
A firm in a
a. If the market
b. Suppose a government study has found that the firm’snew process is polluting the air and estimates the socialmarginal cost of widget production by this firm to be. If the market price is still $20, what is thesocially optimal level of production for the firm? Whatshould be the rate of a government-imposed excise tax tobring about this optimal level of production?
c. Graph your results.
a)
To find: The number of widgets produced by the firm.
Explanation of Solution
The profit maximizing situation exists at the level where market price is equal to the marginal cost.
Thus, P = MC
b)
To find: The socially optimal level of production and rate of tax.
Explanation of Solution
The socially optimal level exists at, P = SMC
Given SMC = 0.5q
The socially optimal level exists at q = 40 widgets.
So the excise tax, T = 20 − 16 = $4
Thus, $4 tax should be applied to bring the optimal level of production.
c)
To find: The graph for the calculated results.
Explanation of Solution
Below graph shows the price and marginal cost on vertical axis while the quantity is on horizontal axis. Moreover, the gap between MC and SMC shows the tax imposed by the government.
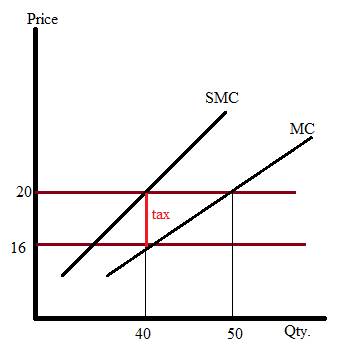
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Microeconomic Theory
- The cost (in dollars) of producing x corkboards is given by x2+20x+500, while the price (in dollars) of each corkboard if there is a demand for x units is given by p(x) = 100 -x. 1. Find the marginal profit producing and selling 15 corkboards. 2. At what production level is the profit at a maximum?arrow_forwardSuppose that the market for apples is perfectly competitive. Production of apples requires two inputs:workers (L) and land (K). The production function for apples is:F(K,L)=3K^(1/3)* L^(2/3) A) Suppose that W=4, R=16, and in the short-run, K=27. Find the firm’s short-run cost function SRC(q)and short-run marginal cost function SRMC(q).B) What is the optimal production of apples if P=4? What are consumer surplus and profit?C) Find the firm’s short-run supply of apples Q(P) when W=4, R=16 and K=27.D) Find the firm’s long-run cost function LRC(q) and long-run marginal cost function LRMC(q) when W=4and R=16. How do these compare to the firm’s short-run cost function and marginal cost function?E) Find the firm’s long-run supply of apples q(P) when W=4 and R=16.arrow_forwardThe cost function for Acme Laundry is: TC(q)=10+10q+q^2 so its marginal cost function is: MC(q)=10+2q where q is tons of laundry cleaned. Derive the firm's average cost and average variable cost curves. What q should the firm choose so as to maximize its profit if the market price is p? How much does it produce if the competitive market price is p = 50?What would it look like in excel?arrow_forward
- The cost function for Acme Laundry is C(q)=50+30q+q2, where q is tons of laundry cleaned. What q should the firm choose so as to maximize its profit if the market price is p?arrow_forwardA firm operates in a perfectly competitive market. The market price of its product is 4 birr and the total cost function is given by TC= 1/3 Q3 - 5Q2+20Q + 50, where TC is the total cost and Q is the level of output.a) What level of output should the firm produce to maximize its profit?b) Determine the level of profit at equilibrium.c) What minimum price is required by the firm to stay in the market?arrow_forwardImagine that the price of input 1 is $16 per unit, the price of input 2 is $25 per unit, and the firm has fixed costs of $60. The firm is in a competitive market where the market price is $240 per unit of output. How much should the firm produce? How much profit does the firm make?arrow_forward
- Microeconomics II is the most fun course you ever took. Explain? A profit-maximizing competitive firm uses just one input, x. Its production function is q= 4(x)^1/2. The price of out-put is $28 and the factor price is $7. The amount of the factor that the firm demands is?arrow_forwardIt is an aspect of microeconomics that helps in analyzing the various types of demand which enables the manger to arrive at reasonable estimates of demand for a product or his company. * market structures theory of the firm demand analysis production functionarrow_forwardConsider a firm that is perfectly competitive in the market for inputs and outputs. The firm hires two types of workers: low-skill (high school graduates and high school dropouts) and high-skill (undergraduate and postgraduate degree) workers. The firm compensates high-skilled workers at the rate w H and low-skill workers at the rate w L . It produces the output subject to a Cobb-Douglas production technology F(L,H) = (AH) α (L) β , where H - is the amount of high-skill hours, L - the amount of low-skill hours, and A - the technology parameter that augments the productivity of the high-skill labour. 1. Find the range of values of α and β that ensure that the production technology has (a) diminishing marginal product of high-skill labour (b) diminishing marginal product of low-skill labour (c) complementarity between high-skill and low-skill labour 2. What is the example of a firm with production technology described in 1. ? For the remained of the question consider β = 0.5 and α = 0.1:…arrow_forward
- Question 12 Refer to Figure 1 If the shop pays its mechanics a wage of $600 per day, then what is the shop's marginal profit from that third mechanic? (Enter your answer without a dollar sign.)arrow_forwardA perfectly competitive rm produces output q with capital K and labor L according to the production function: q = f(K, L) = 4K 1 4L 1 4 The price of labor is w = 4, and the price of capital is r = 4. The rm has xed costs equal to 8. The current market price is 8. (d) Find cost functions T C(q), AT C(q), and MC(q), i.e. as functions of output. At what value of q does the minimum of AT C occur? (e) Find total and marginal revenue as functions of output, i.e. T R(q) and MR(q). (f) Find the pro t maximizing output q ∗ and use that to nd T R(q ∗ ), T C(q ∗ ), π(q ∗ ), L(q ∗ ), and K(q ∗ ).arrow_forwardQuestion A Suppose the short-run production function is q = 1L0.5. If the marginal cost of producing the 10th unit is $8, what is the wage per unit of labor? Question B A consumer has the utility function U(q1,q2) = q10.5 + q2Assume p2 = 1 and Y = 100. What is the equivalent variation of a price increase for good 1 from 1 to 4?arrow_forward
 Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning






