
Concept explainers
The following radioactive isotopes are used in medicine for things such as imaging organs, studying blood circulation, and treating cancer. Give the number of neutrons present in each isotope: 198Au, 47Ca, 60Co, 18F, 125I, 131I, 42K, 43K, 24Na, 32P, 85Sr, 99Tc.
Interpretation:
The total number of neutrons present in the given set of radioactive isotopes needs to be given.
Concept introduction:
The total number of protons in an atom is said to be its atomic number. By using the total number of protons and neutrons all the atoms can be identified. Atomic number is denoted by “Z”. Atomic number is a characteristic of each and every atom in an element.
The total number of neutrons and protons of an atom is said to be its mass number. By using the total number of protons and neutrons all the atoms can be identified. Mass number is denoted by “A”.
Atomic number does not change for atoms present in an element while mass number can change due to difference in number of neutrons. These are known as isotopes.
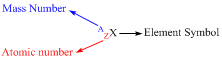
Total number of neutrons present in an atom can be found out of finding the difference between mass number and atomic number.
To Determine: The number of neutrons present in the given radioactive isotopes.
Answer to Problem 2.22QP
The number of neutrons in
The number of neutrons in
The number of neutrons in
The number of neutrons in
The number of neutrons in
The number of neutrons in
The number of neutrons in
The number of neutrons in
The number of neutrons in
The number of neutrons in
The number of neutrons in
The number of neutrons in
Explanation of Solution
To determine the number of neutrons present in
Atom of the element given= gold
Mass number (A)= 198
Total number of protons (Z)=79
The number of neutrons in any atom can be got by finding the difference between mass number and total number of protons.
Therefore, the mass number of
To determine the number of neutrons present in
Atom of the element given= calcium
Mass number (A)= 47
Total number of protons (Z)=20
The number of neutrons in any atom can be got by finding the difference between mass number and total number of protons.
Therefore, the mass number of
To determine the number of neutrons present in
Atom of the element given= cobalt
Mass number (A)= 60
Total number of protons (Z)=27
The number of neutrons in any atom can be got by finding the difference between mass number and total number of protons.
Therefore, the mass number of
To determine the number of neutrons present in
Atom of the element given= fluorine
Mass number (A)= 18
Total number of protons (Z)=9
The number of neutrons in any atom can be got by finding the difference between mass number and total number of protons.
Therefore, the mass number of
To determine the number of neutrons present in
Atom of the element given= iodine
Mass number (A)= 125
Total number of protons (Z)=53
The number of neutrons in any atom can be got by finding the difference between mass number and total number of protons.
Therefore, the mass number of
To determine the number of neutrons present in
Atom of the element given= iodine
Mass number (A)= 131
Total number of protons (Z)=53
The number of neutrons in any atom can be got by finding the difference between mass number and total number of protons.
Therefore, the mass number of
To determine the number of neutrons present in
Atom of the element given= potassium
Mass number (A)= 42
Total number of protons (Z)=19
The number of neutrons in any atom can be got by finding the difference between mass number and total number of protons.
Therefore, the mass number of
To determine the number of neutrons present in
Atom of the element given= potassium
Mass number (A)= 43
Total number of protons (Z)=19
The number of neutrons in any atom can be got by finding the difference between mass number and total number of protons.
Therefore, the mass number of
To determine the number of neutrons present in
Atom of the element given= sodium
Mass number (A)= 24
Total number of protons (Z)=11
The number of neutrons in any atom can be got by finding the difference between mass number and total number of protons.
Therefore, the mass number of
To determine the number of neutrons present in
Atom of the element given= phosphorous
Mass number (A)= 32
Total number of protons (Z)=15
The number of neutrons in any atom can be got by finding the difference between mass number and total number of protons.
Therefore, the mass number of
To determine the number of neutrons present in
Atom of the element given= strontium
Mass number (A)= 85
Total number of protons (Z)=38
The number of neutrons in any atom can be got by finding the difference between mass number and total number of protons.
Therefore, the mass number of
To determine the number of neutrons present in
Atom of the element given= technitium
Mass number (A)= 99
Total number of protons (Z)=43
The number of neutrons in any atom can be got by finding the difference between mass number and total number of protons.
Therefore, the mass number of
The number of neutrons in the given set of radioisotopes was determined.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
CHEMISTRY:ATOMS FIRST-W/ACCESS>CUSTOM<
- Though the common isotope of aluminum has a mass number of 27, isotopes of aluminum have been isolated (or prepared in nuclear reactors) with mass numbers of 24, 25, 26, 28, 29, and 30. How many neutrons are present in each of these isotopes? Why are they all considered aluminum atoms, even though they differ greatly in mass? Write the atomic symbol for each isotope.arrow_forward2.10 Which isotope in each pair contains more neutrons? (A) 35Cl or 33S, (b) 19F or 19Ne, (c) 63Cu or 65Zn, (d) 126I or 127Tearrow_forwardThe following isotopes are important in nuclear power. Write their symbols in the form XZA. a. U-235 b. U-238 c. Pu-239 d. Xe-144arrow_forward
- 1. The mass of an atom of manganese is 54.9380 u. How many neutrons are contained in one atom of this element? 25 29 30 55arrow_forwardThe element gallium, used in gallium arsenide semiconductors, has an atomic weight of 69.72 amu. There are only two isotopes of gallium, Ga with a mass of 6.9257 amu and Ga with a mass of 70.9249 amu. What are the isotopic abundances of gallium? Gallium melts just above room temperaturearrow_forward2.90 Naturally occurring europium has an average atomic weight of 151.964 amu. If the only isotopes of europium present are 151Eu and 153Eu, describe how you would determine the relative abundance of the two isotopes. Include in your description any information that would need to be looked up.arrow_forward
- 2-31 Tin-118 is one of the isotopes of tin. Name the isotopes of tin that contain two, three, and six more neutrons than tin-118.arrow_forward2.87 What is the heaviest element to have an atomic weight that is roughly twice its atomic number? What does this suggest must he true about the nuclei of atoms with higher atomic numbers?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





