
Concept explainers
A thin
FIGURE P2-77
(a)
The location where the oil velocity is zero.
Answer to Problem 81P
The location where the oil velocity is zero is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The cross section of the plate is
The following figure gives the velocity profile of the plate:
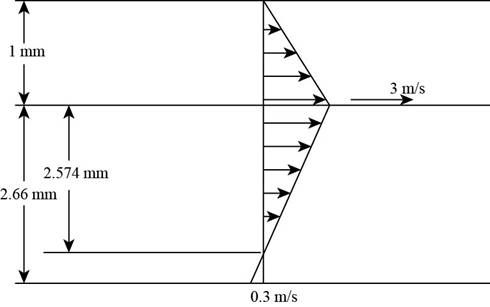
Figure-(1)
Write the expression for the viscous force.
Here, the viscous force is
Write the expression for the thickness of the oil film.
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The location where the oil velocity is zero is
(b)
The force required to maintain the motion.
Answer to Problem 81P
The force required to maintain the motion is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the viscous force.
Here, the viscous force is
Write the expression for the total applied force.
Here, the total force is
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The force required to maintain the motion is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals And Applications
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design (McGraw-Hill Series in Mechanical Engineering)
Fundamentals of Aerodynamics
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Manufacturing Engineering & Technology
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
- The figure below represents a cylinder C i (d = 11 cm) that is inside a hollow cylinder (d = 11.1 cm). The inner cylinder, with a mass of 30 kg and a length of 25 cm (L), is subjected to a pressure P of 50 kPa at its bottom, rising at a constant speed of 2.5 m/s. a) Determine the dynamic viscosity of the lubricating oil that must be placed in the space between the piston and the cylinder; b) Determine the kinematic viscosity knowing that it consists of a mixture of 3 L of oil A (specific mass of 880 kg/m 3 ) and 2200 mL of oil B (specific mass of 940 kg/m 3 ). Data: g = 9.81 m/s 2arrow_forwardThe viscosity of a fluid is to be measured by a viscometer constructed of two 40-cm-long concentric cylinders . The outer diameter of the inner cylinder is 12 cm, and the gap between the two cylinders is 0.15 cm. The inner cylinder is rotated at 300 rpm, and the torque is measured to be 1.8 N⋅m. Determine the viscosity of the fluid.arrow_forwardA thin 30-cm * 30-cm flat plate is pulled at 3 m/s horizontally through a 3.6-mm-thick oil layer sandwiched between two plates, one stationary and the other moving at a constant velocity of 0.3 m/s,. The dynamic viscosity of the oil is 0.027 Pa?s. Assuming the velocity in each oil layer to vary linearly, (a) plot the velocity profile and find the location where the oil velocity is zero and (b) determine the force that needs to be applied on the plate to maintain this motion.arrow_forward
- A frustum-shaped body is rotating at a constant angular speed of 200 rad/s in a container filled with SAE 10W oil at 20°C (? = 0.100 Pa⋅s), as shown in Fig. If the thickness of the oil film on all sides is 1.2 mm, determine the power required to maintain this motion. Also determine the reduction in the required power input when the oil temperature rises to 80°C (? = 0.0078 Pa⋅s).arrow_forwardDetermine the total force required to drag a thin plate which is placed in between two parallel plates 2.6 cm apart with the space filled with a fluid of viscosity of 0.55 Ns/m2.The area of the plate is 0.475 m2 and the speed at which it is dragged is 0.4 m/s. The position of thin plate from the top plate is 0.2 cm?arrow_forwardIn regions far from the entrance, fluid flow through a circular pipe is one dimensional, and the velocity profile for laminar flow is given as u(r) = umax(1 - r2/R2), where R is the radius of the pipe, r is the radical distance from the center of the pipe, and umax is the maximum flow velocity, which occurs at the center. Obtain the following: A relation for the drag force applied by the fluid on a section of the pipe at length L The value of the drag force for water flow at 20°C with R = 0.07 m, L = 35 m, umax = 4 m/s, and μ = 0.0010 kg/m·sarrow_forward
- The distance between the centers of the two arms of a U-tube open to the atmosphere is 30 cm, and the U-tube contains 20 cm high alcohol in both arms. Now the U-tube is rotated about the left arm at 4.2 rad/s. Determine the elevation difference between the fluid surfaces in the tow arms.CHOICES a.0.81 m b.0.96 m c.0.33 m d.0.67 marrow_forwardA 20 cm diameter, 40 cm high vertical cylindrical container is partially filled with 25 cm high water. Now the cylinder is rotated at a constant speed of 15 rad/s. The height of the water at the center of the cylinder is a.25 cm b.27.2 cm c.19.5 cm d.11.5 cmarrow_forwardIn regions far from the entrance, fluid flow through a circular pipe is one dimensional, and the velocity profile for laminar flow is given by u(r) = umax(1 − r2/R2), where R is the radius of the pipe, r is the radial distance from the center of the pipe, and umax is the maximum flow velocity, which occurs at the center. Obtain (a) a relation for the drag force applied by the fluid on a section of the pipe of length L and (b) the value of the drag force for water flow at 20°C with R = 0.08 m, L = 30 m, umax = 3 m/s, and ? =0.0010kg/m⋅s.arrow_forward
- A thin plate moves between two parallel, horizontal, stationary flat surfaces at a constant velocity of 5 m/s. The two stationary surfaces are spaced 4 cm apart, and the medium between them is filled with oil whose viscosity is 0.9 N⋅s/m2. The part of the plate immersed in oil at any given time is 2-m long and 0.5-m wide.If the viscosity of the oil above the moving plate is 4 times that of the oil below the plate, determine the distance of the plate from the bottom surface (h2) that will minimize the force needed to pull the plate between the two oils at constant velocity.arrow_forwardAn oil is contained between 2 identical parallel plates of 2m2area each. The top plate is pulled tothe left (-x direction) with a force of 0.33N at a velocity of 0.3 m/s. The bottom plate is pulled in theopposite direction with a force of 0.11N at a velocity of 0.1 m/s. The plates are 5mm apart. Whatis the viscosity of the oil in cP?arrow_forwardIf 1000 ft3 atmospheric air at zero Fahrenheit temperature are compressed to a volume of 1728 in3 at a temperature of 3000F, The pressure of the air considering the fact that the mass is constant is Answer in Hg. Round-off your answer to the nearest whole number.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





