
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product for the reaction of ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
Concept introduction:
An electrophilic
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
No product will be formed in the reaction of ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
Explanation of Solution
Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. In the dark no bromine free radical will be generated, therefore, no free radical reaction will occur. Carbon tetrachloride does not facilitate the production of positively charged
No reaction takes place between ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
(b)
Interpretation:
The product for the reaction ethylbenzene with
Concept introduction:
An electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction is a type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom of the aromatic ring. Aromatic ring does not easily undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction; however, it undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction easily.
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
The products for the reaction ethylbenzene with
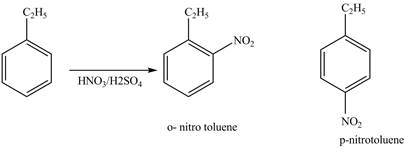
Explanation of Solution
Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. The nitronium ion
The corresponding
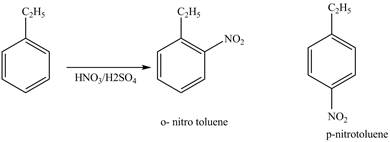
Figure 1
The products for the reaction ethylbenzene with
(c)
Interpretation:
The product for the reaction ethylbenzene with concentrated
Concept introduction:
An electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction is a type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom of the aromatic ring. Aromatic ring does not easily undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction; however, it undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction easily.
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
The products for the reaction ethylbenzene with concentrated
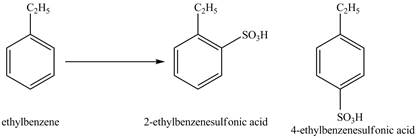
Explanation of Solution
Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. In the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid, the
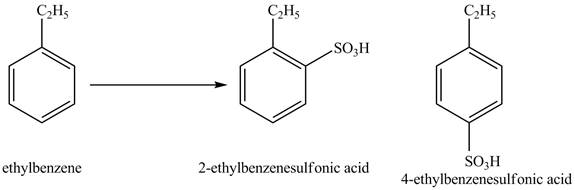
Figure 2
The products for the reaction ethylbenzene with concentrated
(d)
Interpretation:
The product for the reaction ethylbenzene with propionyl chloride and
Concept introduction:
Friedel Craft acylation is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. In this reaction, the synthesis of the monoacylated product takes place from the reaction between aromatic rings and acyl chlorides.
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
The products for the reaction of ethylbenzene with propionyl chloride and
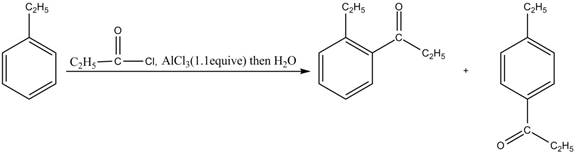
Explanation of Solution
Friedel-Crafts alkylation permits the synthesis of alkylated products by the reaction of arenes with alkyl chlorides in the presence of aluminum chloride (Lewis acid). This alkylation reaction comes under the category of electrophilic aromatic substitution. Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. The acyl group attacks either ortho or para position of ethylbenzene to form the product. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
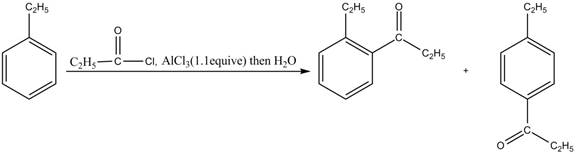
Figure 3
The products for the reaction ethylbenzene with propionyl chloride and
(e)
Interpretation:
The product for the exothermic reaction of ethylbenzene with
Concept introduction:
An electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction is a type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom of the aromatic ring. Aromatic ring does not easily undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction; however, it undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction easily.
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
The product for the exothermic reaction of ethylbenzene with
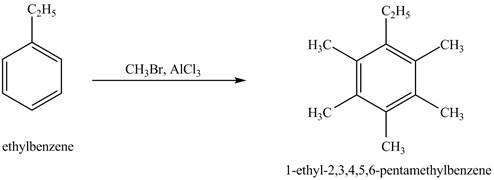
Explanation of Solution
Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. In the presence of
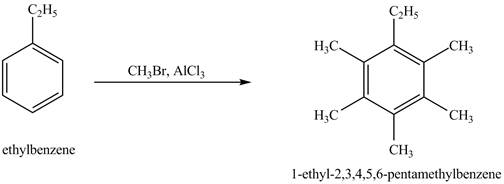
Figure 4
The product for the exothermic reaction of ethylbenzene with
(f)
Interpretation:
The product for the exothermic reaction of ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
Concept introduction:
An electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction is a type of reaction in which an electrophile substitutes a hydrogen atom of the aromatic ring. Aromatic ring does not easily undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction; however, it undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction easily.
Answer to Problem 16.35AP
The products for the exothermic reaction of ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
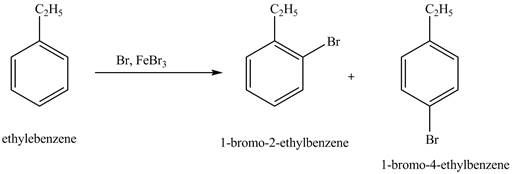
Explanation of Solution
Ethylbenzene is ortho and para directing group, the electrophile will substitute on either ortho or para position of the benzene ring. In this reaction, positively charged
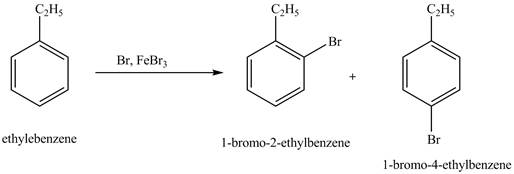
Figure 5
The products for the exothermic reaction ethylbenzene with bromine gas and
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)+ SAPLING ACC >BI
- Draw the resonance structures of [CH3C(OCH3)2]+ and identify its minor and major contributors.arrow_forwardDrawing on what you know about the stereochemistry of alkene addition reactions, a. write the mechanism for the reaction of 2-butyne with one equivalent of Br2. b. predict the configuration of the product of the reaction.arrow_forwardIf you put methylene blue and disperse red 1 mixture into salad dressing, predict what will you observearrow_forward
- 12.4 (j-k)Predict the product and give the name of the reactionarrow_forward3 b and c) Give the productarrow_forwardThe compound acetophenone has a very similar molar mass to that of benzoic acid and benzamide. However, acetophenone has a much lower m.p. (20 °C) than both such that, by contrast, it is a liquid at room temperature. By considering intermolecular forces and comparing functional group structure, account for this big difference in physical properties.arrow_forward
- 5.In the polycondensation of H2N(CH2)6NH2 and HOOC(CH2)4COOH, in equimolar quantities, to form nylon-6,6 what is the molecular weight of the species that has the largest yield by weight at 99% conversion ?arrow_forwardExplain the mechanism-Carboxylation—Reaction of RMgX with CO2arrow_forwardI don't undertaand how you calculated the final ratio of H(2)O at the end of the explaination. How did you come to 6?arrow_forward
- 5c) Write the rate equation for the following SN1 reaction:arrow_forwardCan you please draw and show the mechanism for the changes to help with understanding how phenolpthalein changes rather than just words? As little hard to follow.arrow_forwardI’m currently trying to write a lab report for the synthesis of dimolybdenum tetraacetate [Mo2(O2CCH3)4] from the reaction of molybdenum hexacarbonyl, Mo(CO)6 in glacial acetic acid and acetic anhydride under a nitrogen atmosphere, involving the difficult formation of a quadruple bond and requires high heat and long reaction time (approximately 20 hours). But these are the question I’m stumped on: 1. Why need the reaction be done under nitrogen? We also added dichlorobenzene and hexanes during the reaction. 2. Explain the purpose of dichlorobenzene and hexanes. 3. Why does the reaction take 20 hrs?arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

