
a.
Check whether there is a positive linear relationship between the minimum and maximum width of an object.
a.
Answer to Problem 40E
There is convincing evidence that there is a positive linear relationship between the minimum and maximum width of an object.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The given data provide the dimensions of 27 representative food products.
Here,
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no linear relationship between the minimum and maximum width of an object.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, there is a positive linear relationship between the minimum and maximum width of an object.
Here, the significance level is
Test Statistic:
The formula for test statistic is as follows:
In the formula, b denotes the estimated slope,
A standardized residual plot is shown below:
Standardized residual values and standardized residual plot:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to compute standardized residuals and its plot using MINITAB software:
- Select Stat > Regression > Regression > Fit Regression Model.
- In Response, enter the column of Maximum width.
- In Continuous Predictors, enter the columns of Minimum width.
- In Graphs, select Standardized under Residuals for Plots.
- In Results, select for all observations under Fits and diagnostics.
- In Residuals versus the variables, select Minimum width.
- Click OK.
Output obtained MINTAB software is given below:
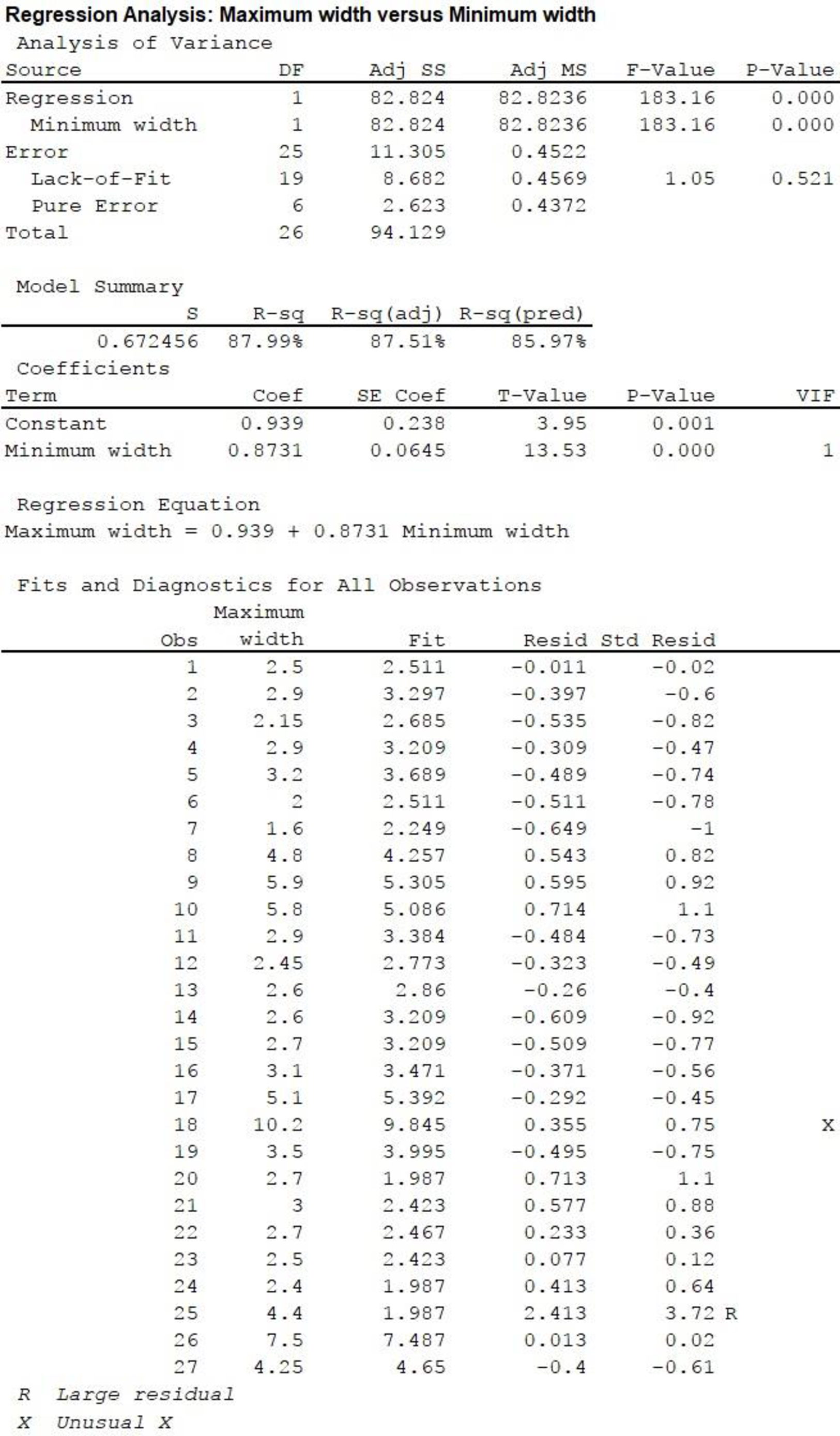
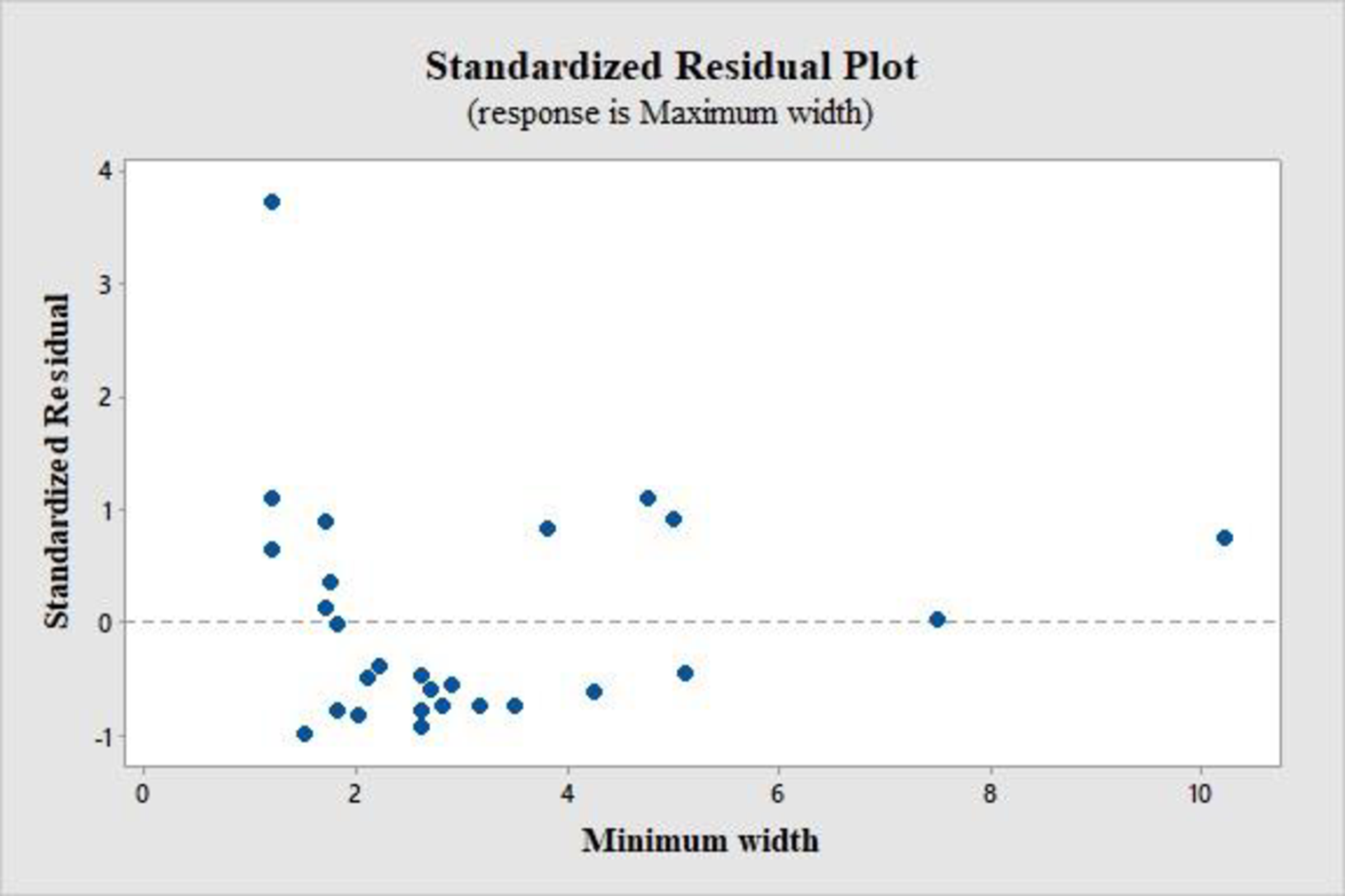
From the standardized residual plot, it is observed that one point lies outside the horizontal band of 3 units from the central line of 0. The standardized residual for this outlier is 3.72, that is, for product 25.
Assumption:
Here, the assumption made is that, the simple linear regression model is appropriate for the data, even though there is one extreme standardized residual.
Test Statistic:
In the MINITAB output, the test statistic value is displayed in the column “T-value” corresponding to “Minimum width”, in the section “Coefficients”. The value is 13.53.
P-value:
From the above output, the corresponding P-value is 0.
Rejection rule:
If
Conclusion:
The P-value is 0 and the level of significance is 0.05.
The P-value is less than the level of significance.
That is,
Therefore, reject the null hypothesis.
Thus, there is convincing evidence that there is a positive linear relationship between the minimum and maximum width of an object.
b.
Compute and interpret
b.
Answer to Problem 40E
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
From the MINITAB output in Part (a), it is clear that
On an average, there is 67.246% deviation of the maximum width in the sample from the value predicted by least-squares regression.
c.
Find the 95% confidence interval for the mean maximum width of products for the minimum width of 6 cm.
c.
Answer to Problem 40E
The 95% confidence interval for the mean maximum width of products for the minimum width of 6 cm is (5.708, 6.647).
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The confidence interval for
From the MINITAB output in Part (a), the estimated linear regression line is
Point estimate:
The point estimate is calculated as follows:
Estimated standard deviation:
For the given x values, the summation values are given in the following table:
| Minimum width (X) | |
| 1.8 | 3.24 |
| 2.7 | 7.29 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 2.6 | 6.76 |
| 3.15 | 9.9225 |
| 1.8 | 3.24 |
| 1.5 | 2.25 |
| 3.8 | 14.44 |
| 5 | 25 |
| 4.75 | 22.5625 |
| 2.8 | 7.84 |
| 2.1 | 4.41 |
| 2.2 | 4.84 |
| 2.6 | 6.76 |
| 2.6 | 6.76 |
| 2.9 | 8.41 |
| 5.1 | 26.01 |
| 10.2 | 104.04 |
| 3.5 | 12.25 |
| 1.2 | 1.44 |
| 1.7 | 2.89 |
| 1.75 | 3.0625 |
| 1.7 | 2.89 |
| 1.2 | 1.44 |
| 1.2 | 1.44 |
| 7.5 | 56.25 |
| 4.25 | 18.0625 |
The value of
Substitute
Formula for degrees of freedom:
The formula for degrees of freedom is as follows:
The number of data value given is 27, that is
Critical value:
From the Appendix: Table of the t-critical values:
- Locate the value 25 in the degrees of freedom (df) column.
- Locate the 0.95 in the row of central area captured.
- The intersecting value that corresponds to df 25 with the confidence level 0.95 is 2.060.
Thus, the critical value for
Substitute
Therefore, one can be 95% confident that the mean maximum width of products with the minimum width of 6 cm will be between 5.708 cm and 6.647 cm.
d.
Find the 95% prediction interval for the mean maximum width of products with the minimum width of 6 cm.
d.
Answer to Problem 40E
The 95% prediction interval for the mean maximum width of products with the minimum width of 6 cm is (4.716, 7.640).
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The confidence interval for
The estimated standard deviation of the amount by which a single y observation deviates from the value predicted by an estimated regression line is
Substitute
From Part (c), the critical value for
Substitute
Therefore, the 95% prediction interval for the mean maximum width of products with the minimum width of 6 cm is (4.716, 7.640).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 13 Solutions
INTRO TO STAT + WEBASSIGN ACCESS CARD
- A U.S. Food Survey showed that Americans routinely eat beef in their diet. Suppose that in a study of 49 consumers in Illinois and 64 consumers in Texas the following results were obtained from two samples regarding average yearly beef consumption: Illinois Texas = 49 = 64 = 54.1lb = 60.4lb S1 = 7.0 S2 = 8.0 Develop a 95% confidence Interval Estimate for the difference between the two population means.arrow_forwardIn Exercises, presume that the assumptions for regression inferences are met.Crown-Rump Length. Following are the data on age of fetuses and length of crown-rump from Exercise. x 10 10 13 13 18 19 19 23 25 28 y 66 66 108 106 161 166 177 228 235 280 a. Determine a point estimate for the mean crown-rump length of all 19-week-old fetuses.b. Find a 90% confidence interval for the mean crown-rump length of all 19-week-old fetuses.c. Find the predicted crown-rump length of a 19-week-old fetus.d. Determine a 90% prediction interval for the crown-rump length of a 19-week-old fetus.ExerciseApplying the Concepts and SkillsIn Exercises, we repeat the information from Exercises. For each exercise here, discuss what satisfying Assumptions 1–3 for regression inferences by the variables under consideration would mean.arrow_forwardIn exercise 7, the data on y = annual sales ($1000s) for new customer accounts andx = number of years of experience for a sample of 10 salespersons provided the estimatedregression equation yˆ = 80 + 4x. For these data x = 7, o(xi − x)2 = 142, and s = 4.6098.a. Develop a 95% confidence interval for the mean annual sales for all salespersons withnine years of experience.b. The company is considering hiring Tom Smart, a salesperson with nine years of experience.Develop a 95% prediction interval of annual sales for Tom Smart.c. Discuss the differences in your answers to parts (a) and (b).arrow_forward
- Find the critical value z a/2 that corresponds to the given confidence level 96arrow_forward11.36 Use the data from Exercise 11.22.a. Estimate the mean time to run 10 km for athletes having a treadmill time of11 minutes.b. Place a 95% confidence interval on the mean time to run 10 km for athleteshaving a treadmill time of 11 minutes.arrow_forwardThe cost of making a batch of a certain product depends on the size of the batch, as shown by the following sample data: Cost $ 30 70 140 270 530 1010 2000 5100 size of the batch 1 5 10 25 50 100 250 500 a) Fit a straight line to said data, with the least squares method, use the lot size as the independent variable. b) Find a 95% confidence interval for alfa that can be interpreted as the fixed overhead cost of manufacture.arrow_forward
- Find the critical z⋆z⋆ for a level 96.38 % confidence interval.arrow_forwardfor a sample size of 12 and a 90% confidence interval, the t statistic used to estimate U would be.arrow_forwardExercise #1 Open the Excel worksheet MPGDATA.XLS from Blackboard>Excel #5 Files. The data in column A of this worksheet represent the miles per gallon gasoline consumption for a random sample of 55 makes and models of passenger cars (source: Environmental Protection Agency) Use the Excel Confidence Interval Template to: Construct a 95% confidence interval for the population mean miles per gallon consumption for passenger cars. Use the Excel Hypothesis Testing Template to: Test the hypothesis that the population mean of miles per gallon gasoline consumption for passenger cars is different from 25 mpg. Use a significance level of 5%. Do we know ? for the mpg consumption? Can we use the normal distribution for the hypothesis test? State the null and alternative hypotheses. Perform the appropriate test and print the output. Look at the p-value in the output. Compare it to ?. Do we reject the null hypothesis or not? Generate the descriptive statistics (mean, standard…arrow_forward
- The table below contains summary statistics about the trading density (sales per square metre, R/m2) for two random and independent samples of 18 housing developments in the Western Cape, and 13 housing developments in the Free State. Assume that the trading densities of the Western Cape and the Free State housing developments are normally distributed. Housing cost Western cape Free state Sample mean (R) 2500.2 2100.7 Sample standard deviation (R) 820.3 694.6 a. Estimate a 95% confidence interval for the standard deviation of the cost of housing developments in the Free State. b. Are the variances of the trading densities of housing developments in the Western Cape and the Free State are the same? Test at the 10% level. (Note: In answering this question, make sure you state the following: null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic and critical value. Write your final answers to 3 decimal places).c. Estimate a 90% confidence interval for the difference between the mean…arrow_forwardIn simple linear regression, at what value of the independent variable, X, will the 95% confidence interval for the average value of Y be narrowest? At what value will the 95% prediction interval for the value of Y for a single n ew observation be narrowest?arrow_forwardWhich of these is a question that would require a z test? Question 6 options: Does a sample of couples who communicate primarily by texting have a higher relationship satisfaction than that of a sample of couples who communicate primarily by phone? Does a sample of nurses in large hospitals get sick more often than a sample of nurses in smaller hospitals? Does a sample of people from rural communities have different levels of social intelligence than a sample of people from urban centers? Does a sample of purebred dogs live longer than dogs in general?arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





