
Concept explainers
(a)
To plot: The velocity-time graph and acceleration-time graph for given situation on a single graph.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The free fall of the professor is for
Initial velocity of the professor is
The acceleration opposite to gravity applied after free fall is
The speed which is maintained until she reaches the ground is
Formula used:
Write expression for the final velocity of the professor during free fall.
Here,
The initial speed when she starts slowing her rate of descent will be same as the final velocity of the free fall.
Write expression for final speed of professor when she reaches
Rearrange above expression for
Here
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
The graph for the velocity and acceleration of the professor is shown in figure 1.
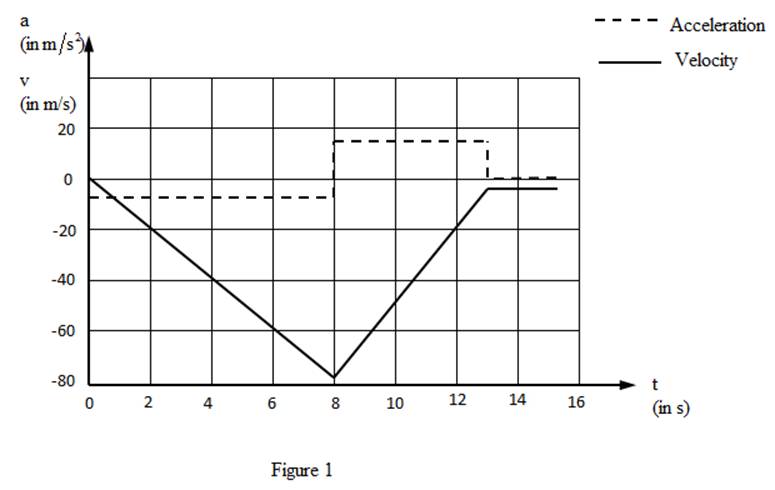
(b)
To find:The speed of professor at the end of first
(b)
Answer to Problem 102P
The speed of professor at the end of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The initial speed of the professor is
The time of fall of the professor is
The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of earth is
Formula used:
The professor jumps out of the helicopter and falls freely under the action of acceleration due to gravity, the motion of the professor for these first
The first equation of motion relates the initial and final velocity of a body falling freely under the gravity. Therefore, the velocity of the professor can be obtained from this expression at the instant of
Write expression for the final velocity of the professor during free fall.
Calculation:
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the speed of professor at the end of
(c)
To find: The duration for which the professor descends her speed.
(c)
Answer to Problem 102P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The initial speed of the professor during descend is
The final speed of the professor at which time is measured is
The deceleration of the professor is
Formula used:
The time taken by the professor during her slow rate of descent can be obtained from Newton’s first equation of motion.
Write expression for final speed of professor.
Rearrange above expression for
Calculation:
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the duration for which she descends her speed is
(d)
To find:Distance covered by the professor when she descends her speed.
(d)
Answer to Problem 102P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The initial speed of the professor during descend is
The deceleration of the professor is
Formula used:
Write expression for final speed of the professor during the descent.
Rearrange above expression for
Calculation:
Substitute
The negative sign shows the direction of motion.
Conclusion:
Thus, the distance covered by the professor during the descent is
(e)
To find:Time required by the professor to reach the ground.
(e)
Answer to Problem 102P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The altitude of helicopter is
Formula used:
Write expression for distance travelled during free fall of the professor.
Write expression for the distance covered when she maintains constant speed of
Here, S is the distance covered during constant speed motion.
Write expression for time taken to when professor maintained constant speed.
Write expression for total time of journey.
Calculation:
Substitute
Here, negative sign shows the direction of motion.
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the total time taken by the professor for complete journey is
(f)
To find:The average velocity of professor for entire trip.
(f)
Answer to Problem 102P
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The distance through which the professor falls is
The time for which the professor falls is
Formula used:
Average velocity is defined as the ratio of total distance covered to the total time taken during the journey.
Write expression for average velocity of the professor.
Here
Calculation:
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the average velocity of the professor is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Physics For Scientists And Engineers
- a rocket initially at rest, is fired vertically with an upward acceleration of 10ms/s. at an altitude of 0.5km, the engine of the rocket cuts off. what is the maximum altitude reached by the rocket ?arrow_forwardAn atom is constrained to move along the horizontal axis only. At time t = 0.5 s, the atom is at x = 0.06 m. At time t = 2.8 s, the atom is at x = 0.46 m. What is the atom's average velocity?arrow_forwardIn a classic clip on Americas Funniest Home Videos, a sleeping cat rolls gently off the top of a warm TV set. Ignoring air resistance, calculate the position and velocity of the cat after (a) 0.100 s, (b) 0.200 s, and (c) 0.300 s.arrow_forward
- The driver of a car slams on the brakes when he sees a tree blocking the road. The car slows uniformly with an acceleration of 5.60 m/s2 for 4.20 s, making straight skid marks 62.4 m long, all the way to the tree. With what speed does the car then strike the tree?arrow_forwardA projectile is launched on the Earth with a certain initial velocity and moves without air resistance. Another projectile is launched with the same initial velocity on the Moon, where the acceleration due to gravity is one-sixth as large. How does the range of the projectile on the Moon compare with that of the projectile on the Earth? (a) It is one-sixth as large. (b) It is the same. (c) It is 6 times larger. (d) It is 6 times larger. (e) It is 36 times larger.arrow_forwardA pilot without special training or equipment can tolerate a horizontal acceleration of up to about 3.80g for a short period of time (about a minute) without losing consciousness. How far would the jet in horizontal flight travel during the time it takes to accelerate from 406 m/s to 700 m/s at an acceleration of 3.80g?arrow_forward
- On the earth, an astronaut throws a ball straight upward; it stays in the air for a total time of 3.0 s before reaching the ground again. If a ball were to be thrown upward with the same initial speed on the moon, how much time would pass before it hit the ground?A. 7.3 s B. 18 s C. 44 s D. 108 sarrow_forwardAt t = 0, one toy car is set rolling on a straight track with initial position 13.0 cm, initial velocity -2.8 cm/s, and constant acceleration 2.30 cm/s2. At the same moment, another toy car is set rolling on an adjacent track with initial position 9.5 cm, initial velocity 6.00 cm/s, and constant zero acceleration. At t = 0, one toy car is set rolling on a straight track with initial position 13.0 cm, initial velocity -2.8 cm/s, and constant acceleration 2.30 cm/s2. At the same moment, another toy car is set rolling on an adjacent track with initial position 9.5 cm, initial velocity 6.00 cm/s, and constant zero acceleration. (a) At what time, if any, do the two cars have equal speeds? (b) What are their speeds at that time?arrow_forwardA sperm whale can accelerate at about 0.140 m/s^2 when swimming on the surface of the ocean. How far will it travel if it starts at a speed of 1.20 m/s and accelerates to a speed of 2.5 m/s? Assume the whale travels in a straight line.arrow_forward
- Most important in an investigation of an airplane crash by the U.S. National Transportation Safety Board is the data stored on the airplane’s flight-data recorder, commonly called the “black box” in spite of its orange coloring and reflective tape.The recorder is engineered to withstand a crash with an average deceleration of magnitude 3450 g during a time interval of 6.49 ms. In such a crash, if the recorder and airplane have zero speed at the end of that time interval, what is their speed at the beginning of the interval?arrow_forwardA pilot without special training or equipment can tolerate a horizontal acceleration of up to about 3.80g for a short period of time (about a minute) without losing consciousness. How long would it take a supersonic jet in horizontal flight to accelerate from 406 m/s to 700 m/s at an acceleration of 3.80g?arrow_forwardSuppose the baseball is struck from the edge of a cliff such that y0 = 30 m and x0 = 0. The components of the initial velocity are v0x = 20 m/s and v0y = 0. What is the x coordinate of the baseball when it lands on the ground at y = 0? (Write only the numerical value rounded to a whole number and exclude the unit)arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
