
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of triacylglycerol formed by two molecules of lauric and one molecule of palmitic acids should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids are
Answer to Problem 19.48P
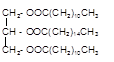
Explanation of Solution
Triacylglycerol are most abundant lipids which are mainly found in animal fat and vegetable oils. They are triesters of glycerol, therefore in the formation of one molecule of triacylglycerol, three molecules of fatty acids react with one molecule of glycerol as given below:
Chemical formula of Lauric acid=
Chemical formula of Palmitic acid=
Hence the triacylglycerol formed by these three fatty acids must be:
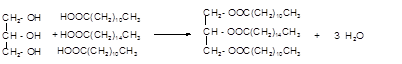
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of unsaturated triacylglycerol formed by fatty acid with three molecules of linoleic acid should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids are biomolecules that are involved in different biochemical reactions. They are special types of organic molecules that can only identify with the help of their physical properties, not by the presence of any certain functional group. In general, lipids contain a large number of C-C and C-H bonds with few polar functional groups such as −OH, -SH, etc; such as triacylglycerol consists of three ester groups whereas Vitamin E is composed of both ether and phenolic groups.
Answer to Problem 19.48P
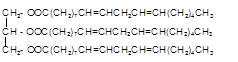
Explanation of Solution
Triacylglycerol is the most abundant lipids which are mainly found in animal fat and vegetable oils. They are triesters of glycerol, therefore, in the formation of one molecule of triacylglycerol, three molecules of fatty acids react with one molecule of glycerol as given below:
The chemical formula of linoleic acid =
Hence the triacylglycerol formed by these three fatty acids must be:
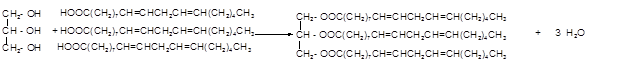
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of trans-triacylglycerol formed by fatty acid with two trans-double bonds should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids are biomolecules that are involved in different biochemical reactions. They are special types of organic molecules that can only identify with the help of their physical properties, not by the presence of any certain functional group. In general, lipids contain a large number of C-C and C-H bonds with few polar functional groups such as −OH, -SH, etc.; such as triacylglycerol consists of three ester groups whereas Vitamin E is composed of both ether and phenolic groups.
Answer to Problem 19.48P
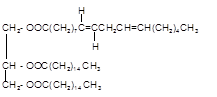
Explanation of Solution
Triacylglycerol are most abundant lipids which are mainly found in animal fat and vegetable oils. They are triesters of glycerol, therefore in the formation of one molecule of triacylglycerol, three molecules of fatty acids react with one molecule of glycerol as given below;
Chemical formula of linoleic acid with two trans-double bonds=
Chemical formula of Palmitic acid=
Hence the triacylglycerol formed by these three fatty acids must be: 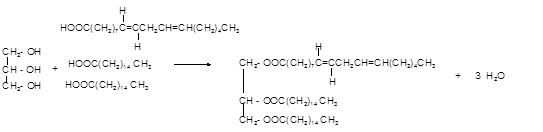
(d)
Interpretation:
An unsaturated triacylglycerol formed from linolenic acid should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Triacylglycerols are esters that are formed by reacting to three molecules of fatty acids with one molecule of glycerol. If all the three fatty acids are identical it is called a simple triacylglycerol and if there are two or more different fatty acids, it is called a mixed triacylglycerol. Depending on whether the fatty acids involved are saturated or unsaturated, there are two types of triacylglycerols.
Answer to Problem 19.48P
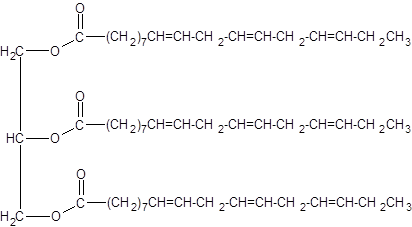
Explanation of Solution
When forming a triacylglycerol, each O atom of glycerol is bonded to the carbonyl carbon in fatty acids leaving the water as the by-product. Linolenic is an 18 carbon polyunsaturated fatty acid with three double bonds.
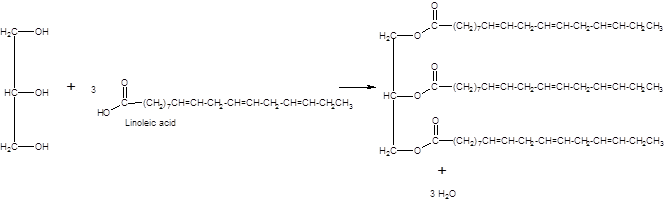
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
GENERAL ORGANIC+BIOCHEM (LL)W/CONNECT
- Which of the terms triacylglycerol, glycerophospholipid, and sphingophospholipid applies to each of the following characterizations? More than one term may apply in a given situation. a. It contains four building blocks. b. All linkages are ester linkages. c. An alcohol building block is present. d. It is an energy-storage lipid.arrow_forwardThe following is a block diagram for a glycerophospholipid where the building blocks are labeled with letters and the linkages between building blocks are labeled with numbers. a. Which building blocks are fatty acid residues? b. Which building blocks are alcohol residues? c. Which linkages are ester linkages? d. Which linkages involve a phosphate residue?arrow_forwardDraw block diagram structures for the three different triacylglycerols that can be produced from glycerol, palmitic acid, stearic acid, and linolenic acid.arrow_forward
 Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning

