
Concept explainers
1 (a)
Calculate the annual rental amounts.
1 (a)
Explanation of Solution
Compute the annual rental amount of Company L, as follows:
Therefore, annual rental amount is $67,673.02.
1 (b)
Explain the way Company T should compute the present value of the lease rights and additional information required to make such calculation.
1 (b)
Explanation of Solution
To determine the present value of the lease rights, Company T should multiply the annual rental payment of $67,673.02 by the PV factor for 6 periods in advance at x%. That x% would be lesser than 14% or incremental borrowing rate of the Company T. Thus the incremental borrowing rate for Company T is the required additional information to compute the PV of lease rights.
2.
Prepare the table summarizing the lease and interest receipts that would be suitable for Company L.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the table summarizing the lease and interest receipts that would be suitable for Company L:
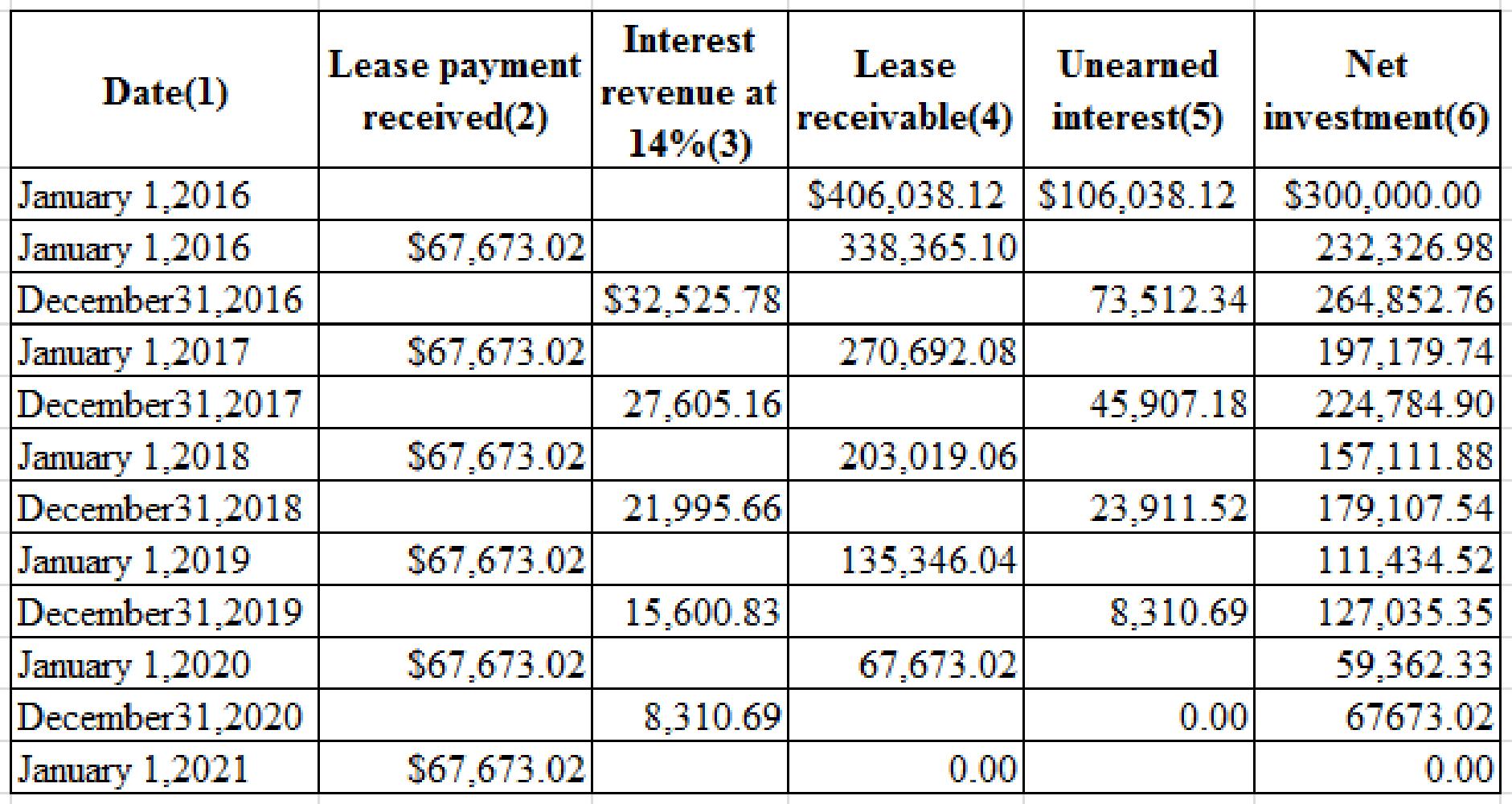
Table (1)
Notes for the above table:
The aforesaid table would also be suitable for Company T, if the incremental borrowing rate is
3.
Prepare
3.
Explanation of Solution
Journal: Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit: Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and
stockholders’ equities . - Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
Prepare journal entries suitable for Company L and Company T for the years 2016 and 2017:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| January 1,2016 | Leased Equipment | 300,000.00 | ||
| Capital Lease Obligation | 300,000.00 | |||
| (To record the capital lease at inception) | ||||
| January 1,2016 | Capital Lease Obligation | 67,673.02 | ||
| Cash | 67,673.02 | |||
| (To record the capital lease payment) | ||||
| During Year | Insurance Expense | 700.00 | ||
| Property Tax Expense | 800.00 | |||
| Cash | 1,500.00 | |||
| (To record the payment for executory costs) | ||||
| December 31, 2016 | 50,000.00 | |||
| Accumulated Depreciation: Equipment | 50,000.00 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) | ||||
| December 31, 2016 | Interest Expense | 32,525.78 | ||
| Accrued Interest on Capital Lease Obligation | 32,525.78 | |||
| (To record the interest expense) | ||||
| January 1,2017 | Accrued Interest on Capital Lease Obligation | 32,525.78 | ||
| Capital Lease Obligation | 35,147.24 | |||
| Cash | 67,673.02 | |||
| (To record the payment of accrued interest and lease payment) | ||||
| During Year | Insurance Expense | 600.00 | ||
| Property Tax Expense | 750.00 | |||
| Cash | 1,350.00 | |||
| (To record the payment for executory costs) | ||||
| December 31, 2017 | Depreciation Expense: Leased Equipment | 50,000.00 | ||
| Accumulated Depreciation: Equipment | 50,000.00 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) | ||||
| December 31, 2017 | Interest Expense | 27,605.16 | ||
| Accrued Interest on Capital Lease Obligation | 27,605.16 | |||
| (To record the interest expense) |
Table (2)
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| January 1,2016 | Equipment Leased to Others | 300,000.00 | ||
| Cash | 300,000.00 | |||
| (To record the payment of capital lease at inception) | ||||
| January 1,2016 | Lease Receivable | 406,038.12 | ||
| Equipment Leased to Others | 300,000.00 | |||
| Unearned Interest: Leases | 106,038.12 | |||
| (To record the lease receivable in a capital lease) | ||||
| January 1,2016 | Cash | 67,673.02 | ||
| Lease Receivable | 67,673.02 | |||
| (To record the receipt lease payment) | ||||
| December31, 2016 | Unearned Interest: Leases | 32,525.78 | ||
| Interest Revenue: Leases | 32,525.78 | |||
| (To recognize the interest revenue for the year) | ||||
| January 1,2017 | Cash | 67,673.02 | ||
| Lease Receivable | 67,673.02 | |||
| (To record the receipt lease payment) | ||||
| December 31, 2017 | Unearned Interest: Leases | 27,605.16 | ||
| Interest Revenue: Leases | 27,605.16 | |||
| (To recognize the interest revenue for the year) |
Table (3)
4.
Prepare income statements and ending balance sheets for both Company L and Company T for the year 2016 and 2017 with appropriate notes.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Balance Sheet: Balance Sheet is one of the financial statements which summarize the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Income statements and ending balance sheets for Company T:
| Company T | ||
| Comparative Income statement(Partial) | ||
| For the year ended December 31 | ||
| 2017 | 2016 | |
| Interest Expense | $27,605.16 | $32,525.78 |
| Insurance Expense | 600.00 | 700.00 |
| Property Tax Expense | 750.00 | 800.00 |
| Depreciation Expense | 50,000.00 | 50,000.00 |
| Comparative Balance Sheet(Partial) | ||
| As on December 31 | ||
| 2017 | 2016 | |
| Assets | ||
| Leased equipment less accumulated depreciation | ||
| (Notes 1 and 2) | $200,000.00 | $250,000.00 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current: | ||
| Capital Lease Obligation | $67,673.02 | $67,673.02 |
| Non-Current: | ||
| Capital Lease Obligation(Notes 1 and 2) | $157,111.88 | $197,179.74 |
Table (4)
Note 1: Description of Leasing Equipment:
Company T is leasing heavy equipment from Company L. The lease term is 6 years and 4 years are still remaining. There are no restrictions and no purchase option too in the lease. The heavy equipment reverts to Company L once the lease period is over.
Note 2: Capital Leases:
The leased property details are as follows:
| 31.12.2017 | 31.12.2016 | |
| Heavy Equipment | $300,000.00 | $300,000.00 |
| Less: Accumulated amortization | $100,000.00 | $50,000.00 |
| Balance | $200,000.00 | $250,000.00 |
Table (5)
Compute the present value of net lease payments under capital leases with future lease payments as of December 31, 2017 as per the following schedule:
| December 31 | Amount($) | |
| 2018 | 67,673.02 | |
| 2019 | 67,673.02 | |
| 2020 | 67,673.02 | |
| 2021 | 67,673.02 | |
| Total Lease Payments | $270,692.08 | |
| Less: Amount that represent interest | (45,907.18) | |
| Present value of lease payments(net) | $224,784.90 | |
Table (6)
Income statements and ending balance sheets for Company L:
| Company L | ||
| Comparative Income statement(Partial) | ||
| For the year ended December 31st | ||
| 2017 | 2016 | |
| Revenue: | ||
| Interest Revenue: Leases | 27,605.16 | 32,525.78 |
| Comparative Balance Sheet(Partial) | ||
| As on December 31st | ||
| 2017 | 2016 | |
| Current Assets | ||
| Net investment in direct financing leases | ||
| (Notes 1 and 2) | $67,673.02 | $67,673.02 |
| Non-Current Assets: | ||
| Net Investment in direct financing leases | ||
| (Notes1 and 2) | $157,111.88 | $197,179.74 |
Table (7)
Note 1: Description of leasing arrangements:
Company L has leased the heavy equipment to Company T. The lease term is 6 years and 4 years are remaining. The heavy equipment reverts to Company L after the expiry of the lease.
Note 2: Net Investment in direct financing leases:
Following are the components of net investments in direct financing leases as on December 31 of the years as depicted in the schedule below:
| 2017 | 2016 | |
| Total lease payment receivable | $270,692.08 | $338,365.10 |
| Less: Unearned interest: leases | 45,907.18 | 73,512.34 |
| Total lease payment receivable(net) | $224,784.90 | $264,852.76 |
Table (8)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
EBK INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING: REPORTING
- Lessor Accounting Issues Ramsey Company leases heavy equipment to Terrell Inc. on March 1, 2019, on the following terms: 1. Twenty-four lease rentals of 2,950 at the beginning of each month are to be paid by Terrell, and the lease is noncancelable. 2. The cost of the heavy equipment to Ramsey was 55,000. 3. Ramsey uses an implicit interest rate of 18% per year and will account for this lease as a sales-type lease. Required: Prepare journal entries for Ramsey (the lessor) to record the lease contract on March 1, 2019, the receipt of the first two lease rentals, and any interest income for March and April 2019. (Round your answers to the nearest dollar.)arrow_forwardDetermining Type of Lease and Subsequent Accounting On January 1, 2019, Ballieu Company leases specialty equipment with an economic life of 8 years to Anderson Company. The lease contains the following terms and provisions: The lease is noncancelable and has a term of 8 years. The annual rentals arc 35,000, payable at the beginning of each year. The interest rate implicit in the lease is 14%. Anderson agrees to pay all executory costs directly to a third party and is given an option to buy the equipment for 1 at the end of the lease term, December 31, 2026. The cost of the equipment to the lessee is 150,000, and the fair value is approximately 185,100. Ballieu incurs no material initial direct costs. It is probable that Ballieu will collect the lease payments. Ballieu estimates that the fair value is expected to be significantly greater than 1 at the end of the lease term. Ballieu calculates that the present value on January 1, 2019, of 8 annual payments in advance of 35,000 discounted at 14% is 185,090.68 (the 1 purchase option is ignored as immaterial). Required: 1. Next Level Identify the classification of the lease transaction from Ballices point of view. Give the reasons for your classification. 2. Prepare all the journal entries tor Ballieu for the years 2019 and 2020. 3. Discuss the disclosure requirements for the lease transaction in Ballices notes to the financial statements.arrow_forwardSales-Type Lease with Guaranteed Residual Value Calder Company, the lessor, enters into a lease with Darwin Company, the lessee, to provide heavy equipment beginning January 1, 2017. The lease is appropriately classified as a sales-type lease. The lease terms, provisions, and related events are as follows: The lease is noncancelable, has a term of 8 years, and has no renewal or bargain purchase option. The annual rentals are 65,000, payable at the end of each year. The interest rate implicit in the lease is 15%. Darwin agrees to pay all executory costs directly to a third party. The cost of the equipment is 280,000. The fair value of the equipment to Calder is 308,021.03. Calder incurs no material initial direct costs. Calder expects that it will be able to collect all lease payments. Calder estimates that the fair value at the end of the lease term will be 50,000 and that the economic life the equipment is 9 years. This residual value is guaranteed by Darwin. The following present value factors are relevant: PV of an ordinary annuity n = 8, i = 15% = 4.487322 PV n = 8, i = 15% = 0.326902 PV n = 1, i = 15% = 0.869565 Required: 1. Determine the proper classification of the lease. 2. Prepare a table summarizing the lease receipts and interest income earned by Calder for this lease. 3. Prepare journal entries for Calder for the years 2019, 2020, and 2021. 4. Next Level Prepare partial balance sheets for December 31, 2019, and December 31, 2020, showing how the accounts should be reported. Use the present value of next years payment approach to classify the lease receivable as current and noncurrent. 5. Next Level Prepare partial balance sheets for December 31, 2019, and December 31, 2020, showing how the accounts should be reported. Use the change in present value approach to classify the lease receivable as current and noncurrent.arrow_forward
- Determining Type of Lease and Subsequent Accounting On January 1, 2019, Caswell Company signs a 10-year cancelable (at the option of either party) agreement to lease a storage building from Wake Company. The following information pertains to this lease agreement: 1. The agreement requires rental payments of 100,000 at the beginning of each year. 2. The cost and fair value of the building on January 1, 2019, is 2 million. The storage building has not been specialized for Caswell. 3. The building has an estimated economic life of 50 years, with no residual value. Caswell depreciates similar buildings according to the straight-line method. 4. The lease does not contain a renewable option clause. At the termination of the lease, the building reverts to the lessor. 5. Caswells incremental borrowing rate is 14% per year. Wake set the annual rental to ensure a 16% rate of return (the loss in service value anticipated for the term of the lease). Caswell knows the implicit interest rate. 6. Executory costs of 7,000 annually, related to taxes on the property, are paid by Caswell directly to the taxing authority on Dec. 31 of each year. Required: 1. Determine what type of lease this is for the lessee. 2. Prepare appropriate journal entries on the lessees books to reflect the signing of the lease agreement and to record the payments and expenses related to this lease for the years 2019 and 2020.arrow_forwardLessee Accounting Issues Timmer Company signs a lease agreement dated January 1, 2019, that provides for it to lease equipment from Landau Company beginning January 1, 2019. The lease terms, provisions, and related events are as follows: The lease is noncancelable and has a term of 5 years. The annual rentals are 83,222.92, payable at the end of each year, and provide Landau with a 12% annual rate of return on its net investment. Timmer agrees to pay all executory costs directly to a third party on December 1 of each year. In 2019, these were insurance, 3,760; property taxes, 5,440. In 2020: insurance, 3,100; property taxes, 5,330. There is no renewal or bargain purchase option. Timmer estimates that the equipment has a fair value of 300,000, an economic life of 5 years, and a zero residual value. Timmers incremental borrowing rate is 16%, it knows the rate implicit in the lease, and it uses the straightline method to record depreciation on similar equipment. Required: 1. Calculate the amount of the asset and liability of Timmer at the inception of the lease. (Round to the nearest dollar.) 2. Prepare a table summarizing the lease payments and interest expense. 3. Prepare journal entries on the books of Timmer for 2019 and 2020. 4. Next Level Prepare a partial balance sheet in regard to the lease for Timmer for December 31, 2019. Use the present value of next years payment approach to classify the finance lease obligation between current and noncurrent. 5. Next Level Prepare a partial balance sheet in regard to the lease for Timmer for December 31, 2019. Use the change in present value approach to classify the finance lease obligation between current and noncurrent.arrow_forwardLessee Accounting Issues Sax Company signs a lease agreement dated January 1, 2019, that provides for it to lease computers from Appleton Company beginning January 1, 2019. The lease terms, provisions, and related events are as follows: 1. The lease term is 5 years. The lease is noncancelable and requires equal rental payments to be made at the end of each year. The computers are not specialized for Sax. 2. The computers have an estimated life of 5 years, a fair value of 300,000, and a zero estimated residual value. 3. Sax agrees to pay all executory costs directly to a third party. 4. The lease contains no renewal or bargain purchase options. 5. The annual payment is set by Appleton at 83,222.92 to earn a rate of return of 12% on its net investment. Sax is aware of this rate. Saxs incremental borrowing rate is 10%. 6. Sax uses the straight-line method to record depreciation on similar equipment. Required: 1. Next Level Examine and evaluate each capitalization criteria and determine what type of lease this is for Sax. 2. Calculate the amount of the asset and liability of Sax at the inception of the lease (round to the nearest dollar). 3. Prepare a table summarizing the lease payments and interest expense. 4. Prepare journal entries for Sax for the years 2019 and 2020.arrow_forward
- Lessee and Lessor Accounting Issues Diego Leasing Company agrees to provide La Jolla Company with equipment under a noncancelable lease for 5 years. The equipment has a 5-year life, cost Diego 25,000, and will have no residual value when the lease term ends. The fair value of the equipment is 30,000. La Jolla agrees to pay all executory costs (500 per year) throughout the lease period directly to a third party. On January 1, 2019, the equipment is delivered. Diego expects a 14% return on its net investment. The five equal annual rents are payable in advance starting January 1, 2019. Required: 1. Assuming this is a sales-type lease for the Diego and a finance lease for the La Jolla, prepare a table summarizing the lease and interest payments suitable for use by either party. 2. Next Level On the assumption that both companies adjust and close books each December 31, prepare journal entries relating to the lease for both companies through December 31, 2020, based on data derived in the table. Assume that La Jolla depreciates similar equipment by the straight line methodarrow_forwardUse the information in RE20-3. Prepare the journal entries that Richie Company (the lessor) would make in the first year of the lease assuming the lease is classified as a sales-type lease. Assume that the lessee is required to make payments on December 31 each year. Also assume that Richie had purchased the equipment at a cost of 200,000.arrow_forwardLessee Accounting with Payments Made at Beginning of Year Adden Company signs a lease agreement dated January 1, 2019, that provides for it to lease non-specialized heavy equipment from Scott Rental Company beginning January 1, 2019. The lease terms, provisions, and related events are as follows: 1. The lease term is 4 years. The lease is noncancelable and requires annual rental payments of 20,000 to be paid in advance at the beginning of each year. 2. The cost, and also fair value, of the heavy equipment to Scott at the inception of the lease is 68,036.62. The equipment has an estimated life of 4 years and has a zero estimated residual value at the end of this time. 3. Adden agrees to pay all executory costs directly to a third party. 4. The lease contains no renewal or bargain purchase options. 5. Scotts interest rate implicit in the lease is 12%. Adden is aware of this rate, which is equal to its borrowing rate. 6. Adden uses the straight-line method to record depreciation on similar equipment. 7. Executory costs paid at the end of the year by Adden are: Required: 1. Next Level Determine what type of lease this is for Adden. 2. Prepare a table summarizing the lease payments and interest expense for Adden. 3. Prepare journal entries for Adden for the years 2019 and 2020.arrow_forward
- Owens Company leased equipment for 4 years at 50,000 a year with an option to renew the lease for 6 years at 2,000 per month or to purchase the equipment for 25,000 (a price considerably less than the expected fair value) after the initial lease term of 4 years. Why would this lease qualify as a finance lease?arrow_forwardSales-Type Lease with Unguaranteed Residual Value Lessor Company and Lessee Company enter into a 5-year, noncancelable, sales-type lease on January 1, 2019, for equipment that cost Lessor 375,000 (useful life is 5 years). The fair value of the equipment is 400,000. Lessor expects a 12% return on the cost of the asset over the 5-year period of the lease. The equipment will have an estimated unguaranteed residual value of 20,000 at the end of the fifth year of the lease. The lease provisions require 5 equal annual amounts, payable each January 1, beginning with January 1, 2019. Lessee pays all executory costs directly to a third party. The equipment reverts to the lessor at the termination of the lease. Assume there are no initial direct costs, and the lessor expects to be able to collect all lease payments. Required: 1. Show how Lessor should compute the annual rental amounts. 2. Prepare a table summarizing the lease and interest receipts that would be suitable for Lessor. 3. Prepare a table showing the accretion of the unguaranteed residual asset. 4. Prepare the journal entries for Lessor for the years 2019, 2020, and 2021.arrow_forwardOn October 1, 2019, Grahams WeedFeed Inc. signs a contract to maintain the grounds for BigData Corp. The contract ends on March 31, 2020, and has a monthly payment of 3,200. The contract does not include any stipulations for additional periods. On June 1, Grahams WeedFeed and BigData sign a new 12-month contract that is retroactive to April 1, 2020. The monthly fee for the new contract is 4,000 per month and is also retroactive to April 1, 2020. During April and May of 2020, while the new contract was being negotiated, Grahams Weed Feed continued to maintain the grounds, and BigData continued to pay 3,200 per month. BigData was satisfied with Grahams WeedFeeds performance, and the only issue during negotiations was the monthly fee. Required: Determine if a valid contract exists between Grahams WeedFeed and BigData during April and May 2020.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning



