
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Concept introduction:
Grignard reagents are
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
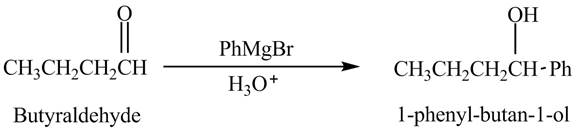
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with
The reduction of butyraldehyde takes place to form the product. The reaction is shown below.

Figure 1
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Concept introduction:
The gain of electrons involved in the particular reaction is termed as reduction. The reduction process also involves the removal of an electronegative atom from a molecule followed by the hydrogen atom addition into that molecule.
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
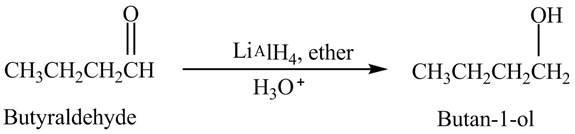
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with
The reduction of butyraldehyde takes place to form the product. The reaction is shown below.
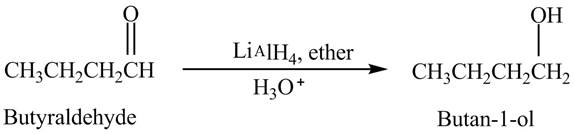
Figure 2
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
(c)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and alkaline
Concept introduction:
Oxidation is the process of addition of oxygen. Oxidation is also defined as loss of electrons. In the oxidation process, there is increase in the oxidation state. The acid is added in the reaction for protonation.
The oxidizing agent is defined as the species which oxidizes others and itself gets reduced.
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
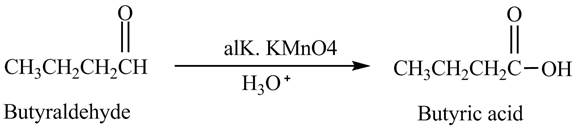
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with
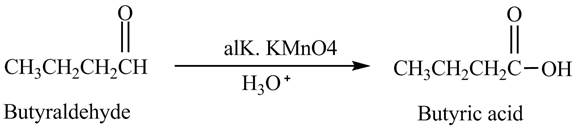
Figure 3
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and alkaline
(d)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and aqueous
Concept introduction:
Oxidation is the process of addition of oxygen. Oxidation is also defined as loss of electrons. In the oxidation process, there is increase in the oxidation state. The acid is added in the reaction for protonation.
The oxidizing agent is defined as the species which oxidizes others and itself gets reduced.
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and aqueous
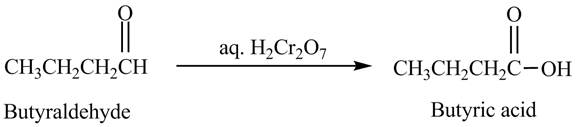
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with aqueous
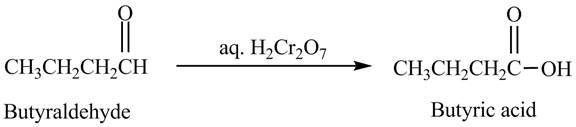
Figure 4
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and aqueous
(e)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Concept introduction:
Oxime belongs to the family of imines. The formula of oxime is
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
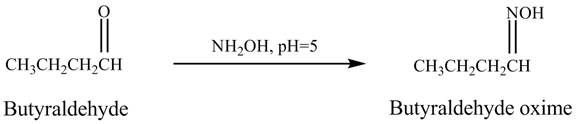
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with ![]() . When the
. When the ![]() is high then the product formed is an
is high then the product formed is an ![]() is low then the product is not formed. The reaction is shown below.
is low then the product is not formed. The reaction is shown below.
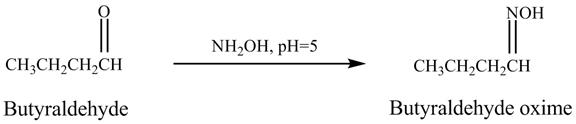
Figure 5
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
(f)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Concept introduction:
Oxidation is the process of addition of oxygen. Oxidation is also defined as loss of electrons. In the oxidation process, there is increase in the oxidation state. The acid is added in the reaction for protonation.
The oxidizing agent is defined as the species which oxidizes others and itself gets reduced.
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
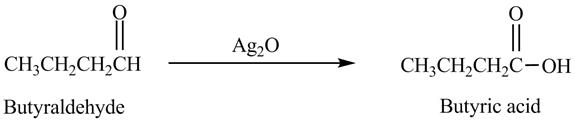
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with
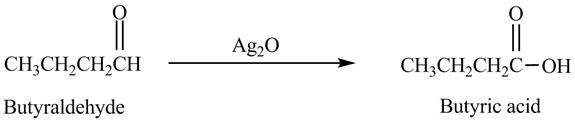
Figure 6
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
(g)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and zinc amalgam in the presence of
Concept introduction:
Clemmensen reduction is defined as the reduction in which aldehydes or
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and zinc amalgam in the presence of
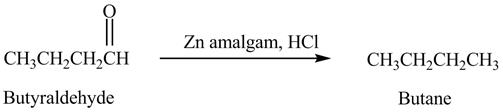
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with zinc amalgam in the presence of

Figure 7
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and zinc amalgam in the presence of
(h)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
Concept introduction:
The Wittig reaction is the
Answer to Problem 19.41AP
The geometrical isomers are formed in the reaction of butyraldehyde and
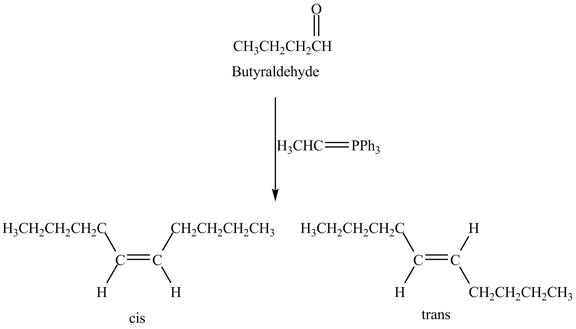
Explanation of Solution
Butyraldehyde reacts with
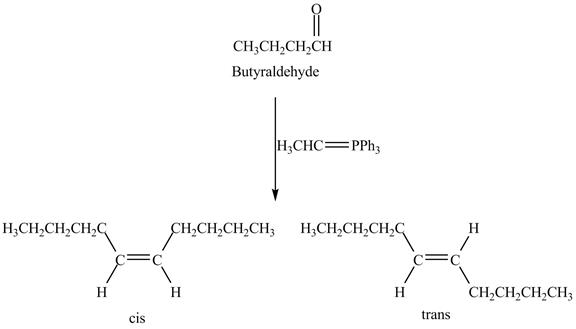
Figure 8
Butyraldehyde reacts with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)+ SAPLING ACC >BI
- Heating toluene in the presence of KMnO4 followed by acification with HCl, converts toluene into benzoic acid. Using this information and any other reactions discussed in this course, show a sequence of reactions showing howing toluene can be converted to p-aminobenzoic acid.arrow_forwardWrite the equilibrium-constant expressions and obtainnumerical values for each constant in. (a) the basic dissociation of aniline, C6H5NH2. (b) the acidic dissociation of hypochlorous acid,HClO. (c) the acidic dissociation of methyl ammoniumhydrochloride, CH3NH3Cl. (d) the basic dissociation of NaNO2. (e) the dissociation of H3AsO3to H3O+and AsO33-. (f) the reaction of C2O42-with H2O to give H2C2O4and OH-. show solutionarrow_forward3b)Give the mechanisms for the following transformations:arrow_forward
- 5. Compound A, C 10H 18O, undergoes reaction with dilute H 2SO 4 at 50 °C to yield a mixture of two alkenes, C 10H 16. The major alkene B, gives only cyclopentanone after ozone treatment followed by reduction with zinc in acetic acid. Which of the following reactions are correct.arrow_forwardExplain why the hydrolysis of [Co(NH3)5Cl]2+ in the presence of base muchfaster than that of [Co(py)5Cl]2+? Illustrate your answer with suitable diagrams.arrow_forwardGive a proposal on the synthesis methods of CoSO4.7H2Oarrow_forward
- 4b)Give the mechanisms for the following:arrow_forwardCompound A, C 10H 18O, undergoes reaction with dilute H 2SO 4 at 50 °C to yield a mixture of two alkenes, C 10H 16. The major alkene B, gives only cyclopentanone after ozone treatment followed by reduction with zinc in acetic acid. Which of the following reactions are correct. Can be more than one answerarrow_forwardThe pKa, of the conjugate acid of morpholine is 8.33. (a) Calculate the ratio of morpholine to morpholinium ion in aqueous solution at pH 7.0. (b) At what pH are the concentrations of morpholine and morpholinium ion equal?arrow_forward
- Aldehydes and ketones react with thiols to yield thioacetals just as they react with alcohols to yield acetals. Predict the product of the following reaction, and propose a mechanism:arrow_forwardAmines are converted into alkenes by a two-step process called Hofmann elimination. SN2 reaction of the amine with an excess of CH3I in the first step yields an intermediate that undergoes E2 reaction when treated with silver oxide as base. Pentylamine, for example, yields 1-pentene. Propose a structure for the intermediate, and explain why it readily undergoes elimination.arrow_forwardWhen A is reacted with hot aqueous NaOH, a compound B of molecular formula C8H11NO is produced. With this information, write the correct structure of B and propose the reaction mechanism (step by step, with the correct use of arrows) to obtain B.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

