
Concept explainers
Draw the products of each reaction. Use the
a.
b. 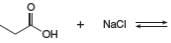
c. 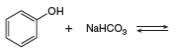
d.
(a)
Interpretation: The products of the given reaction are to be drawn. If the equilibrium favors the starting materials or a product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: According to Bronsted-Lowry theory, when an acid donates a proton the species formed is known as conjugate base and when the base accepts a proton the species formed is known as conjugate acid.
In a reaction which strongly favors the formation of products, the base used to remove proton from the acid should be stronger than the base formed when the proton is removed. In a reaction which favors the products, equilibrium will favors the formation of the weaker acid or weaker base. The
Answer to Problem 2.49P
The products of the given reaction are
Explanation of Solution
The complete reaction between methyl amine and
The
The products of the given reaction are
(b)
Interpretation: The products of the given reaction are to be drawn. If the equilibrium favors the starting materials or a product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: According to Bronsted-Lowry theory, when an acid donates a proton the species formed is known as conjugate base and when the base accepts a proton the species formed is known as conjugate acid.
In a reaction which strongly favors the formation of products, the base used to remove proton from the acid should be stronger than the base formed when the proton is removed. In a reaction which favors the products, equilibrium will favors the formation of the weaker acid or weaker base. The
Answer to Problem 2.49P
The products of the given reaction are
Explanation of Solution
The complete reaction between propanoic acid and sodium chloride is shown below.
The
The products of the given reaction are
(c)
Interpretation: The products of the given reaction are to be drawn. If the equilibrium favors the starting materials or a product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: According to Bronsted-Lowry theory, when an acid donates a proton the species formed is known as conjugate base and when the base accepts a proton the species formed is known as conjugate acid.
In a reaction which strongly favors the formation of products, the base used to remove proton from the acid should be stronger than the base formed when the proton is removed. In a reaction which favors the products, equilibrium will favors the formation of the weaker acid or weaker base. Or the
Answer to Problem 2.49P
The products of the given reaction are
Explanation of Solution
The complete reaction between phenol and sodium hydrogen carbonate is shown below.
The
The products of the given reaction are
(d)
Interpretation: The products of the given reaction are to be drawn. If the equilibrium favors the starting materials or a product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: According to Bronsted-Lowry theory, when an acid donates a proton the species formed is known as conjugate base and when the base accepts a proton the species formed is known as conjugate acid.
In a reaction which strongly favors the formation of products, the base used to remove proton from the acid should be stronger than the base formed when the proton is removed. In a reaction which favors the products, equilibrium will favors the formation of the weaker acid or weaker base. Or the
Answer to Problem 2.49P
The products of the given reaction are
Explanation of Solution
The complete reaction between ethyne and ethyl lithium is shown below.
The
The products of the given reaction are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-W/ACCESS >CUSTOM<
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Thermodynamics, Statistical Thermodynamics, & Kinetics
Chemistry
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
- In each equilibrium, label the stronger acid, the stronger base, the weaker acid, and the weaker base. Also estimate the position of each equilibrium. (a) CH3CH2O + CH3CCH CH3CH2OH + CH3CC (b) CH3CH2O + HCl CH3CH2OH + Cl (c) CH3COOH + CH3CH2O CH3COO + CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardHypochlorous acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate (also known as sodium hydrogen carbonate). What are the products of this reaction? (A) NaCIO4 + H2CO2 (B) NaCIO4 + H2CO3 (C) NaCIO + H2CO2 (D) NaCIO + H2CO3arrow_forwardhow would doubling the concentration of HA affect the rate? Step 1: Fast, reversible HA = H+ + A- Step 2: Fast, reversible X + H+ = HX+ Step 3: Slow HX+ = products rate= k [X][HA]/ [A-]arrow_forward
- All of the reagents in the reaction below are in aqueous form. The initial concentration of A is 4.5 x 10-4 M. The initial concentration of B is 5.3 x 10-3 M. At equilibrium, the concentration of A is 1.2 x 10-4 M. What is the value of Keq? A + 2 B <===> C + 3 D Keq = __________________arrow_forwardWhich side of the equilibrium is favored in this acid/base rxn? pka of product: 6.9arrow_forwardAcetic acid, CH3COOH, is a weak organic acid, pKa 4.76. Write an equation for the equilibrium reaction of acetic acid with each base. Which equilibria lie considerably toward the left? Which lie considerably toward the right? Q.) NaHCO3arrow_forward
- What is the acid and conjugated acid in this reaction H2SO4 + NH3 → HSO4ˉ + NH4⁺?arrow_forwardAcetic acid, CH3COOH, is a weak organic acid, pKa 4.76. Write an equation for the equilibrium reaction of acetic acid with each base. Which equilibria lie considerably toward the left? Which lie considerably toward the right? Q.) NaOHarrow_forwardFor each equilibrium, label the stronger acid, stronger base, weaker acid and weaker base. For each reaction(s), does the position of equilibrium lie toward the right or left? H3PO4 + OH- ⇌ H2PO4- + H2O H2O + Cl- ⇌ HCl + OHarrow_forward
- O3(g) ⇌ O2(g) + O(g)To which direction will the reaction shift if additional O3 is added?arrow_forwardIn each reaction, label the reactants as Lewis acids (electrophiles) or Lewis bases (nucleophiles). Use curved arrows to show the movement of electron pairs in the reactions. Draw any nonbonding electrons to show how they participate in the reactions.(a) (CH3)2NH + HCl ¡ (CH3)2 NH+2 + Cl-(b) (CH3)2NH + CH3Cl ¡ (CH3)3 NH++ Cl-arrow_forwardAll are true or false A) Both LiAlH 4 and NaBH 4 are reducing agents. True or False: Both reagents contain polar metal-hydrogen bonds. The polarity of the B-H bond is less than the polarity of the Al-H bond, so LiAlH 4 is the weaker reducing agent. B) Both Ketones are more sterically hindered and Ketones are less electron deficient due to donation from the two alkyl groups C)Organometallic reagents are strong acids that readily donate a proton to water. D)Organometallic reagents contain a carbon atom bonded to a metal. E) The purpose of a silyl ether to protect alcohols from organometallic reagents and other reagents.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning



