
(a)
Interpretation:
The relative rate of the reaction in the given three containers has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Rate of the reaction is the change in the concentration of reactant or a product with time.
Rate equation for the general reaction
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given first order reaction is,
For first order reaction,
X molecules are placed in three equal-volume containers at the same temperature.
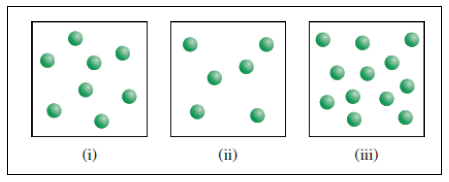
Fig (1)
The relative rates of the reaction in the given three containers can be determined as follows,
For convenience, we can use the number of molecules to represent the concentration. Therefore, the relative
To get the relative rates dividing each rate by
Therefore
Relative rate of the reaction in three containers are
(b)
Interpretation:
To determine the relative rates be affected if the volume of the each container were doubled
Concept introduction:
Rate of the reaction is the change in the concentration of reactant or a product with time.
Rate equation for the general reaction
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given first order reaction is,
For first order reaction,
X molecules are placed in three equal-volume containers at the same temperature.

Fig (1)
The relative rates of the reaction in the given three containers can be determined as follows,
For convenience, we can use the number of molecules to represent the concentration. Therefore, the relative rates of reaction for the three containers are,
To get the relative rates dividing each rate by
Therefore
Relative rate of the reaction in three containers are
The relative rates would be unaffected if the volume of the each container were doubled. Therefore, the relative rates between the three containers would remain same and so the actual rate would decrease by
(c)
Interpretation:
The relative half-life of the reactions in
Concept introduction:
Rate of the reaction is the change in the concentration of reactant or a product with time.
Rate equation for the general reaction
Half-life is the time required for one half of a reactant to react.
For first order reaction
Half-life for a first order reaction is
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given first order reaction is,
For first order reaction,
X molecules are placed in three equal-volume containers at the same temperature.

Fig (1)
We know that, the half-life of a first order reaction is independent on substrate (reactant) concentration; it does not depend on substrate concentration.
Therefore, the relative half-life of the reactions in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Loose Leaf For General Chemistry With Connect Access Card
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





