
Concept explainers
Draw the products formed when phenol
a.
b.
c.
d.
(a)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
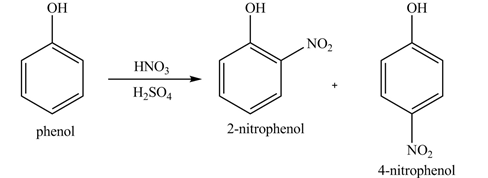
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
Explanation of Solution
Phenol undergoes nitration reaction on treatment with

Figure 1
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
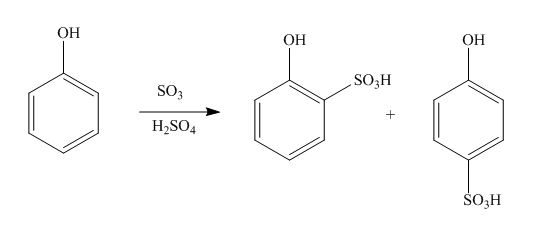
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
Explanation of Solution
An aromatic compound undergoes sulphonation on reaction with

Figure 2
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
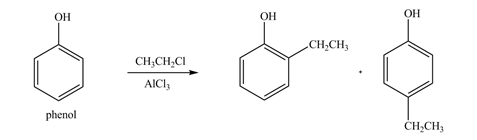
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
Explanation of Solution
An aromatic compound undergoes Friedel-Craft alkylation on reaction with

Figure 3
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
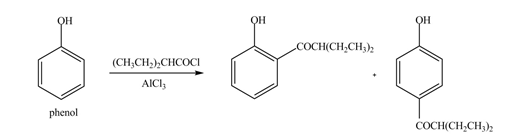
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
Explanation of Solution
An aromatic compound undergoes Friedel-Craft acylation on reaction with

Figure 4
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
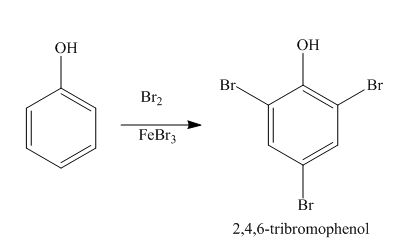
Explanation of Solution
The benzene ring is activated in phenol due to the presence of strong electron donating group. In bromination, bromonium acts as electrophile and produces

Figure 5
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
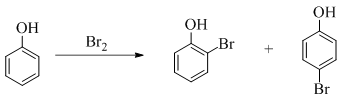
Explanation of Solution
Phenol undergoes mono bromination with bromine without catalyst. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.

Figure 6
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 6.
(g)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
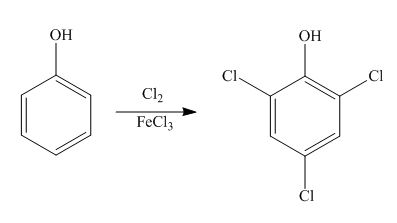
Explanation of Solution
The benzene ring is activated in phenol due to the presence of strong electron donating group. In chlorination, chloronium acts as electrophile and produces

Figure 7
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 7.
(h)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
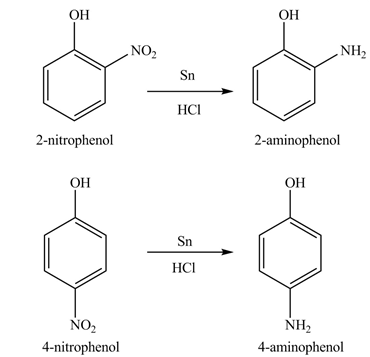
Explanation of Solution
The

Figure 8
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 8.
(i)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
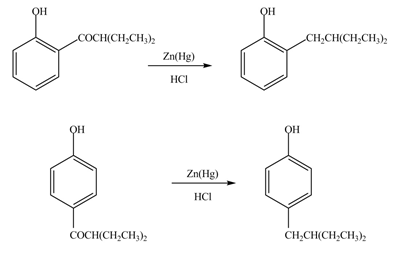
Explanation of Solution
The carbonyl group

Figure 9
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 9.
(j)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
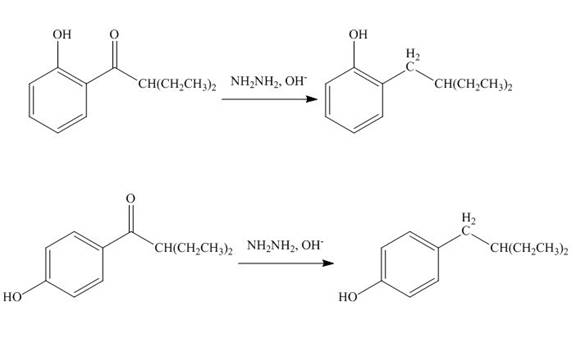
Explanation of Solution
The carbonyl group
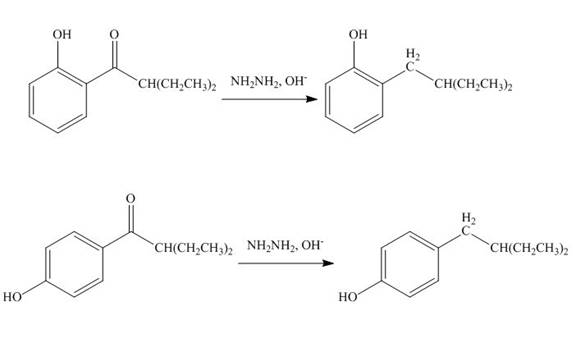
Figure 10
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 10.
(k)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
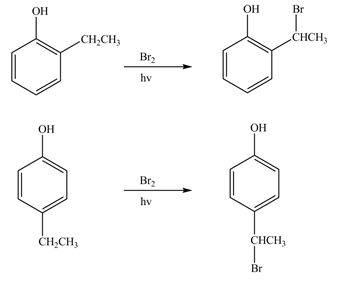
Explanation of Solution
The bromine group attaches to the side chain of the aromatic compound on reaction with

Figure 11
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 11.
(l)
Interpretation: The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron deficient chemical species that contains positive charge are known as electrophile. In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, electrophile takes the position of hydrogen atom by attacking the electron rich carbon atom of benzene.
Answer to Problem 18.36P
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown below:
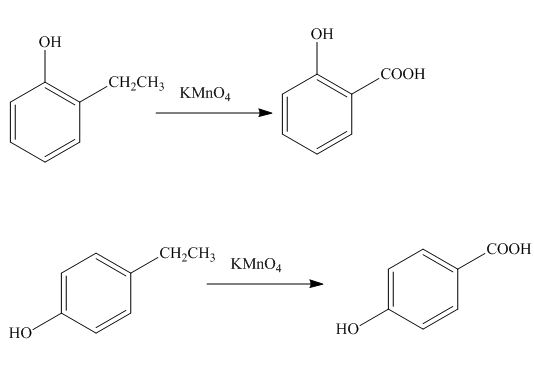
Explanation of Solution
The alkyl group oxidizes to

Figure 12
The products formed by the treatment of phenol with given reagents are shown in Figure 12.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - With Access (Looseleaf) (Custom)
- #20 B Draw structural formulas for all possible carbocations formed by the reaction of each alkene with HCl.arrow_forwardDraw the missing starting material. Reagent 1 is benzene and AlCl3. Reagent B is Zn(Hg) and HCl.arrow_forwardA. OsO4 and NMO B. Br2 and H20 C. Hg(OAc)2, H2O and NaBH4, NaOH D. RCO3H E. BH3-THF and H2O2, NaOH Which reagent will complete this reaction?arrow_forward
- What would be the reagent for each step?arrow_forwardDraw the products formed when phenol(C6H5OH) is treated with each reagent. Give an explanation. a. HNO3, H2SO4 h. product in (a), then Sn, HClarrow_forward7. GIVE AN EXAMPLE OF AN ENOL IN BIOLOGICAL SYSTEM 8. WHAT IS FEHLING'S TEST? WHAT ARE THE CONSTITUENTS OF FEHLING'S REAGENT? 10. HOW DOES FEHLING'S TEST COMPARE TO BENEDICT'S AND TOLLEN'S TEST?arrow_forward
- which reagents complete the reaction?arrow_forwardDraw the product formed when (CH3)2CHOH is treated with each reagent. a.SOCl2, pyridine b. TsCl, pyridine c.H2SO4 d.HBr e.PBr3, then NaCN f.POCl3, pyridinearrow_forwardDraw the product formed when (CH3)2CHOH is treated with each reagent. a. SOCl2, pyridine b. TsCl, pyridine c. H2SO4 d. HBr e. PBr3, then NaCN f. POCl3, pyridinearrow_forward

 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning


