
Concept explainers
Label each compound as a hydrolyzable or nonhydrolyzable lipid.
- prostaglandin
- phosphoacylglycerol
- triacylglycerol
- lecithin
- leukotriene
- cholesterol
- vitamin A
(a)
Interpretation:
Prostaglandin should be labeled as Hydrolyzable or non-hydrolyzable lipid.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids can be grouped as hydrolyzable and nonhydrolyzable. Hydrolyzable lipids can be broken down into smaller molecules by reacting with water. Hydrolyzable lipids usually contain an ester functional group which is hydrolyzable. There are three subgroups of hydrolyzable lipids as waxes, triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Nonhydrolyzable lipids cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis with water. There are subgroups of nonhydrolyzable lipids as steroids, fat-soluble vitamins and eicosanoids.
Answer to Problem 19.29P
Nonhydrolyzable
Explanation of Solution
Prostaglandin is a 20 carbon unsaturated carboxylic acid which contains a five-membered ring. A typical structure for prostaglandin is,
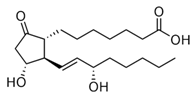
Prostaglandin does not contain an ester group. So, prostaglandin is nonhydrolyzable lipid.
(b)
Interpretation:
Triacylglycerol should be labeled as Hydrolyzable or non-hydrolyzable.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids can be grouped as hydrolyzable and nonhydrolyzable. Hydrolyzable lipids can be broken down into smaller molecules by reacting with water. Hydrolyzable lipids usually contain an ester functional group which is hydrolyzable. There are three subgroups of hydrolyzable lipids as waxes, triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Nonhydrolyzable lipids cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis with water. There are subgroups of nonhydrolyzable lipids as steroids, fat-soluble vitamins and eicosanoids.
Answer to Problem 19.29P
Hydrolyzable
Explanation of Solution
Triacylglycerol is produced by reacting a glycerol molecule with three molecules of fatty acids by an ester linkage.
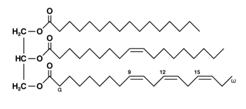
Triacylglycerol has three ester linkages. So, triacylglycerol is a hydrolyzable lipid.
(c)
Interpretation:
Leukotriene should be labeled as Hydrolyzable or non-hydrolyzable.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids can be grouped as hydrolyzable and nonhydrolyzable. Hydrolyzable lipids can be broken down into smaller molecules by reacting with water. Hydrolyzable lipids usually contain an ester functional group which is hydrolyzable. There are three subgroups of hydrolyzable lipids as waxes, triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Nonhydrolyzable lipids cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis with water. There are subgroups of nonhydrolyzable lipids as steroids, fat-soluble vitamins and eicosanoids.
Answer to Problem 19.29P
Nonhydrolyzable
Explanation of Solution
Leukotrienes belong to the family of eicosanoids. Leukotrienes are synthesized by arachidonic acid. A typical structure for leukotriene is,
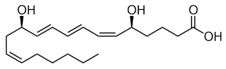
Leukotrienes have no ester linkages. So, leukotrienes are nonhydrolyzable lipids.
(d)
Interpretation:
Vitamin A should be labeled as hydrolyzable or non-hydrolyzable.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids can be grouped as hydrolyzable and nonhydrolyzable. Hydrolyzable lipids can be broken down into smaller molecules by reacting with water. Hydrolyzable lipids usually contain an ester functional group which is hydrolyzable. There are three subgroups of hydrolyzable lipids as waxes, triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Nonhydrolyzable lipids cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis with water. There are subgroups of nonhydrolyzable lipids as steroids, fat-soluble vitamins and eicosanoids.
Answer to Problem 19.29P
Nonhydrolyzable
Explanation of Solution
Vitamin A is a group of several unsaturated fatty acids. It includes retinol which has an alcohol functional group, retinal which is an aldehyde and retinoic acid which is a carboxylic acid.
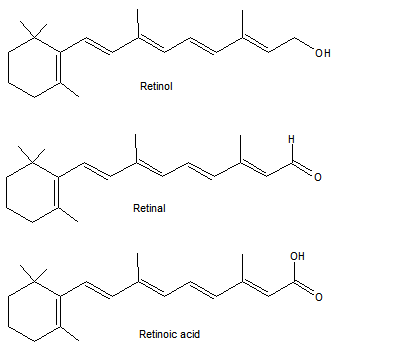
No structure has an ester linkage. So vitamin A is nonhydrolyzable lipid.
(e)
Interpretation:
Phoshoacylglycerol should be labeled as hydrolyzable or non-hydrolyzable.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids can be grouped as hydrolyzable and nonhydrolyzable. Hydrolyzable lipids can be broken down into smaller molecules by reacting with water. Hydrolyzable lipids usually contain an ester functional group which is hydrolyzable. There are three subgroups of hydrolyzable lipids as waxes, triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Nonhydrolyzable lipids cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis with water. There are subgroups of nonhydrolyzable lipids as steroids, fat-soluble vitamins and eicosanoids.
Answer to Problem 19.29P
Hydrolyzable
Explanation of Solution
Phosphoacylglycerols are esterified glycerol in which, two hydroxyl groups of glycerol are esterified with fatty acids and one hydroxyl is esterified with phosphoric acid.
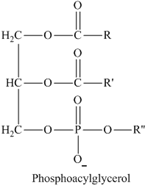
Since phosphoacylglycerol has ester linkages, it is a hydrolyzable lipid.
(f)
Interpretation:
Lecithin should be labeled as hydrolyzable or non-hydrolyzable.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids can be grouped as hydrolyzable and nonhydrolyzable. Hydrolyzable lipids can be broken down into smaller molecules by reacting with water. Hydrolyzable lipids usually contain an ester functional group which is hydrolyzable. There are three subgroups of hydrolyzable lipids as waxes, triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Nonhydrolyzable lipids cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis with water. There are subgroups of nonhydrolyzable lipids as steroids, fat-soluble vitamins and eicosanoids.
Answer to Problem 19.29P
Hydrolyzable
Explanation of Solution
Lecithins are mixtures of glycerophospholipids. As glycerophospholipids are esterified form of glycerol with two fatty acids and phosphoric acid. Lecithin contains ester linkages. So, lecithin is a hydrolyzable lipid. The structure of phosphatidylcholine which is a type of phospholipid in lecithin is given below.
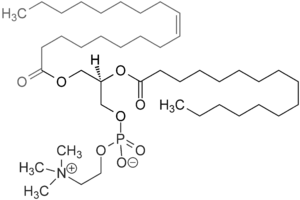
(g)
Interpretation:
Cholesterol should be labeled as hydrolyzable or non-hydrolyzable.
Concept Introduction:
Lipids can be grouped as hydrolyzable and nonhydrolyzable. Hydrolyzable lipids can be broken down into smaller molecules by reacting with water. Hydrolyzable lipids usually contain an ester functional group which is hydrolyzable. There are three subgroups of hydrolyzable lipids as waxes, triacylglycerols and phospholipids. Nonhydrolyzable lipids cannot be broken down into smaller molecules by hydrolysis with water. There are sub groups of nonhydrolyzable lipids as steroids, fat-soluble vitamins and eicosanoids.
Answer to Problem 19.29P
Nonhydrolyzable
Explanation of Solution
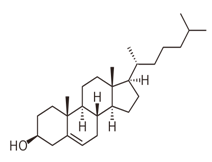
Cholesterol is a type of sterol and has no ester linkages. So, cholesterol is nonhydrolyzable lipid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
GENERAL ORGANIC+BIOCHEM (LL)W/CONNECT
- Classify each of the following as (1) an energy-storage lipid, (2) a membrane lipid, or (3) an emulsification lipid. a. Oils b. Glycocholic acid c. Glycerophospholipids d. Sphingophospholipidsarrow_forwardClassify each of the following types of lipids as (1) glycerol-based, (2) sphingosine-based, (3) steroid nucleus-based, or (4) fatty acid-based. a. Bile acids b. Oils c. Prostaglandins d. Thromboxanesarrow_forwardClassify each of the following types of lipids as (1) glycerol-based, (2) sphingosine-based, (3) steroid nucleus-based, or (4) fatty acid-based. a. Fats b. Cholesterol c. Eicosanoids d. Leukotrienesarrow_forward
- Would you expect lipids to be soluble or insoluble in each of the following solvents? a. CH3(CH2)7CH3 (nonpolar) b. CH3Cl (polar) c. CCl4 (nonpolar) d. CH3CH2OH (polar)arrow_forwardBased on the head and two tails model for the structure of a glycerophospholipid, classify each of the following structural units as being part of its head or being part of its tails. a. fatty acids b. amino alcohol c. phosphate grouparrow_forwardWould you expect lipids to be soluble or insoluble in each of the following solvents? a. H2O (polar) b. CH3CH2OCH2CH3 (nonpolar) c. CH3OH (polar) d. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 (nonpolar)arrow_forward
- What is the biochemical function category for each of the following types of lipids? a. sphingoglycolipids b. eicosanoids c. biological waxes d. phospholipidsarrow_forwardIndicate whether each of the following general statements about lipids is true or false. a. Lipids are compounds soluble in both polar and nonpolar solvents. b. Saponifiable lipid molecules are easily converted into two or more simpler molecules.arrow_forwardIndicate whether each of the following general statements about lipids is true or false. a. The concept that defines a lipid is related to solubility rather than structure. b. Nonsaponifiable lipid molecules undergo hydrolysis in basic aqueous solution.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co



