
(a)
The total marginal benefit
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The total marginal benefit (MB) is the sum total of individual marginal benefits. There are two consumers of mosquito abatement, such as D and L, where the marginal benefit of consumer D is
Therefore, the total marginal benefit is
Marginal benefit: Marginal benefit can be defined as the additional utility derived from the additional consumption of one or more unit of goods and services.
(b)
The optimal level of mosquito abatement.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The optimal level of mosquito abatement is determined at the point where the total marginal benefit is equal to the marginal cost (MC).
The total marginal benefit is
The total marginal cost is given as
Now, set the two expressions to get the value of optimal quantity:
Therefore, the optimal level of mosquito abatement is 40.
Marginal benefit: Marginal benefit can be defined as the additional utility derived from the additional consumption of one or more unit of goods and services.
Marginal cost (MC): Marginal benefit refers to the amount of additional cost incurred in the process of increasing one more unit of output.
(c)
The individual total benefit at the optimal level of mosquito abatement.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Figure 1 illustrates the MB, MC, and the optimal quantity of the mosquito abatement of consumer D as follows:
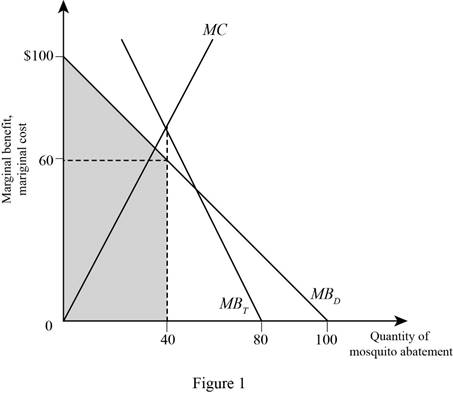
In Figure1, the vertical axis shows the MB and MC of the mosquito abatement and the horizontal axis shows the quantity of mosquito abatement, where the interaction between the total marginal benefit with MC curve determines the optimal quantity of mosquito abatement.
The MB of consumer D can be calculated by substituting the respective value in the MB function of D as follows:
Therefore, 60 is the MB of consumer D.
The MB of consumer L can be calculated by substituting the respective value in the MB function of L as follows:
Therefore, 20 is the MB of consumer D.
Therefore, the total benefit is 80
Now, the total benefit (TB) for consumer D can be calculated using the formula given below:
Now, substitute the respective values in Equation (1) to get the value of total benefit of consumer D.
Therefore, the total benefit of consumer D is 3,200.
Figure 2 illustrates the MB, MC, and the optimal quantity of the mosquito abatement of consumer L as follows:
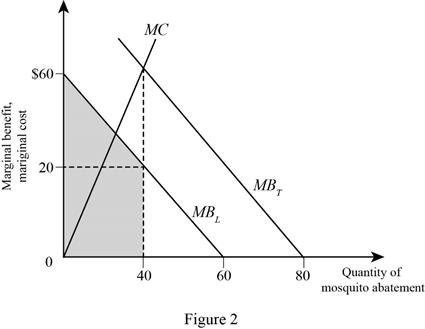
In Figure2, the vertical axis measures the MB and MC of the mosquito abatement and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of mosquito abatement, where the interaction between the total marginal benefit with MC curve determines the optimal quantity of mosquito abatement.
The total benefit (TB) for consumer L can be calculated using the formula given below:
Now, substitute the respective values in Equation (2) to get the value of total benefit of consumer L.
Therefore, the total benefit of consumer L is 1,600.
Marginal benefit: Marginal benefit can be defined as the additional utility derived from the additional consumption of one or more unit of goods and services.
Marginal cost (MC): Marginal benefit refers to the amount of additional cost incurred in the process of increasing one more unit of output.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
LaunchPad for Goolsbee's Microeconomics (Six Month Access)

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





