
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The ratio of A- to [HA] with the help of pH and pKa values should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
The pH of a solution indicates the number of H3 O+ ions in the solution. The mathematical relation between pH and H3 O+ is as given below;.
Acid dissociation constant Ka is related to pKa as;.
Answer to Problem 18.33P
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
pKa = 5.0.
pH = 2.0.
Calculation:
From pH of solution, concentration of hydroxide ion can be calculated as follows:
Also,
Since,
Thus, by putting the values, the ratio
(b)
Interpretation:
The ratio of A- to [HA] with the help of pH and pKa values should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
The pH of a solution indicates the number of H3 O+ ions in the solution. The mathematical relation between pH and H3 O+ is as given below;.
Acid dissociation constant Ka is related to pKa as;.
Answer to Problem 18.33P
Given:
pKa = 5.0.
pH = 5.0.
Hence [H3 O+ ] = 10-pH = 10-5.
And Ka = 10-pKa = 10-5.
Since 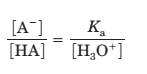
Plug the values of Ka and H3 O+ ions to calculate the ratio of [A- ] to [HA].
[A- ] / [HA] = 10-5 / 10-5 = 1.
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
pKa = 5.0.
pH = 5.0.
Calculation:
From pH of solution, concentration of hydroxide ion can be calculated as follows:
Also,
Since,
Thus, by putting the values, the ratio
(c)
Interpretation:
The ratio of A- to [HA] with the help of pH and pKa values should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
The pH of a solution indicates the number of H3 O+ ions in the solution. The mathematical relation between pH and H3 O+ is as given below;.
Acid dissociation constant Ka is related to pKa as;.
Answer to Problem 18.33P
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
pKa = 5.0.
pH = 7.0.
Calculation:
From pH of solution, concentration of hydroxide ion can be calculated as follows:
Also,
Since,
Thus, by putting the values, the ratio
(d)
Interpretation:
The ratio of A- to [HA] with the help of pH and pKa values should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
The pH of a solution indicates the number of H3 O+ ions in the solution. The mathematical relation between pH and H3 O+ is as given below;.
Acid dissociation constant Ka is related to pKa as;.
Answer to Problem 18.33P
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
pKa = 5.0.
pH = 9.0.
Calculation:
From pH of solution, concentration of hydroxide ion can be calculated as follows:
Also,
Since,
Thus, by putting the values, the ratio
(e)
Interpretation:
The ratio of A- to [HA] with the help of pH and pKa values should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
The pH of a solution indicates the number of H3 O+ ions in the solution. The mathematical relation between pH and H3 O+ is as given below;.
Acid dissociation constant Ka is related to pKa as;.
Answer to Problem 18.33P
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
pKa = 5.0.
pH = 11.0.
Calculation:
From pH of solution, concentration of hydroxide ion can be calculated as follows:
Also,
Since,
Thus, by putting the values, the ratio
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- The pH of a solution that is 0.5 in MA and 0.3 in HA is 5.40; determine the pKa of the acid.arrow_forwardCalculate the pKa of the weak acid HA, given that a solution that is 0.357 in HA and 1.24 in A- has pH = 5.32.Provide your answer rounded to 2 decimal digits.arrow_forward5.20e-03 M solution of a weak base has a pH of 9.60. Calculate the value of pKb for the substance. 5.26 2.94 1.88 The answer is not shown. 6.51arrow_forward
- Calculate the pH of a 3.11 M solution of KA given that for the acid: HA Ka = 4.21⋅10−44.21⋅10-4arrow_forwardA.) Calculate the percent ionization of a 0.394 M solution of nitrous acid.% Ionization = % B.) The acid ionization constant for Sc(H2O)63+ (aq) is 5.0×10-5 . Calculate the pH of a 0.0043 M solution of Sc(NO3)3 .pH =arrow_forwardGive typed explanation not written Consider the following Ka values for phosphoric acid, H3PO4.Ka1 = 7.1 x 10-3Ka2 = 6.3 x 10-8Ka3 = 4.2 x 10-13a.) What is the pH of a 4.0 M solution of H3PO4? b.) Determine the effectiveness of H2PO4acting as a base by calculating its Kb. c.) What is the pH of a 4.0 M solution of Na3PO4 (not H3PO4)?arrow_forward
- Calculate the pH of a 0.50 M solution of oxalic acid (H2C2O4) given the equilibrium constants below. Ka1 = 5.9 × 10–2 Ka2 = 6.4 × 10–5 Enter your response in pH units to the nearest 0.01.arrow_forwardWrite the balanced ionization or dissociation chemical equation of HC6H5CO2 in water. Include all phases. HC6H5CO2 SubmitRequest Answer Part B Determine the pH of a 0.461 M HC6H5CO2 M solution if the Ka of HC6H5CO2 is 6.5 x 10-5. 9.48 2.26 5.48 4.52 11.74arrow_forward18aarrow_forward
- The pH of a 0.12 M solution of acetic acid (HCH3CO2) is measured to be 2.83. Calculate the acid dissociation contant Ka of acetic acid.arrow_forwardCalculate the pKa of the weak acid HA, given that a solution of 0.65 M HA and 0.85 M NaA has a pH of 4.75arrow_forwardGiven that a weak acid has a pKa of 3.45, find the % ionization of a 0.345 M solution of weak acid.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
