
(a)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
Explanation of Solution
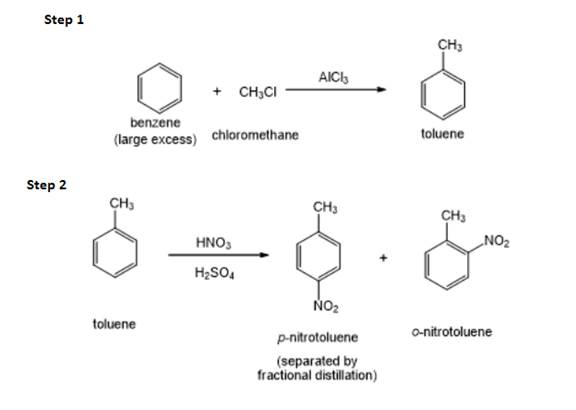
The structure of
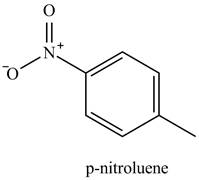
Figure 1
The methyl is an ortho and para directing group and nitro is a meta directing group. the compound is para compound. Therefore, the benzene will first undergo methylation reaction with chloromethane and
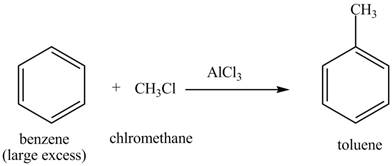
Figure 2
The toluene will undergo nitration reaction with nitric acid in sulfuric acid to from ortho and para-substituted compounds. The para-substituted gets separated from ortho compound with the help of fractional distillation process. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
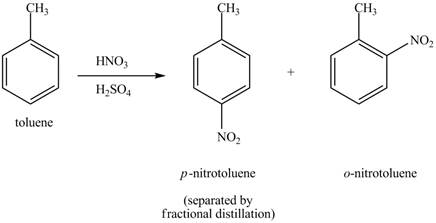
Figure 3
The laboratory synthesis of
(b)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
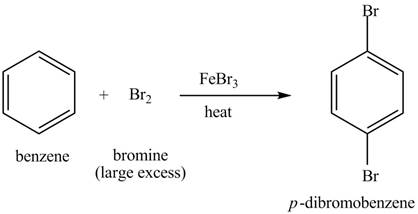
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
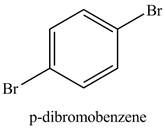
Figure 4
Benzene reacts with an excess of bromine gas in the presence of a
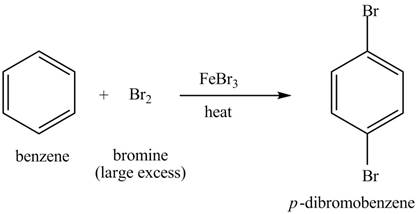
Figure 5
The laboratory synthesis of
(c)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
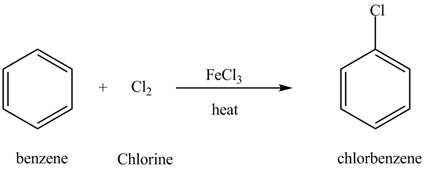
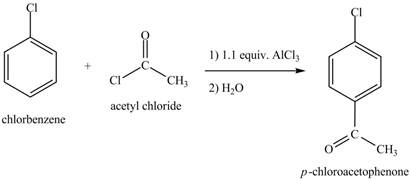
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
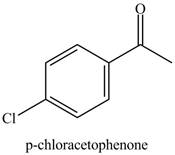
Figure 6
Benzene reacts with chlorine gas in the presence of a catalyst
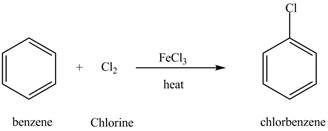
Figure 7
The chlorobenzene undergoes Friedel Craft acylation reaction with acetyl chloride in the presence of
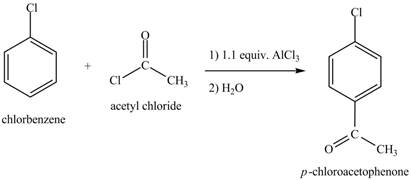
Figure 8
The laboratory synthesis of
(d)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
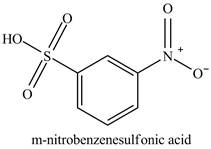
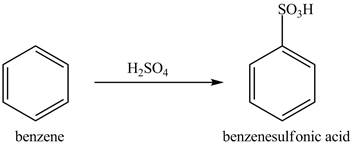
Figure 9
The benzene molecule will undergo sulfonation reaction with sulfuric acid. The electrophile
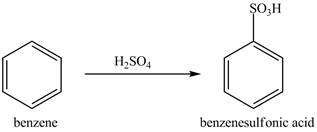
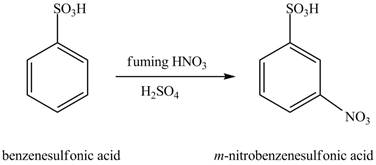
Figure 10
The benzenesulfonic acid will undergo nitration reaction with fuming nitric acid in sulfuric acid to form
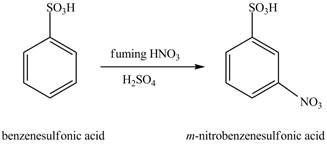
Figure 11
The laboratory synthesis of
(e)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
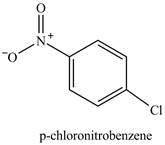
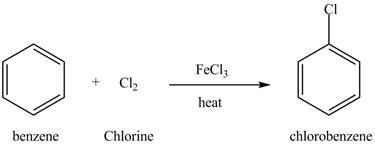
Figure 12
Benzene reacts with chlorine gas in the presence of a catalyst
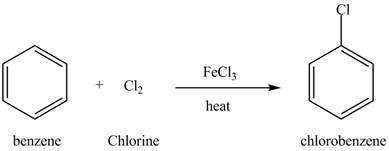
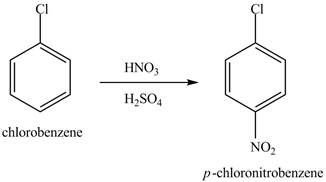
Figure 13
The chlorobenzene will undergo nitration reaction with nitric acid in sulfuric acid to form
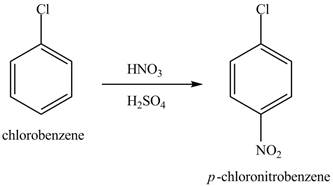
Figure 14
The laboratory synthesis of
(f)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
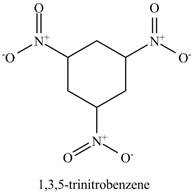
Figure 15
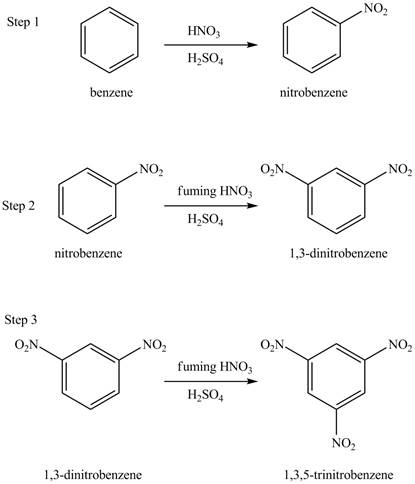
The benzene will undergo nitration reaction with nitric acid in sulfuric acid to form nitrobenzene. The nitro group is a ring deactivating group and meta directing group. Therefore, some strong condition is required to substitute another electrophile on it. The nitrobenzene reacts with fuming nitric acid and sulfuric acid to form
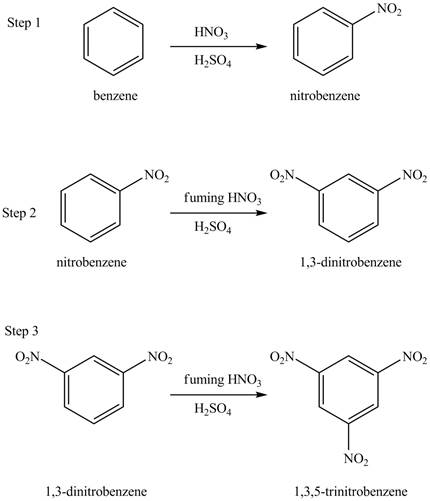
Figure 16
The laboratory synthesis of
(g)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
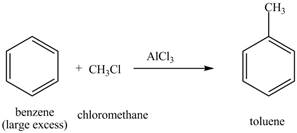
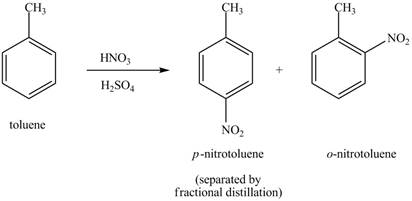
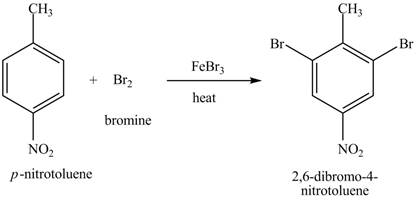
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
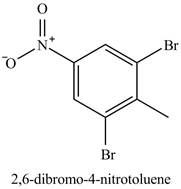
Figure 17
The benzene will first undergo methylation reaction with chloromethane and
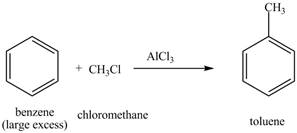
Figure 18
The toluene will undergo nitration reaction with nitric acid in sulfuric acid to form ortho and para-substituted compounds. The para-substituted gets separated from ortho compound with the help of fractional distillation process. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
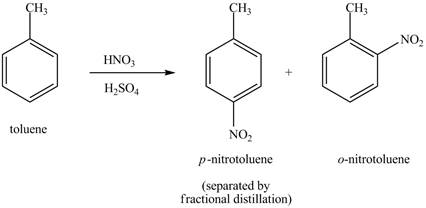
Figure 19
The compound
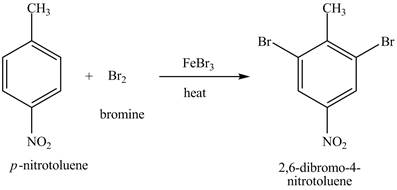
Figure 20
The laboratory synthesis of
(h)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
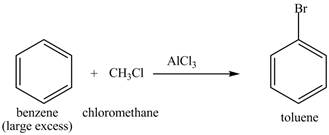
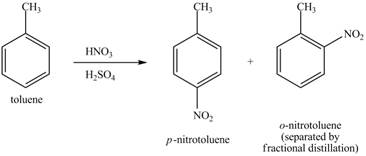
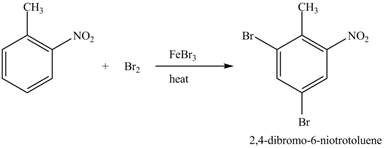
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
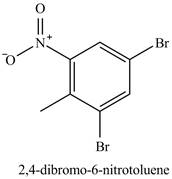
Figure 21
The benzene will first undergo methylation reaction with chloromethane and
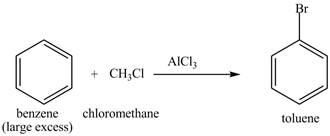
Figure 22
The toluene will undergo nitration reaction with nitric acid in sulfuric acid to form ortho and para-substituted compounds. The para-substituted gets separated from ortho compound with the help of fractional distillation process. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.

Figure 23
The compound
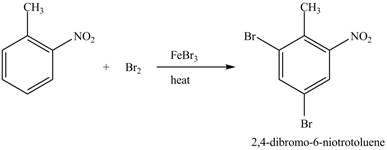
Figure 24
The laboratory synthesis of
(i)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of
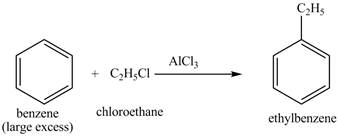
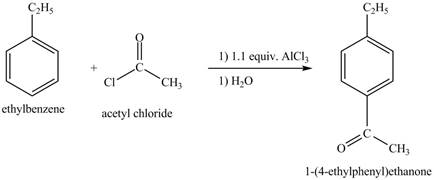
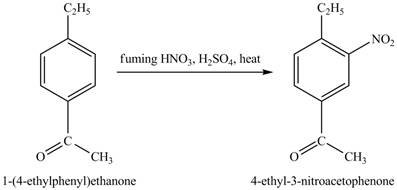
Explanation of Solution
The structure of
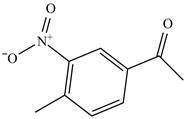
Figure 25
The benzene will first undergo ethylation reaction with chloromethane and
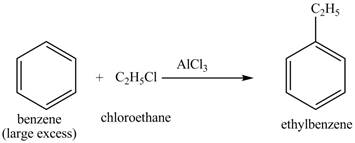
Figure 26
The ethylbenzene undergoes Friedel Craft acylation reaction with acetyl chloride in the presence of
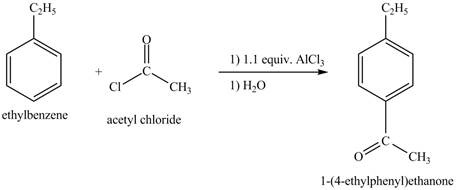
Figure 27
The compound
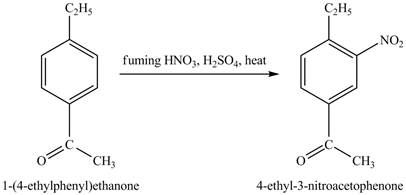
Figure 28
The laboratory synthesis of
(j)
Interpretation:
The laboratory synthesis of cyclopentylbenzene from benzene and any other reagents is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The replacement of hydrogen atom attached to a carbon atom of electron-rich benzene ring by an incoming electrophile is known as electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. The rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction depends on the substituted group on the aromatic ring. The ring deactivating group retards the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and ring activating group enhances the electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Answer to Problem 16.43AP
The laboratory synthesis of cyclopentylbenzene from benzene and any other reagents is shown below.
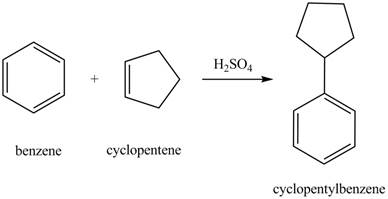
Explanation of Solution
The structure of cyclopentylbenzene is shown below.
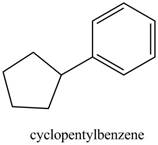
Figure 29
Benzene reacts with cyclopentene in the presence of sulfuric acid to form cyclopentyl benzene. The sulfuric acid acts as a catalyst to generate carbocation from cyclopentene. This carbonation acts as an electrophile and attacks the benzene ring. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.

Figure 30
The laboratory synthesis of cyclopentylbenzene from benzene and any other reagents is shown in Figure 30.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SAPLING ACCESS + ETEX
- Outline the synthesis of the following from either malonic ester or acetoacetic ester or an enamine and using any other reagents of your choice:arrow_forwardThe Lewis structures of both pyridine and pyrrole have an electron pair on the nitrogen atom, suggesting that both substances might possess basic properties. However, the only pyridine reacts readily with HCl to form pyridinium chloride, while pyrrole is rather unreactive. Explain clearly, using relevant diagrams to illustrate/clarify your answer.arrow_forwardCompound X was soluble in water and ether, and its aqueous solution turned litmus blue. It reacted with sodium to give a gas. The compound reacted with benzenesulfonyl chloride and base to give an insoluble product, which was unchanged with acidification. It reacted with nitrous acid to give a yellow solid. Compound A could bearrow_forward
- Give the clear handwritten answer and give the mechanism of given bleow reactionsarrow_forwardGive a clear handwritten answer with explanation needed!!! Give the mechanism...arrow_forwardWith diagrams and detailed explanations, comment on the electrophilic aromatic substitution reactivity of quinoline and isoquinolinearrow_forward
- What is the background on the chemistry of electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, what is the importance of nitration reactions in organic synthesis, and the reactivity of methyl benzoate, a methyl ester of benzoic acid. With referencesarrow_forwardoutline a brief synthesis for 2-methyl-1,2-propanediol from tert-butyl alcohol. State any organic or inorganic reagents that will be necessary for the synthesis.arrow_forwardGive a clear handwritten answer with explanation...give the mechanism of given bleow reactionarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





