
(a)
The formula for the pressure difference
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The following figure shows the two containers with water and oil.
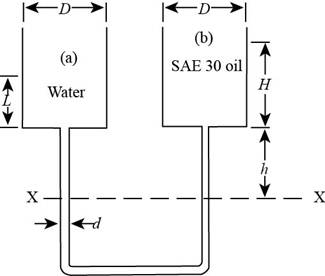
Figure-(1)
The height of oil in container is
Write the hydrostatic equation for the left limb.
Here, the pressure at
Write the hydrostatic equation for the right limb.
Here, the pressure at
The pressure of the right limb and the left limb is same at the datum
Substitute
The figure below shows the rise in limb
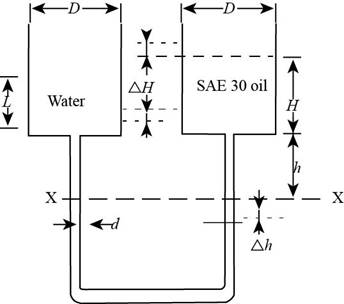
Figure-(2)
Both the containers are of equal diameter hence, the change in height of limb is
The volume rise and fall in both the containers is same.
Write the expression for balance the volume in both containers.
Here, the diameter of the limb is
Write the hydrostatic equation for the left limb at the datum
Write the hydrostatic equation for the right limb at the datum
The pressure at both the limbs is same at the datum.
Substitute
From Equation (IV) and Equation (II).
Substitute
When
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the formula for the pressure difference
(b)
The formula for the pressure difference
The percentage change in pressure difference.
(b)
Answer to Problem 2.34P
The formula for the pressure difference
The percentage change in pressure difference is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for diameter of limb.
Substitute
Write the percentage change in pressure.
Here, the change in pressure in case 1 is
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the formula for the pressure difference
Substitute
Thus, the percentage change in pressure difference is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Loose Leaf For Fluid Mechanics
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





