
Concept explainers
(a)
The direction of the force on the projectile.
(a)
Answer to Problem 124P
The force on the projectile is
Explanation of Solution
The right hand rule states that in the case of a cross product, if the index finger of the right hand points in the direction of the first vector and the second vector points in the direction of the middle finger, then the cross product will point in the direction of the thumb. Magnetic force on a current carrying wire is the product of the current through the wire and the cross product of the vector, whose magnitude is the length of the wire and is points in the direction of current, and the magnetic field.
Right hand rule for the magnetic force on a current carrying conductor can be described as if the index finger of the right hand points in the direction of current, the middle finger in the direction of the magnetic field, then the thumb will point in the direction of the magnetic force. In the given situation, the current flows into the page and the magnetic field is directed upward. According to the right hand rule, the magnetic force on the projectile is directed to the right.
(b)
The speed of the projectile after it has travelled
(b)
Answer to Problem 124P
The speed of the projectile after it has travelled
Explanation of Solution
The free body diagram of the projectile is shown in figure 1.
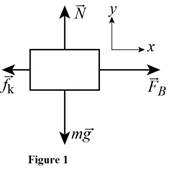
The rod only moves in the
Here,
Refer to figure 1 and write the expression for
Here,
Equate equations (I) and (II).
Write the equation for the force of kinetic friction.
Here,
Put equation (III) in the above equation.
Apply Newton’s second law to the rod for the motion in
Here,
Refer to figure (I) and write the expression for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (V) and rewrite it for
Write the expression for
Here,
Put equations (IV) and (VII) in equation (VI).
Write the second law of motion.
Here,
The rod starts from rest so that its initial speed is zero.
Substitute
Put equation (VIII) in the above equation.
Conclusion:
Given that the mass of the projectile is
Substitute
Therefore, the speed of the projectile after it has travelled
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Loose Leaf For Physics With Connect 2 Semester Access Card
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





