
(a)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Elimination Reaction: It is just reverse reaction of addition where substituent from the given molecule is removed.
E2 mechanism depends on both base and substituents in the reaction.
Elimination reaction of an
Bromination: In bromination reaction, hydrogen atom of a molecule is replaced by a bromine atom.
Hydroboration reaction: The reaction involves addition of
Oxidation: If electrons are moved from a species or oxygen atoms are added to a species or hydrogen atom gets removed from a species during a
Anti-Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
Wittig Reaction: It is an organic reaction where an
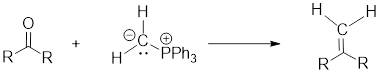
Chromic acid:
(b)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Hydroboration reaction: The reaction involves addition of
Oxidation: If electrons are moved from a species or oxygen atoms are added to a species or hydrogen atom gets removed from a species during a chemical reaction is known as oxidation.
Anti-Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
Wittig Reaction: It is an organic reaction where an aldehyde or a ketone gets converted to an alkene by replacing carbonyl group by a
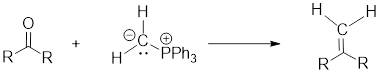
(c)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Elimination Reaction: It is just reverse reaction of addition where substituent from the given molecule is removed.
E2 mechanism depends on both base and substituents in the reaction.
Elimination reaction of an alkyl halide results in the formation of an alkene.
Bromination: In bromination reaction, hydrogen atom of a molecule is replaced by a bromine atom.
Hydroboration reaction: The reaction involves addition of
Oxidation: If electrons are moved from a species or oxygen atoms are added to a species or hydrogen atom gets removed from a species during a chemical reaction is known as oxidation.
Anti-Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
Grignard Reaction: This is an organometallic reaction where an alkyl or aryl-magnesium halides is introduced to the carbonyl group present in an aldehyde and ketone. Here, aldehyde and ketone gets converted to alcohols.
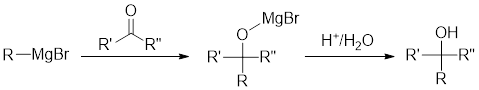
Chromic acid:
(d)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Elimination Reaction: It is just reverse reaction of addition where substituent from the given molecule is removed.
E2 mechanism depends on both base and substituents in the reaction.
Elimination reaction of an alkyl halide results in the formation of an alkene.
Bromination: In bromination reaction, hydrogen atom of a molecule is replaced by a bromine atom.
Grignard Reaction: This is an organometallic reaction where an alkyl or aryl-magnesium halides is introduced to the carbonyl group present in an aldehyde and ketone. Here, aldehyde and ketone gets converted to alcohols.
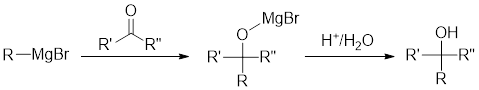
Chromic acid:
Ozonolysis: It is an organic reaction where the unsaturated bonds in alkenes and
(e)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Hydroboration reaction: The reaction involves addition of
Oxidation: If electrons are moved from a species or oxygen atoms are added to a species or hydrogen atom gets removed from a species during a chemical reaction is known as oxidation.
Anti-Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the less substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
In a reaction, PCC (pyridinium chlorochromate) is used to oxidize alcohols to carbonyls. Primary alcohols get converted to aldehydes whereas secondary alcohols get converted to ketones when treated with PCC.
An imine is a compound having
The part of the molecule that is attached to the carbon atom in the
(f)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Friedel-Crafts Acylation: This Lewis acid-catalyzed electrophilic aromatic substitution is the reaction between arenes and acyl chlorides or anhydrides for the synthesis of monoacylated compound. The products are deactivated, as well as do not undergo a second substitution.
Bromination: In bromination reaction, hydrogen atom of a molecule is replaced by a bromine atom.
Wittig Reaction: It is an organic reaction where an aldehyde or a ketone gets converted to an alkene by replacing carbonyl group by a
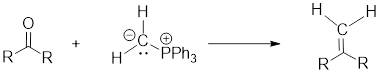
(g)
Interpretation: Synthesis of the given compound has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
An acetal is a compound having structural formula
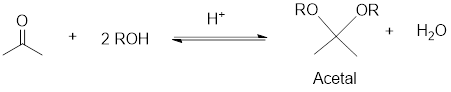
Reduction: If electrons are gained to a species or hydrogen atoms are added to a species or oxygen atom gets removed from a species during a chemical reaction is known as reduction
In a reaction,
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 19 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-NEXTGEN+BOX (2 SEM.)
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





