
(a)
The heat flow into or out of the gas through the four steps of the cycle.
(a)
Answer to Problem 88P
The heat flow to the system during process
Explanation of Solution
The number of moles of the diatomic gas is
The figure below shows the cycle.
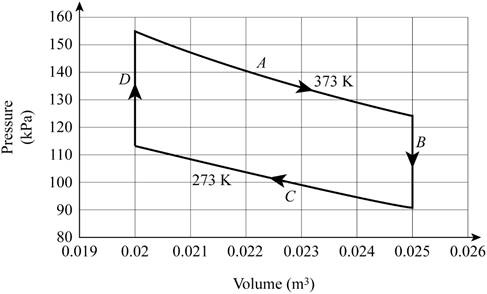
During the process
Write the formula for the heat flow out of the system in process
Here,
During the constant volume process
Write the formula for the heat change of the system during the process
Here,
Write the formula for the specific heat capacity under constant volume for diatomic gases.
Substitute the above equation in equation (II).
During the process
Write the formula for the heat flow out of the system in process
Here,
During the constant volume process
Refer equation (III) and write the formula for the change in heat for the process
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The heat flow to the system during process
(b)
The neat heat change during one cycle.
(b)
Answer to Problem 88P
The net heat change in one cycle is
Explanation of Solution
The number of moles of the diatomic gas is
Write the formula for the net heat change during one cycle.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
The net heat change in one cycle is
(C)
The entropy change of the reservoirs during each of the processes.
(C)
Answer to Problem 88P
The change in entropy during process
Explanation of Solution
The number of moles of the diatomic gas is
The figure below shows the cycle.
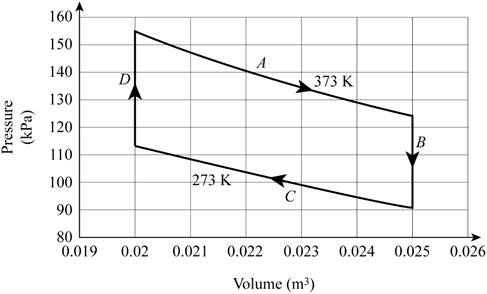
Write the formula for the change in entropy of a system.
Here,
The change in entropy of the reservoir will be negative of the change in entropy of the syste.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The change in entropy during process
(d)
The net entropy change during one cycle of the universe.
(d)
Answer to Problem 88P
The change in entropy during process
Explanation of Solution
The number of moles of the diatomic gas is
Write the formula for the net entropy change of the universe during one cycle.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
The net entropy change of the universe is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Physics
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





