
Concept explainers
Lactonization Methods
In Section we saw that hydroxy substituted carboxylic acids spontaneously cyclize to lactones if a five or six membered ring can be formed.
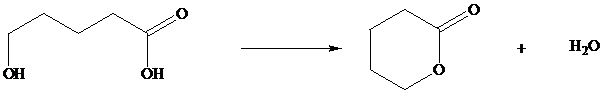
Many natural products are lactones, and chemists have directed substantial attention to developing alternative methods for their synthesis. The most successful of these efforts are based on electrophilic addition to the double bond of unsaturated carboxylic acids. For a generalized electrophilic reagent and, such reactions give a
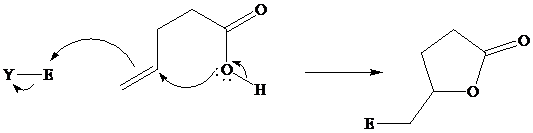
Although the curved arrows show the overall electron flow, the mechanism depends on the electrophilic reagent and normally involves more than one step.
In iodolactonization the electrophilic atom, and represents a source of electrophilic iodine, usually or. In phenylselenolactonization, and is benzeneselenenyl chloride. Anti addition is observed in both iodo andphenylselenolactonization.
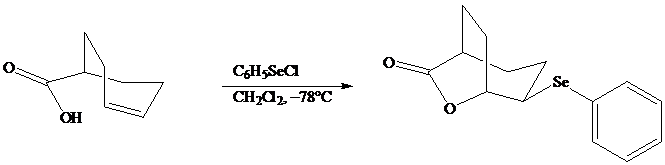
Both iodo andphenylselenolactonization offer the advantage of giving a product containing a functional group capable of further modification. Oxidation of the substituent, for example, gives a selenoxide that undergoes elimination of at room temperature to introduce a double bond into the lactone.
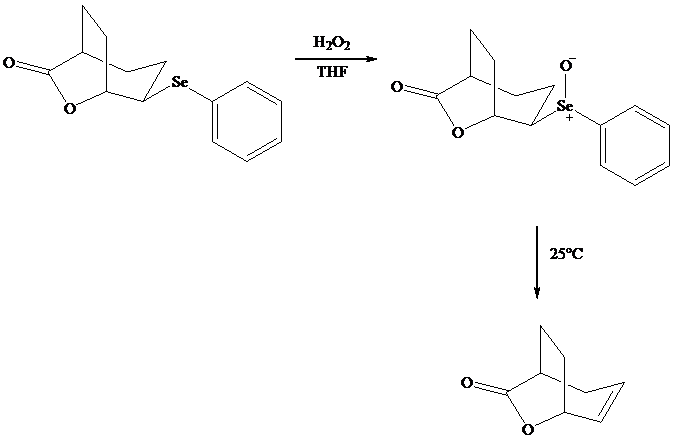
In eliminations of this type, H is always removed from the carbon to selenium that is remote from the lactone oxygen. Elimination is syn.

What is the structure of the
(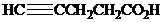 )? Anti addition to the triple bond occurs.
)? Anti addition to the triple bond occurs.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 19 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-W/STUD.SOLN.MAN.
- Provide TWO Grignard reactions, A and B, that can be to make the provided target structure. Give the organic reactant and the Grignard reagent that would be used, yo not need to specify the aqueous acid workup step, but you must specify which of the c-c bonds is being made in the provided traget structure. Ignore stereochemistry in this question.arrow_forwardDraw the arrow pushing mechanism for the reaction of camphor to isoborneol. For each step on the mechanism give one DETAILED sentence on what is occurring and why. Examples: "Loss of water to form a tertiary carbocation", "nucleophilic attack of ____ to increase acidity of ____", "methyl shift of ____ to form ____", etc. Thank you!arrow_forwardProvide a reasonable stepwise mechanism for the following transformation. Show the structure of any intermediates and use the arrow formalism to account for electron flow. Draw the structure of the regioisomer that might form and suggest a reason why it would not be produced.arrow_forward
- please help with the following Ochem question... In theory a poorly planned Claisen condensation between 2 different esters, isopropyl butanoate and tertbutyl propanoate, can produce how many different products? Provide the bond line structures and the IUPAC names of the products obtainedarrow_forwardOutline (not mechanism) all steps in a possible laboratory synthesis of the following from benzene and/or toluene, using any necessary aliphatic or inorganic reagents and critical conditions. Assume a pure para isomer can be separated from an ortho/para mixture. a. 2-phenylpropene b. p-bromobenzyl bromidearrow_forwardWhich of the following is statements is/are TRUE about the experiment on the relative rates of electrophilic aromatic substitution?I. The experiment must be performed in dark conditions. II. Using the same solvents, a faster decolorization will be observed in aniline as compared to ethylbenzene. III. Chlorobenzene will react faster than methoxybenzene. IV. The use of AlCl3 in the halogenation of aromatic compounds using elemental bromine could hasten the reaction.arrow_forward
- What is the major organic product obtained form the following sequence of reactions (assume that mixtures of ortho and para disubstituted compounds can be separated; continue the synthesis with either one)?arrow_forwardGive the two major organic products for the following reactionarrow_forwardNitration is an example of electrophic aromatic substitution indicate the nucleophile and electrophile of the reaction outlined in the scheme above.arrow_forward
- What is the background on the chemistry of electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, what is the importance of nitration reactions in organic synthesis, and the reactivity of methyl benzoate, a methyl ester of benzoic acid. With referencesarrow_forwardChoose one nucleophile, and conditions for the reaction to include temperature (low heat vs high heat) and specific solvent that would be most suitable to promote the following alkyl halide to undergo an SN1 mechanism. Indicate on your alkyl halide the electrophilic region, on your nucleophile specify the nucleophilic region and the partial charge on the LG clearly using δδ- and δδ+ (or +/- if more applicable). Be very specific. Draw the mechanism including hydride/alkyl shifts, intermediates, and ALL transition states as applicable. Draw products indicating the stereochemistry as applicable using appropriate wedges and dashes. Nu: Solvent: Temperature: Mechanism:arrow_forwardGive the major organic product of the following reaction for a) or b)arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

