
Concept explainers
(a)
The speed with which the
(a)
Answer to Problem 128P
The speed with which the
Explanation of Solution
The kinetic energy gained by the ion must be equal to the potential energy lost.
Write the equation for the conservation of energy.
Here,
Write the equation for
Here,
Write the equation for
Here,
Put equations (II) and (III) in equation (I).
Here,
Write the relation for the speed of
Here,
Write the relation for the speed of
Here,
Take the ratio of the above two equations.
Conclusion:
The charge of the ion
Substitute
Therefore, the speed with which the
(b)
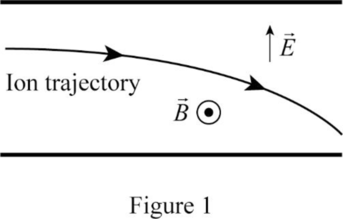
The sketch of the trajectory of
(b)
Answer to Problem 128P
The sketch of the trajectory of
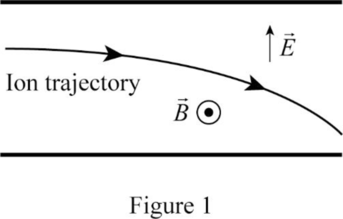
Explanation of Solution
In a velocity selector, for an ion with speed
Write the equation for the magnetic force.
Here,
In the velocity selector,
Conclusion:
Thus, the sketch of the
(c)
The diameter of the path of
(c)
Answer to Problem 128P
The diameter of the path of
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for the magnitude of the magnetic force on ions using equation (V).
Here,
The magnetic force provides the
Write the relationship between the magnetic force and the centripetal force.
Here,
Write the equation for the magnitude of the centripetal force on ions.
Here,
Write the equation for the radius of a circle.
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (VIII).
Put equations (VI) and (IX) in equation (VII).
Since
Write the relationship between the diameters of the paths of
Here,
Rewrite the above relationship for
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the diameter of the path of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Physics
- The magnetic field in a cyclotron is 1.25 T, and the maximum orbital radius of the circulating protons is 0.40 m. (a) What is the kinetic energy of the protons when they are ejected from the cyclotron? (b) What Is this energy in MeV? (c) Through what potential difference would a proton have to be accelerated to acquire this kinetic energy? (d) What is the period of tire voltage source used to accelerate the piotons? (e) Repeat tire calculations for alpha-particles.arrow_forwardCY-1 A cyclotron has an outer radius Rwith a magnetic field B=25.0T. An alternating potential difference of 150,000V exists between the D's. Protons (q=+1.60x10-19C, m=1.673x10-27kg) are injected into the cyclotron near the center with a very low speed. d) By how many eV does the kinetic energy of the proton increase per revolution? e) Find N the number of revolutions needed for B the proton to reach Ekf. f) Use any equation from part a) to find the symbolicexpression for the period T - the time for one revolution of the proton. g) Find the numerical value of T.arrow_forwardAn electron (rest mass 9.11x10-31kg, charge is -1.60-19C) is moving opposite to an electric field of magnitude E=5x105N/C. All other forces are negligible in comparison to the electrtic field force. Using formula for γ, what is the relativistic factor at the instants when v1 = 0.010c, v2 = 0.90c, and v3 = 0.99c, where c = 3x108 m/s. a. γ1=1.00; γ=2.29; γ3=7.09 b. γ1=1.20; γ=2.29; γ3=7.09 c. γ1=1.00; γ=2.49; γ3=7.09 d. a. γ1=1.00; γ=2.29; γ3=7.90arrow_forward
- A rocket cruises past a laboratory at 0.400×106m/s in the positive x-direction just as a proton is launched with velocity (in the laboratory frame)v⃗ =(1.55×106i^+1.55×106j^)m/s. a. What is the proton's speed in the laboratory frame? b. What is the angle from the y-axis of the proton's speed in the laboratory frame? c. What is the the proton's speed in the rocket frame? d. What is the angle from the y-axis of the proton's speed in the rocket frame?arrow_forwardWhat is the total energy of a proton moving at a speed of 2.30 × 108 m/s? (proton mass is 1.67 × 10−27 kg and c = 3.00 × 108 m/s) Possible answers: 1.92E–10 J 1.76E–10 J 2.34E–10 J 2.42E–10 J 9.65E–11 Jarrow_forwardPlease help with my homework An electron and a proton are detected in a cosmic ray experiment, the first with kinetic energy 10 keV, and the second with 100 keV. Which is faster, the electron or the proton ? Obtain the ratio of their speeds.(Electron mass =9.11×10−31kg=9.11×10-31kg, proton mass =1.67×10−27kg,1eV=1.60×10−19J)=1.67×10-27kg,1eV=1.60×10-19J).arrow_forward
- Scientists working with a particle accelerator determine that an unknown particle has a speed of 1.35 ×108 m/s and a momentum of 2.52 × 10−19 kg m/s. From the curvature of the particle’s path in a magnetic field, they also deduce that it has a positive charge. Using this information, identify the particle.arrow_forwardAn unstable particle at rest breaks into two fragments of unequal mass. The mass of the lighter fragment is 1.75 MeV/c2 and that of the heavier particle is 3.50 MeV/c2: The lighter fragment has a speed of 0.956 c after the breakup. (i) What is the speed of the heavier fragment? Express your answer as a fraction of c, the waythe speed of the lighter fragment is expressed above.(ii) What is the kinetic energy of the lighter fragment, in electron volts (eV)?(iii) What is the speed of the lighter fragment as seen by the heavier fragment? Express your answer as a fraction of c.arrow_forwardIf an electron having total energy of 10J moves in a circle constant distance of 10nm from a static proton, its velocity will be?arrow_forward
- The mass of an electron is 9.109 381 88 * 10-31 kg.To eight significant figures, find the following for the given electron kinetic energy: (a) gama and (b) b for K =1.000 000 0 keV, (c) g and (d) b for K = 1.000 000 0 MeV, and then (e) g and (f) b forK = 1.000 000 0 GeV.arrow_forwardThrough what potential difference would an electron initially at rest need to be accelerated to have its total energy be five times its rest energy? ( me = 9.11 × 10 –31 kg, c = 3.00 × 10 8 m/s, and qe = 1.6 × 10 −19 C)arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

 Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





