
The specific growth rate of a yeast that produces an antibiotic is a function of the food concentration c,
As depicted in Fig. P16.4, growth goes to zero at very low concentrations due to food limitation. It also goes to zero at high concentrations due to toxicity effects. Find the value of c at which growth is a maximum.
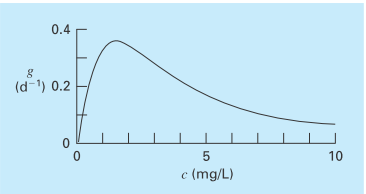
FIGURE P16.4
The specific growth rate of a yeast that produces an antibiotic versus the food concentration.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 16 Solutions
Numerical Methods For Engineers, 7 Ed
- Theorem 6.5.1. Newton's Law of Cooling. The temperature T at a time x of a cooling object follows the function T=A+Be^kx A is the ambient (or room) temperature. B and k are constants that depend on the object. Suppose a forensics technician arrived at a murder scene and recorded the temperature of the surroundings as well as the body. The technician decides it is fair to assume that the room temperature has been holding steady at about 68 °F. A thermometer was placed in the liver of the corpse and the following table of values was recorded. Table 6.5.2. Time and Temperature Actual Time Minutes Elapsed (x) Temperature, ,T, of the Body (°F) 2:00 pm 0 85.90 2:20 pm 20 85.17 2:40 pm 40 84.47 3:00 pm 60 83.78 The key to estimating time of death is to estimate ,A, ,B, ,k, and x in First question: Recall that the technician thinks the room temp was 68 °F. By substituting this number and the first recording (0, 85.9) into the Cooling Equation, find: A: B Second Question:…arrow_forwardThe following data are given for a biogas digester suitable for the output of six cows. The volume of digester is 8.3 m3 , the volume of gas holder is 2.2 m3 and the retention time is 22 days. Find the height of gas holder in centimeter.arrow_forwardtwo kinds of bacteria are found in a sample of tainted food. it is found that the population size of type 1, N1 and of type 2, N2 satisfy the equation dn/dt=-0.3/N1 dn/dt=0.4/N2 N1 is equal to 1500 at time equal to zero, while N2 is equal to 30 at time equal to zero. then the population sizes are equal N1 = N2 at what time? (4 decimal places)arrow_forward
- Q\. The first law of thermodynamics involves three main components, if we know the behavior of two components, estimate the behavior of the third component. ( Conclusion ) : a. If heat is added to the system, then the internal energy of the system increases. ..... .. b. If heat leaves the system, then the internal energy of the system decreases .... c. If the work is done by the system, then the internal energy of the system decreases ... ....... d. If the work is done on the system, then the internal energy of the system increases.. .......arrow_forward4. In a culture of yeast, the amount A of active yeast grows at a rate proportional to the amount present. If the original amount A, doubles in 2 hours, how long does it take for the original amount to triple? drarrow_forwardIf T = 30 °C and T = 60 °C . C, is equal to : a. C, = 0.5C2 b. C = 2C2 C. C = v2 C2 d. C, = v0.5 C2 ww. %3D %3D %3D %3Darrow_forward
- Topic : Mixture Flow Problem A tank initially holds 100 gal of salt solution in which 50 Ib of salt has been dissolved. A pipe fills the tank with brine at the rate of 3 gpm, containing 2 lb of dissolved salt per gallon. Assuming that the mixture is kept uniform by stirring, a drain pipe draws out of the tank at 2pm. Find the amount of salt at the end of 30 minutes. Ans. 171.24 Ibarrow_forward4. A nuclear power facility produces a vast amount of heat, which is usually discharged into aquatic systems. This heat raises the temperature of the aquatic system, resulting in a greater concentration of chlorophyll a, which in turn extends the growing season. To study this effect, water samples were collected monthly at 3 stations for a period of 12 months. Štation Á is located closest to a potential heated water discharge, station Č is located farthest away from the discharge, and station B is located halfway between stations A and C. The following concentrations of chlorophyll a were recorded. Station Month January February March A B C 9.867 3.723 8.416 4.410 14.035 11.100 10.700 20.723 4.470 April Мay June July August September October November December 13.853 9.168 8.010 7.067 4.778 34.080 11.670 9.145 8.990 7.357 8.463 3.350 3.358 4.086 4.500 4.210 4.233 6.830 3.630 2.320 5.800 2.953 3.843 3.480 2.640 3.610 3.020 Perform an analysis of variance and test the hypothesis, at the…arrow_forward1. In general, the internal energy U depends on both temperature and volume, U=U(TV). The volume dependence comes from the potential energy due to the interactions among the particles. For free particles, there are no interactions, thus, the internal energy U should be independent of the volume, i.e., = 0. Verify this result for ideal gas pV = RT. au avarrow_forward
- A bottle filling operation in a manufacturing facility fills 16 oz. water bottles is uniformly distributed with α = 15.750 oz. and β = 16.250 oz. What is the probability that a sample taken will weigh between 15.805 oz. and 16.015 oz.?arrow_forwardbliuzodt to mopolb 9. If machine parts are degreased by means of kerosene as shown in the diagram, how much kerosene make-up is needed per day? How much kerosene has to enter the degreasing vat per day? There are about 3 lb of grease per 100 lb of machine parts, and 60 tons of machine parts are processed each day. Five thousand pounds of kerosene (the 10% solution) are carried away by the machine parts each day but drip off and are caught and put back in the degreasing vat. Two hundred pounds of the 10% solution are lost each day from the vat by evaporation, spillage, or by being carried away.arrow_forward2. For each of the situations described below, use an initial value problem to model the situation. Clearly define any variables and functions used. Do not solve the initial value problems. a. A 60kg ball is released from rest 3km above the Earth. Its drag force has a proportionality constant of 50 . Model its velocity as a function of time. m b. Air conditioning is turned off in an empty building. Initially, at 6PM, it has an interior temperature of 60°F. The building has a time constant of 4 hours. (Note: This is the time constant, not the constant of proportionality in Newton's Law.) The outdoor temperature fluctuates sinusoidally, reaching a maxmimum of 100°F at noon and a minimum of 60°F at midnight every day. Assume there are no heating or cooling effects on the build aside from Newton's Law of Cooling. Model the building's temperature as a function of time.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





