
Concept explainers
Draw all resonance structures of the conjugate bases formed by removal of the labeled protons
a.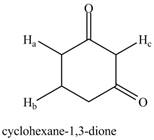 b.
b.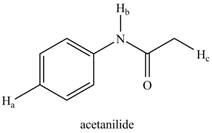
(a)
Interpretation: The resonance structure of the conjugate bases formed by the removal of the labeled protons
Concept introduction: Most of the organic structures cannot be represented using single Lewis structure. Therefore, there exists more than one Lewis structure for representing a molecule or ion. These structures are known as resonance structures. These are the hypothetical structures and do not specify the exact structure. These resonance structure combine together to give resonance hybrid that is lower in energy and is the most stable structure.
The delocalization of electrons results in the formation resonance structure.
Answer to Problem 19.50P
The resonance structure of the conjugate bases formed by the removal of the labeled protons
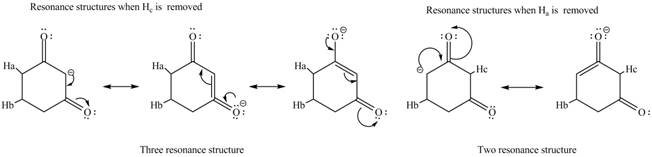
Figure 1
The increasing order of acidity of protons is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
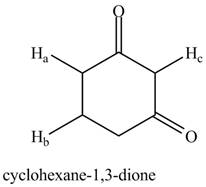
Figure 2
The conjugate base formed by the removal of
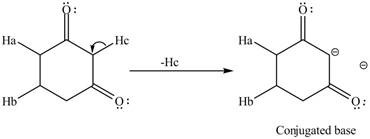
Figure 3
Therefore, the resonance structure of the conjugate base formed by the removal of the
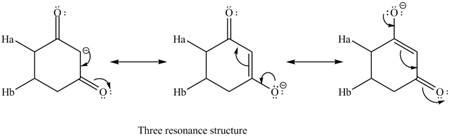
Figure 4
The conjugate base formed by the removal of
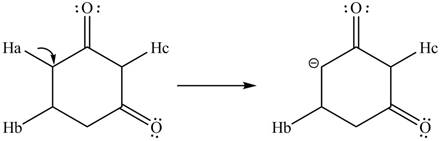
Figure 5
Therefore, the resonance structure of the conjugate base formed by the removal of the
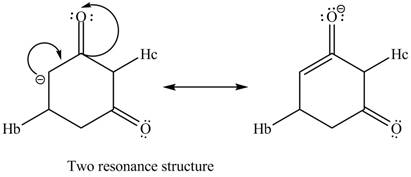
Figure 6
The stability of resonance structures depends upon the following rules:
• The stability of resonance structure is more if it possesses more bonds and fewer charges.
• Resonance structure will be more stable if atoms of the resonance structure have complete octet.
• The stability of resonance structure is more if negative charge is on more electronegative atom
The removal of
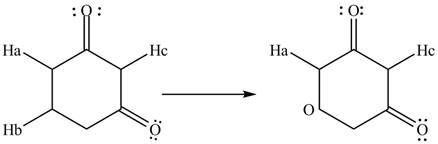
Figure 7
Proton acidity depends upon the stability of conjugated bases. More the number of resonance structures more will be the stability of molecule. Therefore, the increasing order of acidity of protons is
The resonance structures of the conjugate bases formed by the removal of the labeled protons
(b)
Interpretation: The resonance structure of the conjugate bases formed by the removal of the labeled protons
Concept introduction: Most of the organic structures cannot be represented using single Lewis structure. Therefore, there exists more than one Lewis structure for representing a molecule or ion. These structures are known as resonance structures. These are the hypothetical structures and do not specify the exact structure. These resonance structure combine together to give resonance hybrid that is lower in energy and is the most stable structure.
The delocalization of electrons results in the formation resonance structure.
Answer to Problem 19.50P
The resonance structure of the conjugate bases formed by the removal of the labeled protons
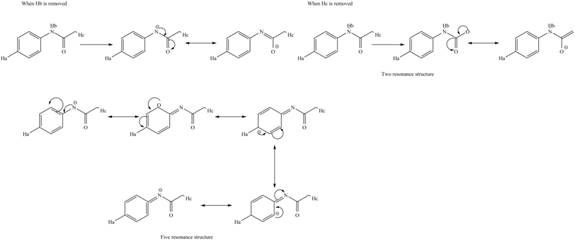
Figure 8
The increasing order of acidity of protons is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
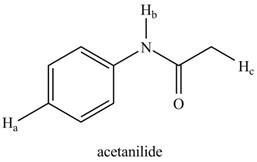
Figure 9
The conjugate base formed by the removal of
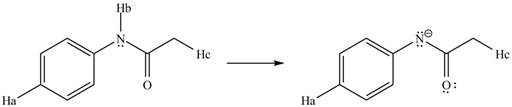
Figure 10
Therefore, the resonance structure of the conjugate base formed by the removal of the
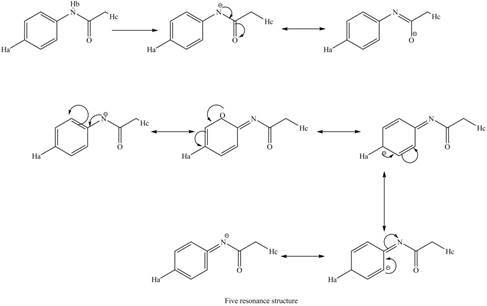
Figure 11
Similarly, the resonance structure of the conjugate base formed by the removal of the
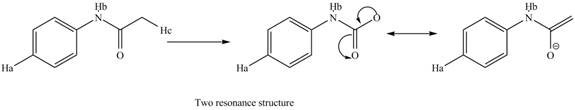
Figure 12
The stability of resonance structures depends upon the following rules:
• The stability of resonance structure is more if it possesses more bonds and fewer charges.
• Resonance structure will be more stable if atoms of the resonance structure have complete octet.
• The stability of resonance structure is more if negative charge is on more electronegative atom
The removal of
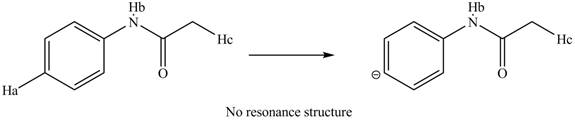
Figure 13
Proton acidity depends upon the stability of conjugated bases. More the number of resonance structures more will be the stability of molecule. Therefore, the increasing order of acidity of protons is
The resonance structures of the conjugate bases formed by the removal of the labeled protons
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
ORG.CHEMISTRY W/ACCESS+MODEL KIT PKG
- Draw a mechanism of a reversible reaction of acetophenone and strong acid (H-A) to form a protonated acetophenone and a weak base. Draw all the electron pairs of the molecules and the arrows. Predict 1H NMR spectra of acetophenone and the protonated acetophenone.arrow_forwardTreatment of indene with NaNH2 forms its conjugate base in a Brønsted– Lowry acid–base reaction. Draw all reasonable resonance structures for indene's conjugate base, and explain why the pKa of indene is lower than the pKa of most hydrocarbons.arrow_forward1. Why does H2 not give an IR spectrum? 2. Explain why primary amines and unsubstituted amides have two NH stretching absorptions. 3. Why do anhydrides show two carbonyl peaks? 4. HCl is known to give addition reactions to carbon-carbon double bonds. Why is this behavior not observed in this reaction? 5. Predict the structure of the product expected from addition of molecular bromine to maleic acid.arrow_forward
- Which is the stronger base: N-methylaniline (C6H5NHCH3) or benzylamine (C6H5CH2NH2). Explain your reasoning, supporting it with appropriate resonance contributors.arrow_forwardHow many signals would the product of the following reaction show in a. its 1H NMR spectrum? b. its 13C NMR spectrum?arrow_forwarda. Compound X is benzene, Y is acetic anhydride acid. Complete the following scheme and determine Z! b. Determine which reagents except acetic acid anhydrides can replace Y!arrow_forward
- Rank the compounds below in order of increasing acidity HF, H2O, NH3arrow_forwardRank the pKa values of acetic acid, ethanol, phenol, and explain the reason in detailarrow_forwardUse the four compounds shown below to answer the following questions: a. Why are the ortho-halo-substituted benzoic acids stronger acids than benzoic acid? b. Why is o-fluorobenzoic acid the weakest of the ortho-halo-substituted benzoic acids? c. Why do o-chlorobenzoic acid and o-bromobenzoic acid have similar pKa values?arrow_forward
- Use the four compounds shown below to answer the following questions: a. Why are the ortho-halo-substituted benzoic acids stronger acids than benzoic acid?b. Why is o-fluorobenzoic acid the weakest of the ortho-halo-substituted benzoic acids?c. Why do o-chlorobenzoic acid and o-bromobenzoic acid have similar pKa values?arrow_forward1. Arrange the following compounds in decreasing order of reactivity towards NaI in acetone: I. Methyl bromide II. Isopropyl bromide III. Ethyl bromide IV. t-butyl bromide 2. Rank the following compounds in order of increasing basicity: I. p-nitroaniline III. N-methylaniline II. p-aminobenzaldehyde IV. p-methylaniline 3. Order the following acids with respect to increasing acidity: I. Fluoroacetic acid III. Chloroacetic acid II. 3-chloropropanoic acid IV. Propanoic acid 4. Arrange the ff. in their decreasing order (easiest first) of relative ease in the acid-catalyzed esterification of ethyl alcohol: I. (CH3)2CHCOOH II. CH3CH2COOH III. (CH3)3COOHarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


