
Concept explainers
(a)
The velocity of block B
(a)
Answer to Problem 13.23P
The velocity of block B
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the block A
The mass of the block B
The force (P) acting at block A is 250 N.
The coefficient of static friction between block A and horizontal surface
The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and horizontal surface
Calculation:
Show the system with the distance as in Figure (1).
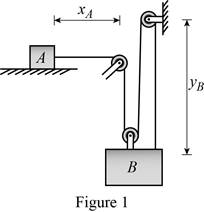
When the block A moves one unit left, block B moves 3 units upwards,
Write the expression for the constraint of the cable from Figure (1) as follows:
Here,
Show the free body diagram of block B with all the forces acting on it as in Figure (2).
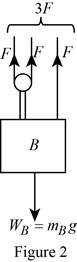
Check the equilibrium position of the blocks to verify whether the blocks move.
From Figure (2), for block B to remain in equilibrium, the net resultant force acting on the block B should be zero.
Here, g is the acceleration due to gravity and F is the tension in the cable.
Substitute 25 kg for
Show the free body diagram of block B with all the forces acting on it as in Figure (3).
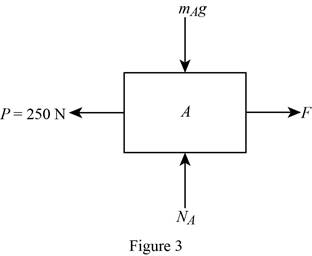
Calculate the net forces acting on the block A in Y-axis direction using the relation:
Here,
Substitute 30 kg for
Calculate the net forces acting on block A in X-axis direction using the relation:
Substitute 250 N for
Calculate the available static friction acting on block A
Substitute 0.25 for
Since
Show the free body diagram of block B with kinetic frictional force acting on it as in Figure (4).
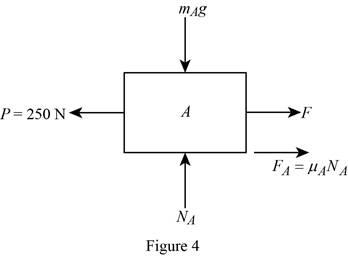
Consider the block A.
The kinetic energy of block A
The expression for the final kinetic energy of the block A
Write the expression for the kinetic frictional force acting on the block A
Write the expression for the work done by the block A
Apply the principle of work and energy to block A.
Work and energy principle states that kinetic energy of the particle at a displaced point can be obtained by adding the initial kinetic energy and the work done on the particle during its displacement.
Write the expression for the work and energy principle as follows:
Substitute 0 for
Substitute 250 N for
Consider the block B.
The kinetic energy of block B
The expression for the final kinetic energy
Write the expression the work done by the block B in moving through a distance of
Apply the principle of work and energy to the block B.
According to the work and energy principle,
Substitute 0 for
Substitute 25 kg for
Add equation (2) and equation (4) to eliminate
Therefore, the velocity of block B
(b)
The tension (F) in the cable.
(b)
Answer to Problem 13.23P
The tension (F) in the cable is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the block A
The mass of the block B
The force (P) acting at block A is 250 N.
The coefficient of static friction between block A and horizontal surface
The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and horizontal surface
Calculation:
Calculate the tension (F) in the cable:
Substitute
Therefore, the tension (F) in the cable is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics - With Access
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





