
Clinical Case Study A Fatal Case of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
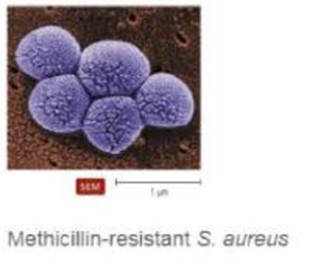
A five-year-old girl was admitted to the hospital with a temperature of 103°F and pain in her right hip. After pus was surgically drained from the hip joint, she was treated with a semisynthetic cephalosporin. Her physicians changed the antibiotic regimen after 24-hour cultures of blood and pus revealed the presence of MRSA. On the third day, she suffered respiratory failure and empyema and was placed on mechanical ventilation. She died from pulmonary hemorrhage and pneumonia after five weeks of hospitalization. The girt had been previously healthy with no recent hospitalizations. She had skinned her knee while learning to ride a bicycle two days before admittance to the hospital.
- 1. How might the girt have been infected?
- 2. How did her hip joint become infected?
- 3. Describe the series of diseases she suffered.
- 4. What was likely the second antibiotic she received?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
Microbiology with Diseases by Taxonomy (5th Edition)
- This 35-year-old woman reported that she had experienced three bouts of urticaria of unknown origin about 10 years ago. The urticaria affected her mucous membranes and skin. She had experienced similar symptoms after repair of a fractured femur caused by a skiing accident. These symptoms were attributed to an antibiotic reaction. As an emergency room nurse, she observed occasional localized hives after the use of latex gloves. Even when she used hypoallergenic latex gloves, she continued to have hives every few months. Increased urticaria, at times generalized, continued to occur. Within 30 minutes of having a routine vaginal examination performed by a health care provider wearing latex gloves, she had an anaphylactic reaction that required resuscitation and hospitalization. A vaginal biopsy 1 week later required a latex-free environment for her safety. A short time later, she was forced to retire from nursing because of symptoms of asthma. She had also developed food allergies to…arrow_forwardGram positive case on the first day back to class at the local university, a student noticed a small abscess on his right elbow but didn't think much about it. Over the next couple days, however the abscess became more swollen and painful. The student decided to visit the health centet he told the doctor it looked like a spider bite but didn't recall being bitten. The doctor took a swab of the lesion and prescribed an antibiotic cream as it looked infected. The swab was sent to the lab for testing within a few days of treatment, the student lesion was healed. what is the overview of the etiological agent?( including basic characteristics of the organism, diseases it cause and use in industry) Broad to get a sense of what this organism isarrow_forwardGram positive case on the first day back to class at the local university, a student noticed a small abscess on his right elbow but didn't think much about it. Over the next couple days, however the abscess became more swollen and painful. The student decided to visit the health centet he told the doctor it looked like a spider bite but didn't recall being bitten. The doctor took a swab of the lesion and prescribed an antibiotic cream as it looked infected. The swab was sent to the lab for testing within a few days of treatment, the student lesion was healed. What is the overview of the disease? How did the patient most likely acquire it? How else does this organism spread to cause this disease?arrow_forward
- Gram positive case on the first day back to class at the local university, a student noticed a small abscess on his right elbow but didn't think much about it. Over the next couple days, however the abscess became more swollen and painful. The student decided to visit the health centet he told the doctor it looked like a spider bite but didn't recall being bitten. The doctor took a swab of the lesion and prescribed an antibiotic cream as it looked infected. The swab was sent to the lab for testing within a few days of treatment, the student lesion was healed. list appearance on plate media and gram stain result and list test results And ID based on the dichotomousarrow_forwardGram positive case on the first day back to class at the local university, a student noticed a small abscess on his right elbow but didn't think much about it. Over the next couple days, however the abscess became more swollen and painful. The student decided to visit the health centet he told the doctor it looked like a spider bite but didn't recall being bitten. The doctor took a swab of the lesion and prescribed an antibiotic cream as it looked infected. The swab was sent to the lab for testing within a few days of treatment, the student lesion was healed. Answer questions: plate morphology: (example: SBR agar-small, translucent, round colonies showing beta hemolysis) gram stain: catalase: caugulase: bactiracin: TSI:arrow_forwardGram positive case on the first day back to class at the local university, a student noticed a small abscess on his right elbow but didn't think much about it. Over the next couple days, however the abscess became more swollen and painful. The student decided to visit the health centet he told the doctor it looked like a spider bite but didn't recall being bitten. The doctor took a swab of the lesion and prescribed an antibiotic cream as it looked infected. The swab was sent to the lab for testing within a few days of treatment, the student lesion was healed. answer the questions: plate morphology: gram stain: catalase: coagulase: bactracin: TSIarrow_forward
- Pathogenesis for chlamydia This paragraph described the disease caused by infection with this pathogen. Answer briefly: What type of infection does this pathogen establish? (acute, chronic, latent, etc.) What are some of the distinguishing symptoms of the infection? Are there known complications from this infectious disease? What is the usual or expected recovery time? What is the outcome of this infectious disease? (full recovery, chronic issues, fatal, etc.) Does the person develop a protective immunity to re-infection with this pathogen?arrow_forwardDISEASE PATHOGEN SYMPTOMS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT 1. Candidiasis 2. Bacterial Vaginosis 3. Trichomoniasisarrow_forwardBacillus thuringiensis: production of endotoxin and mechanism of actionarrow_forward
- Case Study . A journalist returning from a trip experienced severe fever, vomiting, chills, and muscle aches, followed by symptoms of meningitis and kidney failure. Early tests were negative for septicemia; throat cultures were negative; and penicillin was an effective treatment. Doctors believed the patient’s work in the jungles of South America was a possible clue to his disease. What do you think might have been the cause?arrow_forwardA patient presented to the emergency room complaining of a nonproductive cough (no sputum) that had persisted for six weeks. The clinician prescribed a 7-day course of cephalosporin. After day 7 the patient returned, no better than when he started. Laboratory tests later showed the infection was caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Explain why the antibiotic did not work.arrow_forwardL. monocytogenes (Listeriosis) Identification tests (specifically for listeriosis/L. monocytogenes)arrow_forward
- Understanding Health Insurance: A Guide to Billin...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337679480Author:GREENPublisher:Cengage
