
Concept explainers
Credit Policy at Howlett Industries
Sterling Wyatt, the president of Howlett Industries, has been exploring ways of improving the company’s financial performance. Howlett manufactures and sells office equipment to retailers. The company’s growth has been relatively slow in recent years, but with an expansion in the economy, it appears that sales may increase more rapidly in the future. Sterling has asked Andrew Preston, the company’s treasurer, to examine Howlett’s credit policy to see if a change can help increase profitability.
The company currently has a policy of net 30. As with any credit sales, default rates are always of concern. Because of Howlett’s screening and collection process, the default rate on credit is currently only 1.6 percent. Andrew has examined the company’s credit policy in relation to other vendors, and he has found three available options.
The first option is to relax the company’s decision on when to grant credit. The second option is to increase the credit period to net 45, and the third option is a combination of the relaxed credit policy and the extension of the credit period to net 45. On the positive side, each of the three policies under consideration would increase sales. The three policies have the drawbacks that default rates would increase, the administrative costs of managing the firm’s receivables would increase, and the receivables period would increase. The effect of the credit policy change would impact all four of these variables to different degrees. Andrew has prepared the following table outlining the effect on each of these variables:
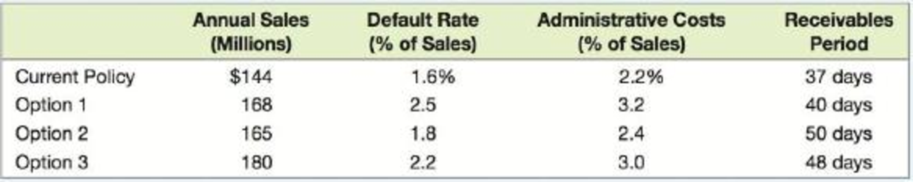
Howlett’s variable costs of production are 45 percent of sales, and the relevant interest rate is a 6 percent effective annual rate.
1. Which credit policy should the company use?
To evaluate: The credit policy of the firm.
Introduction:
Credit policy refers to a set of procedures that include the terms and conditions for providing goods on credit and principles for making collections.
Answer to Problem 1M
Company H should select Option 1, because it has the highest net present value (NPV) of $34,226,117.98 compared to other two options.
Explanation of Solution
The formula to calculate the average daily sales under current policy:
Hence, the average sales under current policy is $394,520.55.
The formula to calculate average daily variable costs under current policy:
Hence, the variable costs under current policy is $177,534.25.
The formula to calculate the average daily default under current policy:
Hence, the average daily default under current policy is $6312.33.
The formula to calculate average daily administrative cost under current policy:
Hence, the average administrative costs under current policy is $8,679.45.
The formula to calculate the interest rate for the collection period:
Hence, the interest rate is 0.61%.
The formula to calculate the net present value (NPV) under current policy:
Hence, the NPV under current policy is $32,936,321.48.
Option 1:
The formula to calculate the average daily sales under option 1:
Hence, the average daily sales under option 1 is $460,273.97.
The formula to calculate average daily variable costs under option 1:
Hence, the average daily variable costs under option 1 is $207,123.29.
The formula to calculate average daily default under option 1:
Hence, average daily default under option 1 is $11,506.85.
The formula to calculate average daily administrative cost under option 1:
Hence, the average daily administrative costs under option 1 is $14,728.77.
The formula to calculate interest rate for the for collection period:
Hence, the interest rate is 0.659%.
The formula to calculate the net present value (NPV) under option 1:
Hence, the NPV under option 1 is $34,226,117.98.
Option 2:
The formula to calculate the average daily sales under option 2:
Hence, the average daily sales under option 2 is $452,054.79.
The formula to calculate average daily variable costs under option 2:
Hence, the average daily variable costs under option 2 is $203,424.66.
The formula to calculate average daily default under option 2:
Hence, the average daily default under option 2 is $8,136.99.
The formula to calculate average daily administrative cost under option 2:
Hence, the average daily administrative costs under option 2 is $10,849.32.
The formula to calculate interest rate for the for collection period:
Hence, the interest rate is 0.852%.
The formula to calculate NPV under option 2:
Hence, the NPV under option 2 is $27,632,189.89.
Option 3:
The formula to calculate the average daily sales under current policy:
Hence, the average daily sales under option 3 is $493,150.68.
The formula to calculate average daily variable costs under option 3:
Hence, the average daily variable costs under option 3 is $221,917.81.
The formula to calculate average daily default under option 3:
Hence, the average daily default under option 3 is $10,849.32.
The formula to calculate average daily administrative cost under option 3:
Hence, the average daily administrative costs under option 3 is $14,794.52.
The formula to calculate interest rate for collection period:
Hence, the interest rate is 0.792%.
The formula to calculate NPV under option 3:
Hence, the NPV under option 3 is $30,786,798.099.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 20 Solutions
FUND OF CORPORATE FINANCE LL W/ACCESS
- Ethics and Revenue Recognition Alan Spalding is CEO of a large appliance wholesaler. Alan is under pressure from Wall Street Analysts to meet his aggressive sales revenue growth projections. Unfortunately, near the end of the year he realizes that sales must dramatically improve if his projections are going to be met. To accomplish this objective, he orders his sales force to contact their largest customers and offer them price discounts if they buy by the end of the year. Alan also offered to deliver the merchandise to a third-party warehouse with whom the customers could arrange delivery when the merchandise was needed. Required: Do you believe that revenue from these sales should be recognized in the current year? Why or why not?arrow_forwardGlencoe First National Bank operated for years under the assumption that profitability can be increased by increasing dollar volumes. Historically, First Nationals efforts were directed toward increasing total dollars of sales and total dollars of account balances. In recent years, however, First Nationals profits have been eroding. Increased competition, particularly from savings and loan institutions, was the cause of the difficulties. As key managers discussed the banks problems, it became apparent that they had no idea what their products were costing. Upon reflection, they realized that they had often made decisions to offer a new product which promised to increase dollar balances without any consideration of what it cost to provide the service. After some discussion, the bank decided to hire a consultant to compute the costs of three products: checking accounts, personal loans, and the gold VISA. The consultant identified the following activities, costs, and activity drivers (annual data): The following annual information on the three products was also made available: In light of the new cost information, Larry Roberts, the bank president, wanted to know whether a decision made two years ago to modify the banks checking account product was sound. At that time, the service charge was eliminated on accounts with an average annual balance greater than 1,000. Based on increases in the total dollars in checking, Larry was pleased with the new product. The checking account product is described as follows: (1) checking account balances greater than 500 earn interest of 2 percent per year, and (2) a service charge of 5 per month is charged for balances less than 1,000. The bank earns 4 percent on checking account deposits. Fifty percent of the accounts are less than 500 and have an average balance of 400 per account. Ten percent of the accounts are between 500 and 1,000 and average 750 per account. Twenty-five percent of the accounts are between 1,000 and 2,767; the average balance is 2,000. The remaining accounts carry a balance greater than 2,767. The average balance for these accounts is 5,000. Research indicates that the 2,000 category was by far the greatest contributor to the increase in dollar volume when the checking account product was modified two years ago. Required: 1. Calculate rates for each activity. 2. Using the rates computed in Requirement 1, calculate the cost of each product. 3. Evaluate the checking account product. Are all accounts profitable? Compute the average annual profitability per account for the four categories of accounts described in the problem. What recommendations would you make to increase the profitability of the checking account product? (Break-even analysis for the unprofitable categories may be helpful.)arrow_forward“We really need to get this new material-handling equipment in operation just after the new year begins. I hope we can finance it largely with cash and marketable securities, but if necessary we can get a short-term loan down at MetroBank.” This statement by Beth Davies-Lowry, president of Intercoastal Electronics Company, concluded a meeting she had called with the firm’s top management. Intercoastal is a small, rapidly growing wholesaler of consumer electronic products. The firm’s main product lines are small kitchen appliances and power tools. Marcia Wilcox, Intercoastal’s General Manager of Marketing, has recently completed a sales forecast. She believes the company’s sales during the first quarter of 20x1 will increase by 10 percent each month over the previous month’s sales. Then Wilcox expects sales to remain constant for several months. Intercoastal’s projected balance sheet as of December 31, 20x0, is as follows: Cash $ 35,000 Accounts receivable 270,000…arrow_forward
- QuickBank has decided to lower the interest rate it charges on business loans in order to attract more business. It has succeeded in boosting the number of loan applications, but it finds that many of the applicants turn out to be very poor credit risks. This illustrates the problem known as adverse selection moral hazard the principal-agent porblem diversificationarrow_forwardGregg’s Shipping Supplies Ltd (GSSL) trades in the buying and selling of ship spares and has several branches within the Caribbean. Recently the company has seen a rapid increase in demand of its products across all branches and is therefore in need of additional financing to adequately boost its supply inventory. The corporate banking head of Bankers Choice Bank is requesting a full set of financial statements to ensure that granting the loan to GSSL would be financially feasible during a period when many businesses are facing financial challenges. The company financial year ends on June 30 each year and you have been tasked with the responsibility to prepare the financial information for the branch that is linked to your first name initial. Trinidad Branch Required:a) Prepare the necessary adjusting journal entries on June 30, 2022 b) Prepare the Adjusted Trial balance at June 30, 2022. c) Prepare the company’s multiple-step income statement for the period ending June 30, 2022 d)…arrow_forwardOutsourcing Call Centers; Strategy; Ethics; Present-Value Analysis (Chapter 12) Merchants’Bank (MB) is a large regional bank operating in 634 locations in the southeastern United States.Until 2014, the bank operated a call center for customer inquiries out of a single location in Atlanta,Georgia. MB understood the importance of the call center for overall customer satisfaction andmade sure that the center was managed effectively. However, in early 2013, it became clear that thecost of running the center was increasing very rapidly, along with the firm’s growth, and that someissues were arising about the quality of the service. To improve the quality and dramatically reducethe cost of the service, MB moved its call center to Bangalore, India, to be run by an experiencedoutsourcing firm, Naftel, which offers similar services to other banks like MB.The Naftel contract was for 5 years, and in late 2017 it was time to consider whether to renewthe contract, change to another call center…arrow_forward
- A lending officer at C Bank has insisted that your firm improve the current ratio of 0.8 before the bank will consider a loan. Which of the following actions would INCREASE the ratio? Group of answer choices: Selling some of the existing inventory at cost Using cash to pay off current liabilities Borrowing long-term debt to pay off short-term bank loan Paying off long-term debt. Collecting some of the current accounts receivablearrow_forwardSuppose you are the marketing manager of the credit card department of a financial institution. After examining current market conditions, the objective is to support the company’s growth through a market penetration strategy. How would you apply this strategy to increase the profitability of the credit card?arrow_forwardSuppose a company’s current credit terms are 1/10,net 30, but management is considering changingits terms to 2/10, net 40, relaxing its credit standards, and putting less pressure on slow-payingcustomers. How would you expect these changesto affect (a) sales, (b) the percentage of customerswho take discounts, (c) the percentage of customers who pay late, and (d) the percentage of customers who end up as bad debts?arrow_forward
- I am currently working on a study guide and came across the following question. Which of the following statements correctly reflects the effects of granting credit to customers? a) total revenues may increase if both the quantity sold and the price per unit increase when credit is granted b) a firm's cash cycle generally increases if credit is granted, all else equal c) both the cost of default and the cost of discounts must be considered before granting credit d) a firm may have to increase its borrowing if it decides to grant credit to its new customers e) all of the above My professor stated that the answer is all of the above, but after going through the readings and resources provided I could not find a way to understand how each answer is considered to be correct. I also e-mailed my professor and am waiting for a response, so I decided to post my question here as well.arrow_forwardHow would each of the following factors affectratio analysis? (a) The firm’s sales are highly seasonal. (b) The firm uses some type of windowdressing. (c) The firm issues more debt and usesthe proceeds to repurchase stock. (d) The firmleases more of its fixed assets than most firmsin its industry. (e) In an effort to stimulate sales,the firm eases its credit policy by offering 60-daycredit terms rather than the current 30-day terms.How might one use sensitivity analysis to helpquantify the answers?arrow_forwardYou are a Corporate Credit Analyst for your bank. A new corporate customer in the manufacturing sector approached your bank for a large credit facility in the sum of $20 million for production equipment and warehousing. The customer submitted the following financials to you. List two strengths and two weaknesses of the borrower in relation to credit.arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning




