
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
A Plot of
Concept Introduction:
The effect of a substrate concentration on first-order growth rate of a microbial population follows the Monod equation:
Where,
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Calculation of first-order growth rate:
By taking all the above data, a graph between
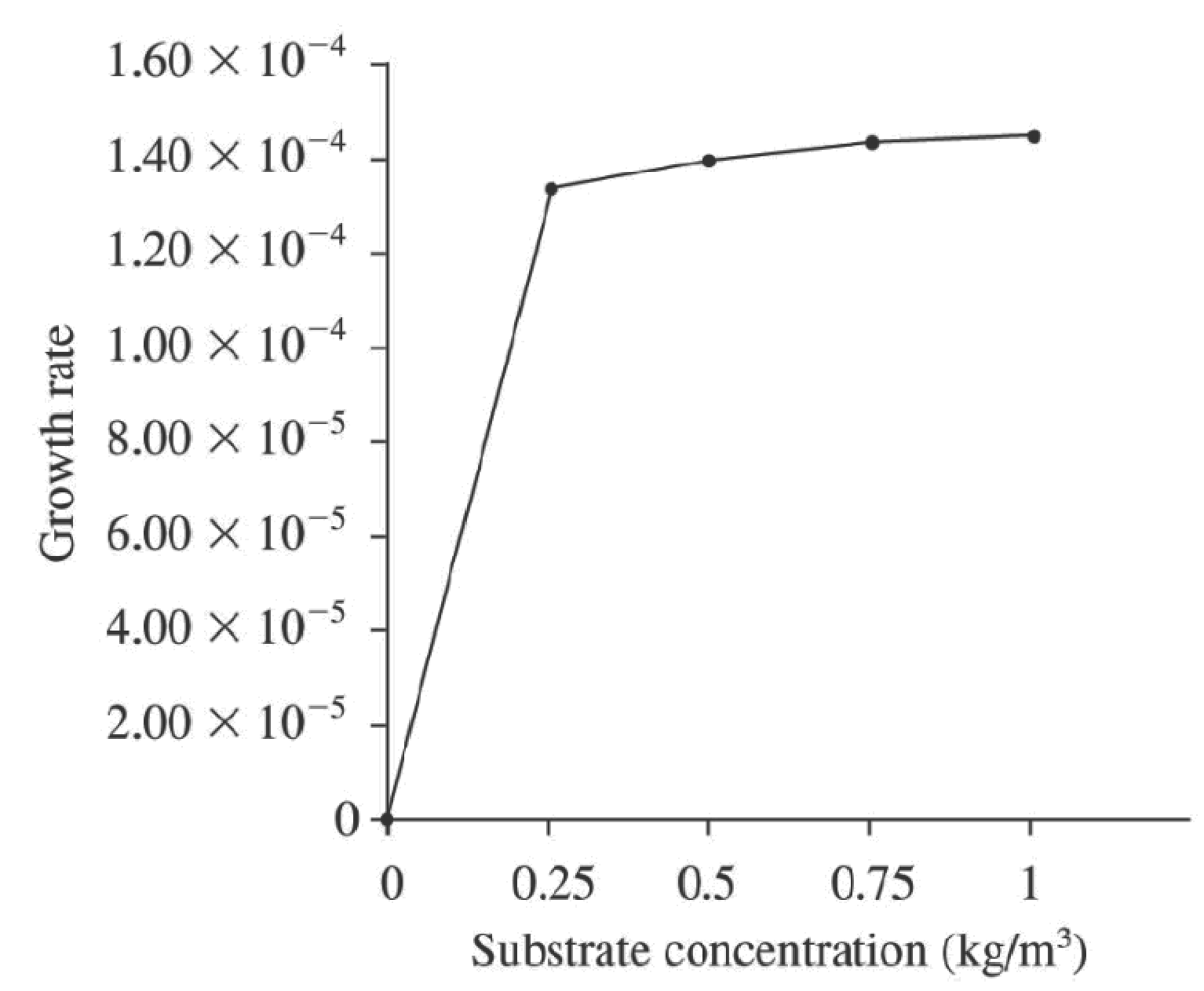
Figure.1
(b)
Interpretation:
The density after one hour if the initial
Concept Introduction:
The effect of a substrate concentration on first-order growth rate of a microbial population follows the Monod equation:
Where,
The first-order reaction kinetics,
Where,
(b)
Answer to Problem 16.120P
The density after one hour has been determined as
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Calculation of first-order growth rate:
According to the first-order kinetics,
Therefore, the density after one hour is found out to be
(c)
Interpretation:
The density after one hour if the initial
Concept Introduction:
The effect of a substrate concentration on first-order growth rate of a microbial population follows the Monod equation:
Where,
The first-order reaction kinetics,
Where,
(c)
Answer to Problem 16.120P
The density after one hour if the initial
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Calculation of first-order growth rate:
According to the first-order kinetics,
Therefore, the density after one hour is found out to be
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
GEN CMB CHEM; CNCT+;ALEKS 360
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





