to maturity, selling for 93.1 percent of par; the bonds have a $1,000 par value each…arrow_forwardAcme Semiconductor is expanding its facility and needs to add equipment. There are three process tools under consideration. You have been asked to perform an economic analysis to select the most appropriate tool to acquire. You have gathered the following information for evaluation. Each of these tools has a useful life of seven years. Acme’s accounting staff has established a company-wide MARR of 8% per year.Which one of the process tools should be selected?arrow_forwardYou must analyze a potential new product --- a caulking compound that Korry Materials’ R&D people developed for use in the residential construction industry. Korry’s marketing manager thinks they can sell 115,000 tubes per year at a price of $3.25 each for 3 years, after which the product will be obsolete. The required equipment would cost $125,000, plus another $25,000 for shipping and installation. Current assets (receivables and inventories) would increase by $35,000, while current liabilities (accounts payables and accruals) would rise by $15,000. Variable costs would be 60 percent of sales revenue, fixed costs (exclusive of depreciation) would be $70,000 per year, and the fixed assets would be depreciated under MACRS with a 3-year life. When production ceases after 3 years, the equipment should have a market value of $15,000. Korry’s tax rate is 40 percent, and it uses a 10 percent WACC for average risk projects. The R&D costs for the new product were $30,000, and…arrow_forward
- As supervisor of a facilities engineering department, you consider mobile cranes to be critical equipment. The purchase of a new, medium-sized truck-mounted crane is being evaluated. The economic estimates for the two best alternatives are shown in the following table. MARR is at 15% per year. You can use the assumption of repeatability in this case. Show that the same selection is made for the following methods: a. PW method b. FW method c. EUAC method Alternative A B Capital investment ALTERNATIVE A $272,000 ALTERNATIVE B $346,000 Annual expenses ALTERNATIVE A $28,800 1 ALTERNATIVE B $9,300 Useful life (years) ALTERNATIVE A =6 ALTERNATIVE B =9 Salvage value ALTERNATIVE A $ 25,000 ALTERNATIVE B $40,000arrow_forwardSuppose you have been hired as a financial consultant to Defense Electronics, Incorporated (DEI), a large, publicly traded firm that is the market share leader in radar detection systems (RDSs). The company is looking at setting up a manufacturing plant overseas to produce a new line of RDSs. This will be a five-year project. The company bought some land three years ago for $3 million in anticipation of using it as a toxic dump site for waste chemicals, but it built a piping system to safely discard the chemicals instead. The land was appraised last week for $6.1 million on an aftertax basis. In five years, the aftertax value of the land will be $6.5 million, but the company expects to keep the land for a future project. The company wants to build its new manufacturing plant on this land; the plant and equipment will cost $32.7 million to build. The following market data on DEI’s securities are current: Debt: 250,000 bonds with a coupon rate of 6.1 percent outstanding, 24…arrow_forwardSuppose you have been hired as a financial consultant to Defense Electronics, Incorporated (DEI), a large, publicly traded firm that is the market share leader in radar detection systems (RDSs). The company is looking at setting up a manufacturing plant overseas to produce a new line of RDSs. This will be a five-year project. The company bought some land three years ago for $3 million in anticipation of using it as a toxic dump site for waste chemicals, but it built a piping system to safely discard the chemicals instead. The land was appraised last week for $6.1 million on an aftertax basis. In five years, the aftertax value of the land will be $6.5 million, but the company expects to keep the land for a future project. The company wants to build its new manufacturing plant on this land; the plant and equipment will cost $32.7 million to build. The following market data on DEI’s securities are current: Debt: 250,000 bonds with a coupon rate of 6.1 percent outstanding, 24…arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College



