
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
There are two classes of hydrocarbon compounds, saturated and
Answer to Problem 14.33AP
The synthesis of
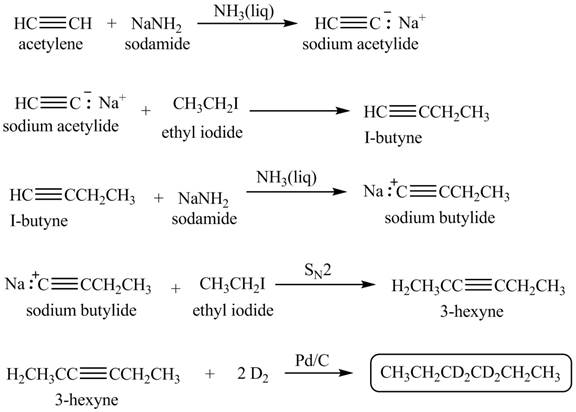
Explanation of Solution
When acetylene reacts with sodamide in
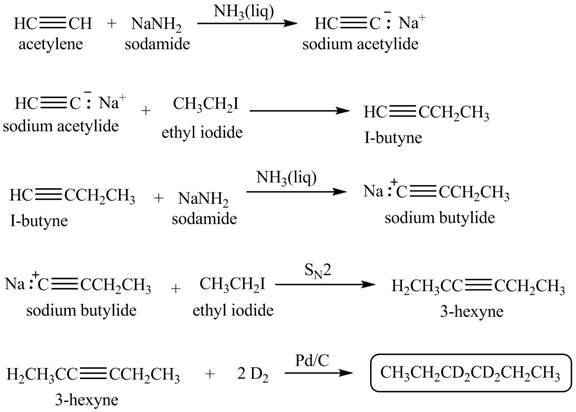
Figure 1
The synthesis of
(b)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
There are two classes of hydrocarbon compounds, saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Unsaturated hydrocarbon is of two types, alkenes and alkynes. The alkene contains a double bond between two carbon atoms. The alkynes contain a triple bond between two carbon atoms and follow a general formula
Answer to Problem 14.33AP
The synthesis of
Explanation of Solution
When acetylene reacts with sodamide in

Figure 2
The synthesis of
(c)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
There are two classes of hydrocarbon compounds, saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Unsaturated hydrocarbon is of two types, alkenes and alkynes. The alkene contains a double bond between two carbon atoms. The alkynes contain a triple bond between two carbon atoms and follow a general formula
Answer to Problem 14.33AP
The synthesis of
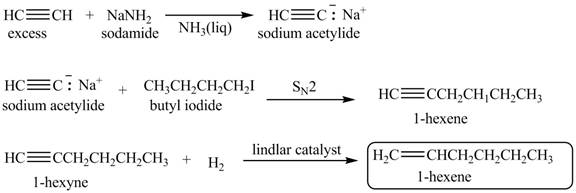
Explanation of Solution
When acetylene reacts with sodamide in
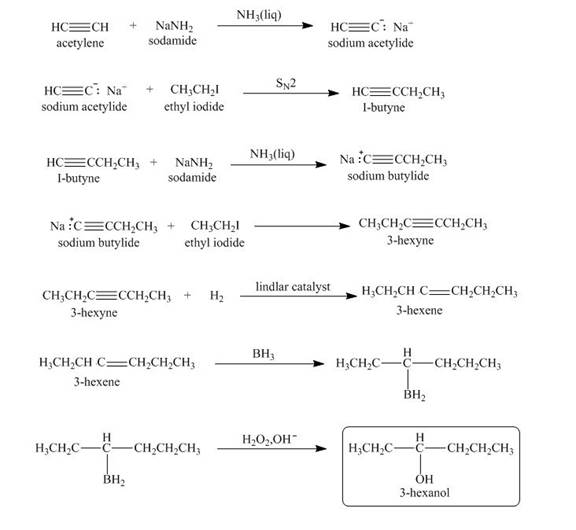
Figure 3
The synthesis of
(d)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
There are two classes of hydrocarbon compounds, saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Unsaturated hydrocarbon is of two types, alkenes and alkynes. The alkene contains a double bond between two carbon atoms. The alkynes contain a triple bond between two carbon atoms and follow a general formula
Answer to Problem 14.33AP
The synthesis of
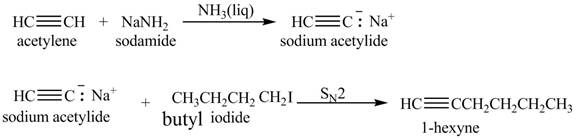
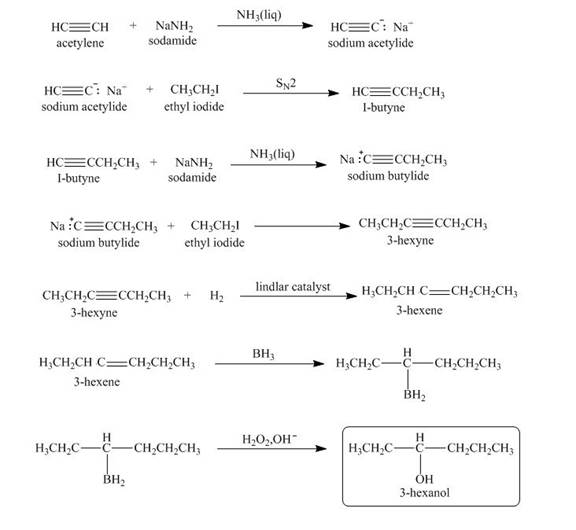
Explanation of Solution
When acetylene reacts with sodamide in

Figure 4
The synthesis of
(e)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
There are two classes of hydrocarbon compounds, saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Unsaturated hydrocarbon is of two types, alkenes and alkynes. The alkene contains a double bond between two carbon atoms. The alkynes contain a triple bond between two carbon atoms and follow a general formula
Answer to Problem 14.33AP
The synthesis of
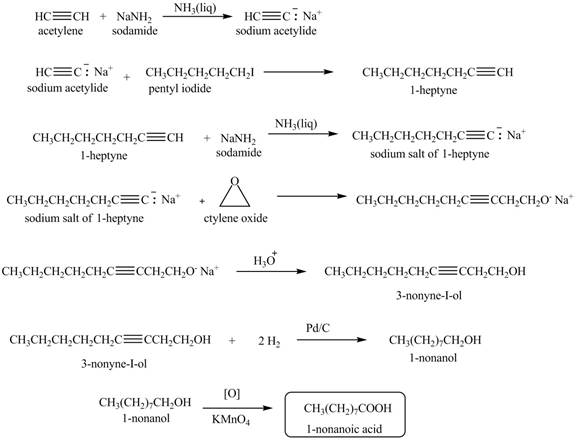
Explanation of Solution
When acetylene reacts with sodamide in
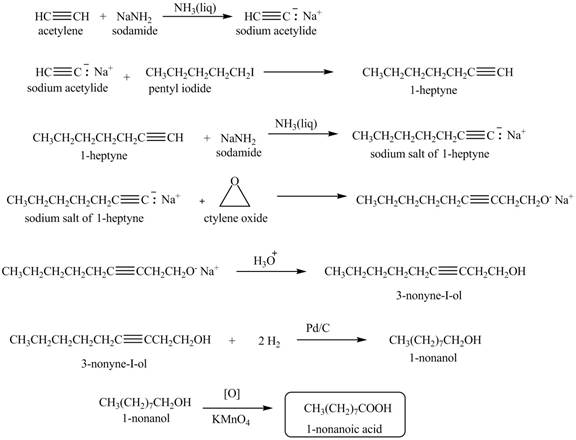
Figure 5
The synthesis of
(f)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
There are two classes of hydrocarbon compounds, saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Unsaturated hydrocarbon is of two types, alkenes and alkynes. The alkene contains a double bond between two carbon atoms. The alkynes contain a triple bond between two carbon atoms and follow a general formula
Answer to Problem 14.33AP
The synthesis of
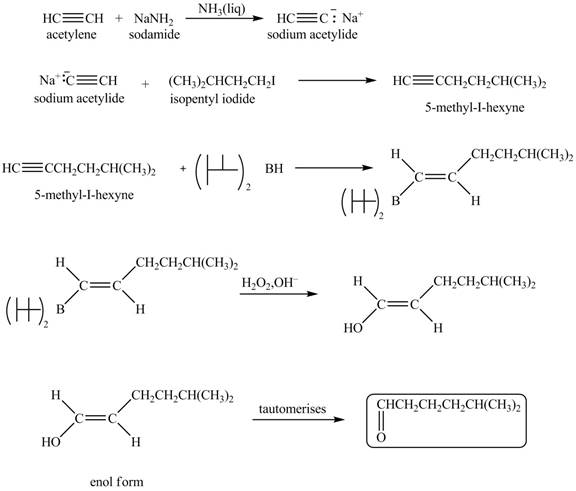
Explanation of Solution
When acetylene reacts with sodamide in

Figure 6
The synthesis of heptanal from acetylene is written as shown in Figure 6.
(g)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
There are two classes of hydrocarbon compounds, saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Unsaturated hydrocarbon is of two types, alkenes and alkynes. The alkene contains a double bond between two carbon atoms. The alkynes contain a triple bond between two carbon atoms and follow a general formula
Answer to Problem 14.33AP
The synthsis of
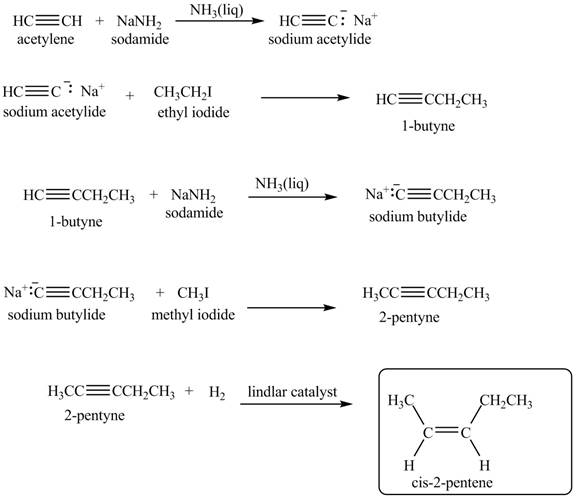
Explanation of Solution
When acetylene reacts with sodamide in

Figure 7
The synthesis of
(h)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
There are two classes of hydrocarbon compounds, saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Unsaturated hydrocarbon is of two types, alkenes and alkynes. The alkene contains a double bond between two carbon atoms. The alkynes contain a triple bond between two carbon atoms and follow a general formula
Answer to Problem 14.33AP
The synthesis of
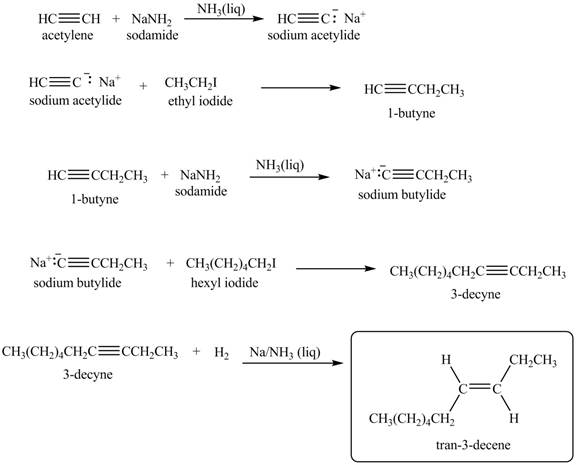
Explanation of Solution
When acetylene reacts with sodamide in

Figure 8
The synthesis of
(i)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
There are two classes of hydrocarbon compounds, saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Unsaturated hydrocarbon is of two types, alkenes and alkynes. The alkene contains a double bond between two carbon atoms. The alkynes contain a triple bond between two carbon atoms and follow a general formula
Answer to Problem 14.33AP
The synthesis of
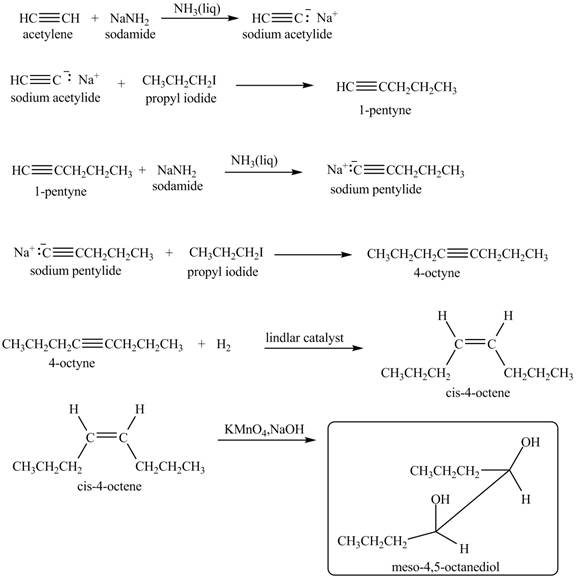
Explanation of Solution
When acetylene reacts with sodamide in

Figure 9
The synthesis of
(j)
Interpretation:
The synthesis of
Concept introduction:
There are two classes of hydrocarbon compounds, saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Unsaturated hydrocarbon is of two types, alkenes and alkynes. The alkene contains a double bond between two carbon atoms. The alkynes contain a triple bond between two carbon atoms and follow a general formula
Answer to Problem 14.33AP
The synthesis of
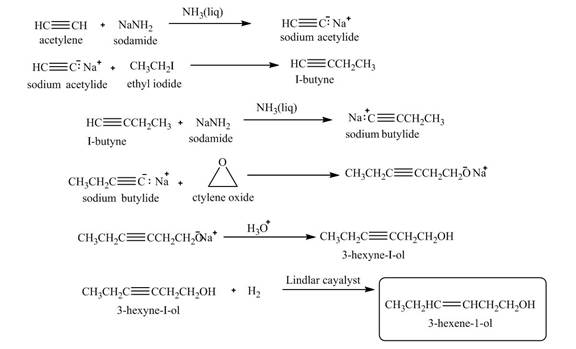
Explanation of Solution
When acetylene reacts with sodamide in

Figure 10
The synthesis of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)+ SAPLING ACC >BI
- Compound A, C3H7Br, does not react with cold dilute potassium permanganate solution. Upon treatment with potassium hydroxide in ethanol, A gives only product B, C3H6. Unlike A, B decolourises potassium permanganate solution. Ozonolysis of Bgives C, C2H4O, and D, CH2O. Suggest the structural formulae of A, B, C and D.Write the equations for all the reactions involved.arrow_forwardOn being heated with a solution of sodium ethoxide in ethanol, compound A (C7H15Br) produced a mixture of two alkenes B and C, each of which had the molecular formula C7H14. Catalytic hydrogenation of major isomer B or minor isomer C gave only 3-ethylpentane. Suggest structures and mechanisms for compounds A, B, and C consistent with these observations.arrow_forwardTwo moles of organic compound ‘A’ on treatment with a strong base gives two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ on dehydrogenation with Cu gives ‘A’ while acidification of ‘C’ yields carboxylic acid ‘D’ with molecular formula of CH2O2. Identify the compounds A, B, C and D and write all chemical reactions involved.arrow_forward
- The sex attractant of the housefly has the formula C23H46. When treated with warm potassium permanganate, this pheromone gives two products: CH3(CH2)12COOH and CH3(CH2)7COOH. Suggest a structure for this sex attractant. Explainwhich part of the structure is uncertainarrow_forwardAn organic compound A of unknown structure was found to have a molecular formula C8H16. When A was poured in water and heated, compound B having a molecular formula C8H18O was formed. B upon heating with sulfuric acid was converted to C as the major product which is identical to A. Ozonolysis of C gave one molecule each of two different products D and E, both having a molecular formula C4H8O. Write the reactions involved and determine the structure of A,B,C,D and E.arrow_forwardA hydrocarbon (X), with the molecular formula: C8H14 is reduced in presence of sodium and liquid ammonia to give the only product (Y) with the molecular formula: C8H16. Compounds X and Y both resulting 2,5-dimethylhexane when treated with hydrogen and platinum catalyst (H2/Pt). As a result of the oxidative cleavage of compound Y (by using KMnO4 / H2SO4), a single carboxylic acid derivative with C4H8O2 molecular formula is formed. Again, as a result of the reaction of Y with perbenzoic acid, the chiral compound C8H14O is observed, but the reaction of compound Y with bromine gives the achiral C8H14Br2 as the product.arrow_forward
- Wolff-Kishner reduction of compound W gave compound A. Treatment of A with m-chloroperbenzoic acid gave B which on reduction with LiAH4 gave C. Oxidation of compound C with chromic acid gave D (C9H14O). Suggest the structures for A, B, C, and D.arrow_forwardOn being heated with a solution of sodium ethoxide in ethanol, compound A (C7H15Br) yielded a mixture of two alkenes B and C, each having the molecular formula C7H14. Catalytic hydrogenation of the major isomer B or the minor isomer C gave only 3-ethylpentane. Suggest structures for compounds A, B, and C consistent with these observations.arrow_forwardCompound P (C2H4) which is an alkene undergoes reaction with HCl to produce compound Q (C2H5Cl). Reaction of compound Q with benzene in the presence of AlCl3 as catalyst produces compound R. Then, nitration of compound R in the presence ofnH2SO4 produces two compounds, S and T. But when compound R is reacted with a hot acidified solution of alkaline KMnO4 gives compound U. Deduce the structure of compounds P to U.arrow_forward
- Provide the structure of the major organic product of the following reaction and? explain the stereochemistry which results in this product. 2-Pentanol reacting with 1.) PBr3, pyridine 2.) NaCNarrow_forwardGive the reagents and conditions necessary for the following conversion. A to B, B to D, B to C, B to E, E to F, E to G, G to H, H to I. Hence deduce the name and structural formula of the compounds C and I. Compare the procedure for converting F and E to G.arrow_forwardAn organic compound A which has a characteristic odour is treated with 50% NaOH to give B (C7H8O)and C which is a sodium salt of an organic acid . Oxidation of B gives back A. Heating C with soda lime yields an aromatic hydrocarbon D . Deduce the structures of A,B,C and Darrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





