
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
Concept introduction: Free radicals are classified as
Halogens react with
Answer to Problem 15.10P
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
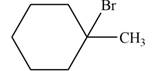
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
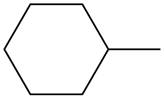
Figure 1
Three types of radicals can be formed from cleavage of
The number of alkyl substituents increases, the stability of radical increases. The order of stability is
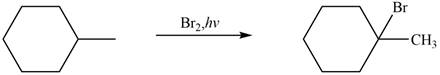
Figure 2
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
(b)
Interpretation: The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
Concept introduction: Free radicals are classified as
Halogens react with alkanes in presence of heat or light to form alkyl halides. This is known as halogenation reaction. This is a free radical substitution reaction. In this the halogen substitutes the hydrogen atom from
Answer to Problem 15.10P
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
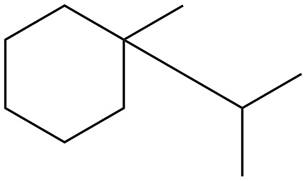
Figure 3
Three types of radicals can be formed from cleavage of
The number of alkyl substituents increases, the stability of radical increases. The order of stability is
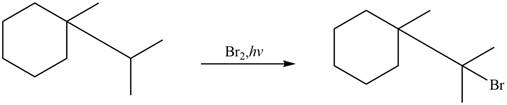
Figure 4
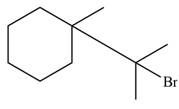
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
(c)
Interpretation: The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
Concept introduction: Free radicals are classified as
Halogens react with alkanes in presence of heat or light to form alkyl halides. This is known as halogenation reaction. This is a free radical substitution reaction. In this the halogen substitutes the hydrogen atom from
Answer to Problem 15.10P
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
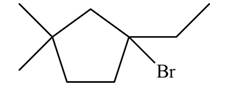
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
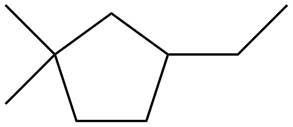
Figure 5
Three types of radicals can be formed from cleavage of
The number of alkyl substituents increases, the stability of radical increases. The order of stability is
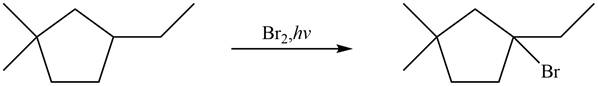
Figure 6
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
(c)
Interpretation: The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
Concept introduction: Free radicals are classified as
Halogens react with alkanes in presence of heat or light to form alkyl halides. This is known as halogenation reaction. This is a free radical substitution reaction. In this the halogen substitutes the hydrogen atom from
Answer to Problem 15.10P
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
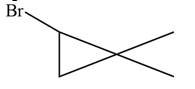
Explanation of Solution
The given species is,
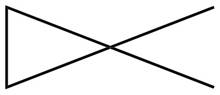
Figure 7
Two types of radicals can be formed from cleavage of
The number of alkyl substituents increases, the stability of radical increases. The order of stability is
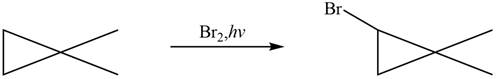
Figure 8
The major product formed when given cycloalkane is heated with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Access (Custom)
- Draw the major product formed when each cycloalkane is heated with Br2.arrow_forwardWhat alkenes are formed when each alcohol is dehydrated with TsOH? Label the major product when a mixture resultsarrow_forwardDraw the products formed when (CH3)2C=CH2 is treated with following reagent. Cl2arrow_forward
- Draw the products (including stereoisomers) formed when benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) is treated with each Wittig reagent.arrow_forwardDraw the structure corresponding to each IUPAC name: (a) 5,5-dimethyl-3-heptyne; (b) 1,3-dimethylcyclohexene.arrow_forwardALCOHOLS 1. WHY IS ETHANOL MORE SOLUBLE IN WATER THAN 1-HEXANOL? 2. WHAT IS DENATURED ALCOHOL? AND WHY IS ALCOHOL DENATURED? ETHER 1. WHY DOES DIETHYL ETHER HAVE MUCH LOWER BOILING POINT THAN 1-BUTANOL?arrow_forward
- Draw the structure of each compound. ) m-chlorotoluenearrow_forwardAnswer each question using the ball-and-stick model of compound A. Draw a stereoisomer for A and give its IUPAC name.Draw a constitutional isomer that contains an OH group and give itsIUPAC name.arrow_forwardDraw all constitutional isomers formed by monochlorination of each attachedalkane with Cl2 and hv.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

