
(a)
Interpretation: The overall balance
Concept Introduction:
In a chemical reaction to be occurred; two most important requirements are activation energy to reactant molecule and correct orientation of reactant molecules to colloid and form product.
(a)
Answer to Problem 129CP
Explanation of Solution
On the basis of number of steps in a chemical reaction, the reactions can be classified as elementary reactions and multi-step reaction. The elementary step of a chemical reaction can be defined as the primary step of the reaction which comprise together to show the complete conversion of a reactant to product in the multi-step reaction.
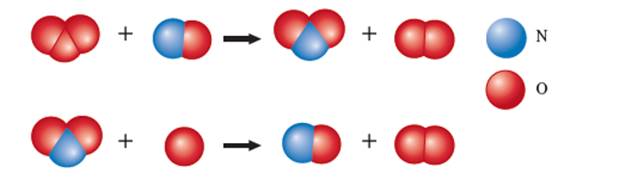
The given ball and stick model for the chemical reaction is:
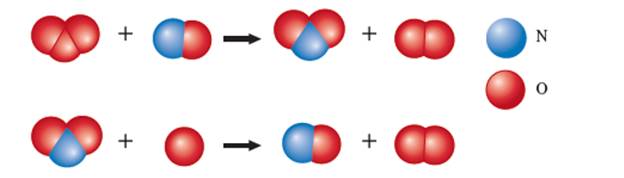
Hence the steps of the given reaction can be written as:
(b)
Interpretation: The species which act as catalyst for the ozone destruction needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical kinetic is the branch of chemistry that deals with kinetic or rate of a chemical reaction. The rate of reaction can be defined as the change in the concentration of reactant and product with time. The rate of reaction mainly depends on the activation energy.
In a chemical reaction to be occurred; two most important requirements are activation energy to reactant molecule and correct orientation of reactant molecules to colloid and form product.
(b)
Answer to Problem 129CP
NO must be catalyst for the given reaction.
Explanation of Solution
Catalyst can be defined as the substance which enhance the rate of reaction and again regenerate at the end of reaction.
In the given reaction NO involves in step-1 and again regenerate in step-2 therefore it is not part of overall reaction. Hence NO must be catalyst for the given reaction.
(c)
Interpretation: The species which act as intermediate for the ozone destruction needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical kinetic is the branch of chemistry that deals with kinetic or rate of a chemical reaction. The rate of reaction can be defined as the change in the concentration of reactant and product with time. The rate of reaction mainly depends on the activation energy.
In a chemical reaction to be occurred; two most important requirements are activation energy to reactant molecule and correct orientation of reactant molecules to colloid and form product.
(c)
Answer to Problem 129CP
Explanation of Solution
The species which is formed during the reaction and will convert to product at the end of reaction is called as intermediate.
In the given reaction
(d)
Interpretation: The rate law for the given ozone destruction reaction if the step-1 is slow and step-2 is fast step needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical kinetic is the branch of chemistry that deals with kinetic or rate of a chemical reaction. The rate of reaction can be defined as the change in the concentration of reactant and product with time. The rate of reaction mainly depends on the activation energy.
In a chemical reaction to be occurred; two most important requirements are activation energy to reactant molecule and correct orientation of reactant molecules to colloid and form product.
(d)
Answer to Problem 129CP
Explanation of Solution
Given:
In the given reaction, the step-1 is slow step and step-2 is fast step therefore the rate law will be determined with the help of step-1. In step-1; O3 and NO take part therefore the rate law can be written as:
(e)
Interpretation: The two step mechanism with second step and overall balance reaction for the rate law for ozone destruction by chlorine which are formed by reaction of Freons with light needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Chemical kinetic is the branch of chemistry that deals with kinetic or rate of a chemical reaction. The rate of reaction can be defined as the change in the concentration of reactant and product with time. The rate of reaction mainly depends on the activation energy.
In a chemical reaction to be occurred; two most important requirements are activation energy to reactant molecule and correct orientation of reactant molecules to colloid and form product.
(e)
Answer to Problem 129CP
Explanation of Solution
The destruction of ozone with NO is given below:
Freons can form active Cl atoms in the presence of light which can further react with ozone to form oxygen gas. The mechanism can be written as:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
CHEM.PRINC.W/OWL2+REBATE+2 SUPPL.>IP<
- What are the main sources of halogen-containing compounds? Why is it important to know their concentration in the atmosphere? Use of chemical reactions are welcomedarrow_forwardWhich of the following is responsible for the rise in temperature in the stratosphere? a. height of the stratosphere b. position of the stratosphere c. presence of the ozone d. nearness to the sunlightarrow_forwardWhat additional reactions do these NOx and SOx compounds undergo in the atmosphere that lead to the formation of acidic compounds? Write balanced equations for these reactions.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





