
(a)
The natural rate of
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The
Here, the people make their expectations about inflation on the basis of the weighted average of the past two year's inflations. When the inflation rate is stable at 5 percent, it means that the actual inflation is same as the expected inflation and so,
Natural Rate of Unemployment: The natural rate of unemployment is the rate of unemployment that is persisting in the economy when the labor market of the economy is in its equilibrium.
(b)
The short run trade-off between the inflation and unemployment.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The Phillips curve of the economy is given to be
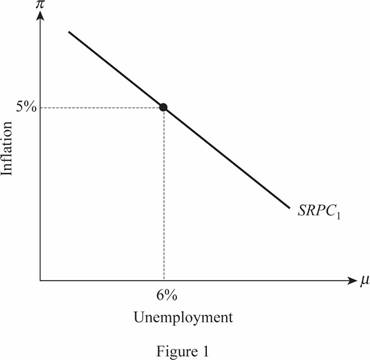
Thus, the short run trade-off between the inflation which is stable at 5 percentage point and the unemployment which is at its natural rate of 6 percentage point is indicated at point A.
(c)
The impact of fall in aggregate demand short run trade-off between the inflation and unemployment.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The Phillips curve of the economy is given to be
When the unemployment in the economy rises by 4 percentage points and becomes 10 percentage, the impact on the Phillips curve will be different because the expected inflation in the economy does not change. Thus, the Phillips curve determined the inflation rate and this can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the point B that indicates the change in the trade-off between the unemployment and inflation in the economy which will be on the same short run Phillips curve and can be illustrated as follows:
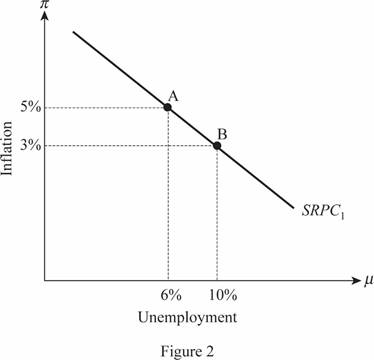
(d)
The economy during higher unemployment and after 2 years at natural rate for 10 years.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The Phillips curve of the economy is given to be
When the unemployment in the economy rises by 4 percentage points and becomes 10 percentage, the impact on the Phillips curve will be different because the expected inflation in the economy does not change. Thus, the economy's inflation rate will be 3%. The unemployment rate, inflation rate, expected inflation rate, and the rate of output growth for the 10 years can be calculated in the following table:
| Year | Unemployment Rate | Inflation Rate | Expected Inflation Rate | Rate of Output Growth |
| 1 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 3 |
| 2 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 3 |
| 3 | 10 | 3 | 5 | −5 |
| 4 | 10 | 1.6 | 3.6 | 3 |
| 5 | 6 | 2.02 | 2.02 | 11 |
| 6 | 6 | 1.89 | 1.89 | 3 |
| 7 | 6 | 1.93 | 1.93 | 3 |
| 8 | 6 | 1.92 | 1.92 | 3 |
| 9 | 6 | 1.92 | 1.92 | 3 |
| 10 | 6 | 1.92 | 1.92 | 3 |
(e)
The impact of fall in aggregate demand short run trade-off between the inflation and unemployment.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The Phillips curve of the economy is given to be
When the unemployment in the economy rises by 4 percentage points and becomes 10 percentage, the impact on the Phillips curve will be different because the expected inflation in the economy does not change. Thus, the Phillips curve determined the inflation rate and this can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the point B that indicates the change in the trade-off between the unemployment and inflation in the economy will be on the same short run Phillips curve. When the unemployment rate falls, the expected inflation rate would fall in the economy. This leads to the downward shift in the short run Phillips curve in the economy. From the table above, it is identified that the expected inflation rate in the economy at the end of the 10th year is 1.92 percent but the unemployment rate is 6 percent. This combination is illustrated at the point C as follows:
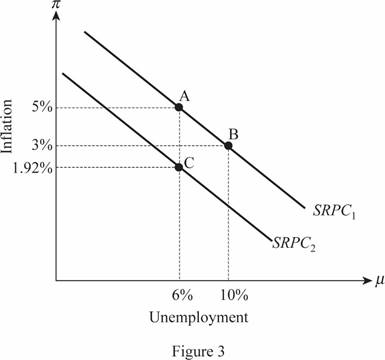
(f)
Before recession and after recession equilibrium.
(f)
Explanation of Solution
The Phillips curve of the economy is given to be
After recession, equilibrium is indicated at point C where the inflation rate is 1.92 and the unemployment rate is 6 percentage points. This indicates that the inflation in the economy has been decreased by 3.08 percent points in the economy. While looking at the table for the rate of growth of output, it is identified that there were a loss of 8 percent during from year 2 to year 3, whereas there were a gain of 8 percent from year 3 to year 4. From year 5 to 10, the rate of output growth remained the same which means that there is no long run sacrifice in reducing the inflation rate by the economy.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
MACROECONOMICS+SAPLING+6 M REEF HC>IC<
- If the actual unemployment rate falls below the natural unemployment rate, how does the actual inflation rate change? The actual inflation rate ________. A. doesn't change, but the short-run Phillips curve shifts leftward B. rises up along the short-run Phillips curve C. doesn't change, but the expected inflation rate rises D. rises and the natural unemployment rate fallsarrow_forwardAccording to the Phillips curve, the inflation rate depends on all of these EXCEPT: a. previously expected inflation. b. an exogenous supply shock. c. the real interest rate. d. the deviation of output from its natural rate.arrow_forwardHow does the money wage rate change along the Phillips curves? Along the short-run Phillips curve, the money wage rate _______, and along the long-run Phillips curve, the money wage rate _______. A. rises by the same percentage as the inflation rate; rises by the same percentage as the inflation rate B. is constant; is constant C. rises by the same percentage as the inflation rate; is constant D. is constant; rises by the same percentage as the inflation rate s thank s screenshot atttachedarrow_forward
- The inflation rate is 2 percent a year, and the quantity of money is growing at a pace that will maintain that inflation rate. The natural unemployment rate is 7 percent, and the current unemployment rate is 9 percent. In what direction will the unemployment rate change? How will the short-run Phillips curve and the long-run Phillips curve shift?arrow_forwardWhat policies can government put in place in ensure a balance between unemployment and inflations knowing the Phillips Curve hypothesizes that there is a correlation between inflation and unemployment. When inflation is high, unemployment is low. Conversely, when inflation is low, unemployment levels increase.arrow_forwardExplain all options, please. The modern view of the Phillips curve suggests that a.when inflation is less than anticipated, unemployment will fall below the natural rate. b.when inflation is steady, actual unemployment will equal the natural rate of unemployment. c.systematic demand stimulus policies will be unable to affect prices in the long run. d.there will be a trade-off between inflation and unemployment in the long run.arrow_forward
- For this question, assume that the Phillips curve equation is represented by the following equation: πt - πt-1 = (m + z) - αut. A reduction in the unemployment rate will cause A) a reduction in the markup over labor costs (i.e., a reduction in m). B) an increase in the markup over labor costs. C) an increase in the inflation rate over time. D) a decrease in the inflation rate over time. E) none of the abovearrow_forwardUsing the Phillips curve: imagine a country is having a higher unemployment rate than usual for a longperiod of time (higher than the natural rate). What should happen in the short term and in the longterm?arrow_forwardTrue, False, or uncertain: If people assume that inflation will be the same as last year's inflation, the Phillips curve relation will be a relation between the change in the inflation rate and the unemployment rate.arrow_forward


 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning





