
Concept Introduction:
Marginal Cost (MC): It refers to the rate by which the total cost of the produced good changes when the production increases by a single unit. As fixed cost is constant irrespective of production, so the marginal cost depends on the variable cost only in the short run.
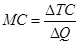
Here,
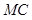 is the marginal cost.
is the marginal cost. 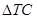 is the change in total cost
is the change in total cost 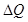 is the change in quantity.
is the change in quantity.
Marginal
Rival and Non-rival goods: If a good or service consumed by a person alone at a time and its consumption is prevented from the other persons at that point of time then this kind of good is known as a rival good,
If a good or service consumed by a person alone and its consumption is not prevented from the other persons at that point of time, then this kind of good is known as a non-rival good. Generally, private goods are treated as rival goods and public goods are treated as non-rival goods.
Excludable and Non-Excludable goods: If people are prevented from the use of the good they have not paid for, then such goods are treated as excludable goods, whereas if people cannot be prevented from the use of the good they have not paid for, then such goods are treated as non-excludable goods.
Marginal social benefit: The increased benefit for the society by any of the activity of an individual or firm is known as a marginal social benefit, it is calculated by summing up marginal external benefit and marginal private benefit.
Individual Marginal benefit: The increased benefit for an individual by any of the activity of an individual or firm is known as the individual marginal benefit.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





