
(a)
The natural rate of
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The IS LM framework of the economy deals with the closed economy and does not consider the international trade and Balance of Payments into consideration. This leads to the generation of the new model that incorporated the Balance of Payment into the calculations which is known as the Mundell - Fleming model. The
The natural rate of unemployment is the unemployment rate in the economy at the time when the labor market is in equilibrium. Thus, it consists of the structural and frictional unemployment in the economy when the economy is operating efficiently. This natural rate of unemployment is a case where the inflation in the economy will be equivalent to the expected rate of inflation. Thus, there will be no deviation to the actual level of inflation from the expected.
Thus, the expected inflation in this case will be equal to the last period's inflation in the economy. Thus, setting the inflation to the last period's inflation,
Natural Rate of Unemployment: The natural rate of unemployment is the rate of unemployment that is persisting in the economy when the labor market of the economy is in its equilibrium.
(b)
The short run and long run relationship between the inflation and unemployment.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The inflation and the unemployment are the two important aspects that an economy has to handle very carefully. When the measure to tackle and reduce the inflation is taken, it will increase the unemployment and vice versa in the economy. This happens in the short run and thus, they both are inversely related with each other. This short run or single period relation between the inflation and the unemployment is explained using the Phillips curve for the economy. Here, the expected inflation rate is equal to the last period's inflation rate and the slope of the Phillips curve will be 0.5. The short run Phillips curve will pass through the point where the
The long run period or the multi period relation is different from the short run relation. The expected inflation of the economy will be equal to the actual level of inflation in the economy. Thus,
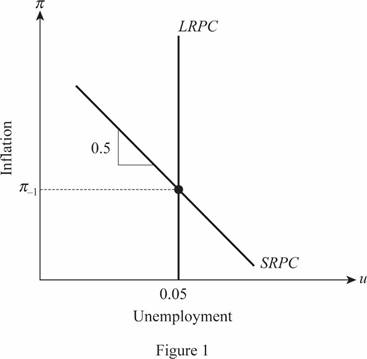
(c)
The cyclical unemployment required to reduce the inflation by 4 percentage points.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The Phillips curve of the economy is given to be
When the inflation has to be reduced, the unemployment in the economy should be above its natural level of unemployment according to the Phillips curve. Thus, the required fall in the inflation rate should be plugged into the left side of the Phillips curve equation as follows:
Thus, it indicates that there should be 8 percent more cyclical unemployment in the economy in order to bring the inflation by 4 percentage. The Okun's law states that an increase in the unemployment by 1 percent will correspond to the 2 percent fall in the total
The sacrifice ratio is the ratio of the percentage of GDP that the economy must foregoin order to reduce the inflation by 1 percentage point. Here, the total GDP foregone is 16 percentage points and the total inflation reduced is 4 percentage points. Thus, the sacrifice ratio can be calculated by dividing the total GDP foregone with the inflation reduced as follows:
Thus, the sacrifice ratio of the economy is 4.
(d)
The scenarios to reduce the inflation by 4 percentage points.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The Phillips curve of the economy is given to be
In order to reduce the inflation by 4 percentage points, the economy should have to face the higher unemployment rate of 13 percent for the short run as calculated above. Thus, the first measure that the government can relay is to make the unemployment rate very high at 13 percent in order to reduce the inflation by 4 percentage points.
The second measure that the government can relay is to fix the level of unemployment at 7 percent for 4 years which would slowly reduce the level of inflation in the economy by 4 percentage points. These are the two different measures that the government can relay up on in order to reduce the inflation by 4 percentage points.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
MACROECONOMICS+SAPLING+6 M REEF HC>IC<
- Suppose that an economy has the Phillips curvep=p-1 - O.S(u - 0.06),a) What is the natural rate of unemployment?b) Graph the short-run and long-run relationships between inflation and unemployment.c) How much cyclical unemployment is necessary to reduce inflation by S percentage points?d) Using Okun's law, compute the sacrifice ratio e.e)Inflation is running at 10 percent. The Fed wants to reduce it to 5 percent. Give Iwoscenarios that will achieve that goal.arrow_forwardSuppose that the government in the economy of the diagram below regards 9 percent unemployment as unacceptable. If the government insists on reducing the unemployment rate from 9 percent to 7 percent, regardless of the consequences, thena. pressure will build in the economy to continuously reduce the rate of inflation.b. the long-run Phillips curve becomes horizontal, freezing the rates of inflation and unemployment.c. the inflation rate will increase but the unemployment rate will stay at 7 percent.d. in the long run the rate of unemployment remains unchanged, but inflation will likely accelerate. Give explanations for the correct onearrow_forwardThe Philips curve in an economy is given by a = Επ- 0.5 (u - 6). Assume that the economy starts out at its natural unemployment rate and expected inflation Ex = 5.25%. If output decreases by 2%, using Okun's Law and the Phillips curve relation, what is actual inflation π ?arrow_forward
- Consider the Phillips Curve shown in Figure 1. The current inflation rate is I%, and the current unemployment rate is U%. Suppose the inflation rate suddenly falls by half. How will this inflation drop affect the unemployment rate in the short run? A) The unemployment rate will decrease. B) The unemployment rate will increase. C) The unemployment rate will not change. D) Impossible to say.arrow_forwardSuppose πt = πt−1 −2(ut −0.04) is the Phillips Curve equation in the economy. Answer thefollowing questions.a. What is the natural rate of unemployment?b. Graph the short run and the long run relationship between inflation and unemployment.c. How much cyclical unemployment is necessary to reduce inflation by 10 percentagepoint?d. The inflation is running at 12 percent. The Central Bank wants to reduce it to 9 percent.Give two scenarios that will achieve the goal.arrow_forwardDerive the original Phillips curve and answer the following questions:a) What effect does an increase in the expected price level have on the price level?b) What effect does an increase in the unemployment rate have on the price level?c) What effect does a decrease in business competition have on inflation?d) What is the effect of liberalizing foreign trade?e) What effect does the formation of trade unions have?arrow_forward
- Suppose that an economy has the Phillips curve p = p−1 – 0.5(u − 0.06). A. How much cyclical unemployment is necessary to reduce inflation by 5 percentage points? Using Okun’s law, compute the sacrifice ratio. B. Inflation is running at 10 percent. The Fed wants to reduce it to 5 percent. Give two scenarios that will achieve that goal.arrow_forward1. An economy has the following equation for the Phillips Curve: π = Eπ − 0.5(u − 6)People form expectations of inflation by taking a weighted average of the previous two years of inflation: Okun’s law for this economy is: Eπ = 0.7π−1 + 0.3π−2 (Y −Y−1)/(Y-1)=3.0−2.0(u−u−1) Th economy begins at its natural rate of unemployment with a stable inflation rate of 5 percent. Graph the short-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment that this economy faces. Label the point where the economy begins as A. (Be sure to give numerical values for point A.) A fall in aggregate demand leads to a recession, causing the unemployment rate to rise 4 percentage points above its natural rate. On your graph in part (b), label the point the economy experiences that year as point B.(Be sure to give numerical values.) Unemployment remains at this high level for two years (the initial year described in part (c) and one more), after which it returns to its natural rate. Create a table showing…arrow_forwardExplain all options, please. The modern view of the Phillips curve suggests that a.when inflation is less than anticipated, unemployment will fall below the natural rate. b.when inflation is steady, actual unemployment will equal the natural rate of unemployment. c.systematic demand stimulus policies will be unable to affect prices in the long run. d.there will be a trade-off between inflation and unemployment in the long run.arrow_forward
- Suppose short-run output exceeds full potential output by 3 percent. a. According to Okun's law, what is the effect on unemployment? b. Assuming that inflationary expectations are constant, what is the effect on wages?arrow_forwardSOLVE IT CORRECTLY AND DETAILS Q)Explain the relationship between inflation and unemployment, as well as concerns when enacting mismatched policies in a Phillips curve.arrow_forwardExplanation it correctly and details Q)According to the Phillips curve, if current output equals potential output: a. unemployment is zero. b. inflation fluctuates a lot. c. inflation is steady. d. unemployment is negative e. the economy is boomingarrow_forward
 Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971509Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971509Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning


