
Concept explainers
Spreadsheet and Statement of Cash Flows The following information was taken from Lamberson Company’s accounting records:
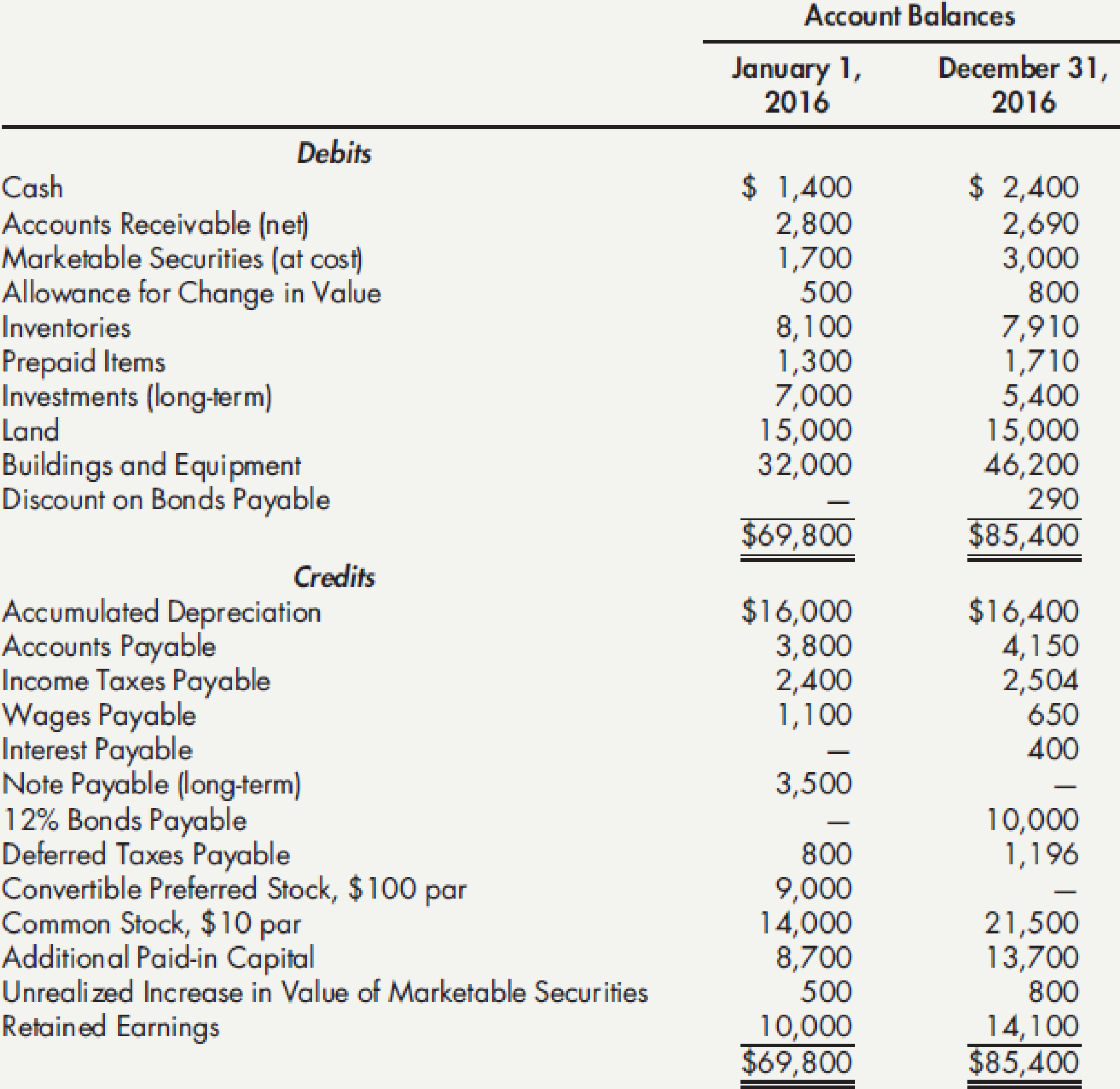
Additional information for the year:
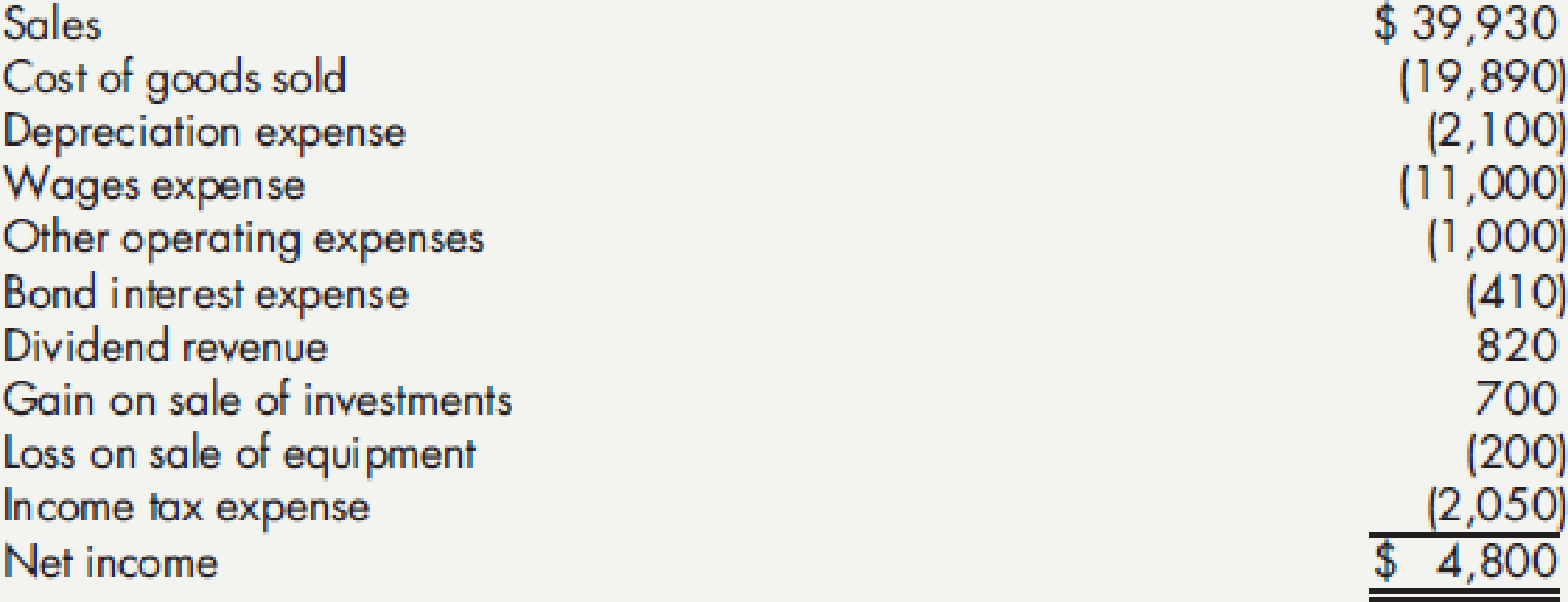
- a. Dividends declared and paid totaled $700.
- b. On January 1, 2016, convertible
preferred stock that had originally been issued at par value were converted into 500 shares of common stock. The book value method was used to account for the conversion. - c. Long-term nonmarketable investments that cost $1,600 were sold for $2,300.
- d. The long-term note payable was paid by issuing 250 shares of common stock at the beginning of the year.
- e. Equipment with a cost of $2,000 and a book value of $300 was sold for $100. The company uses one Accumulated
Depreciation account for all depreciable assets. - f. Equipment was purchased at a cost of $16,200.
- g. The 12% bonds payable were issued on August 31, 2016, at 97. They mature on August 31, 2026. The company uses the straight-line method to amortize the discount.
- h. Taxable income was less than pretax accounting income, resulting in a $396 increase in
deferred taxes payable. - i. Short-term marketable securities were purchased at a cost of $1,300. The portfolio was increased by $300 to a $3,800 fair value at year-end by adjusting the related allowance account.
Required:
- 1. Prepare a spreadsheet to support Lamberson Company’s 2016 statement of cash flows.
- 2. Perpare the statement of cash flows.
- 3. Next Level Compute the cash flow from operations to sales ratio and the profit margin ratio for 2016. What is the primary reason for the difference in the results of the ratios?
1.
Prepare a statement of cash flows using spreadsheet method.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of cash flows: This statement reports all the cash transactions which are responsible for inflow and outflow of cash, and result of these transactions is reported as ending balance of cash at the end of reported period. Statement of cash flows includes the changes in cash balance due to operating, investing, and financing activities.
Worksheet: A worksheet is a spreadsheet used while preparing a financial statement. It is a type of form having multiple columns and it is used in the adjustment process. The use of a worksheet is optional for any organization. A worksheet can neither be considered as a journal nor a part of the general ledger.
Prepare a statement of cash flows using spreadsheet method.
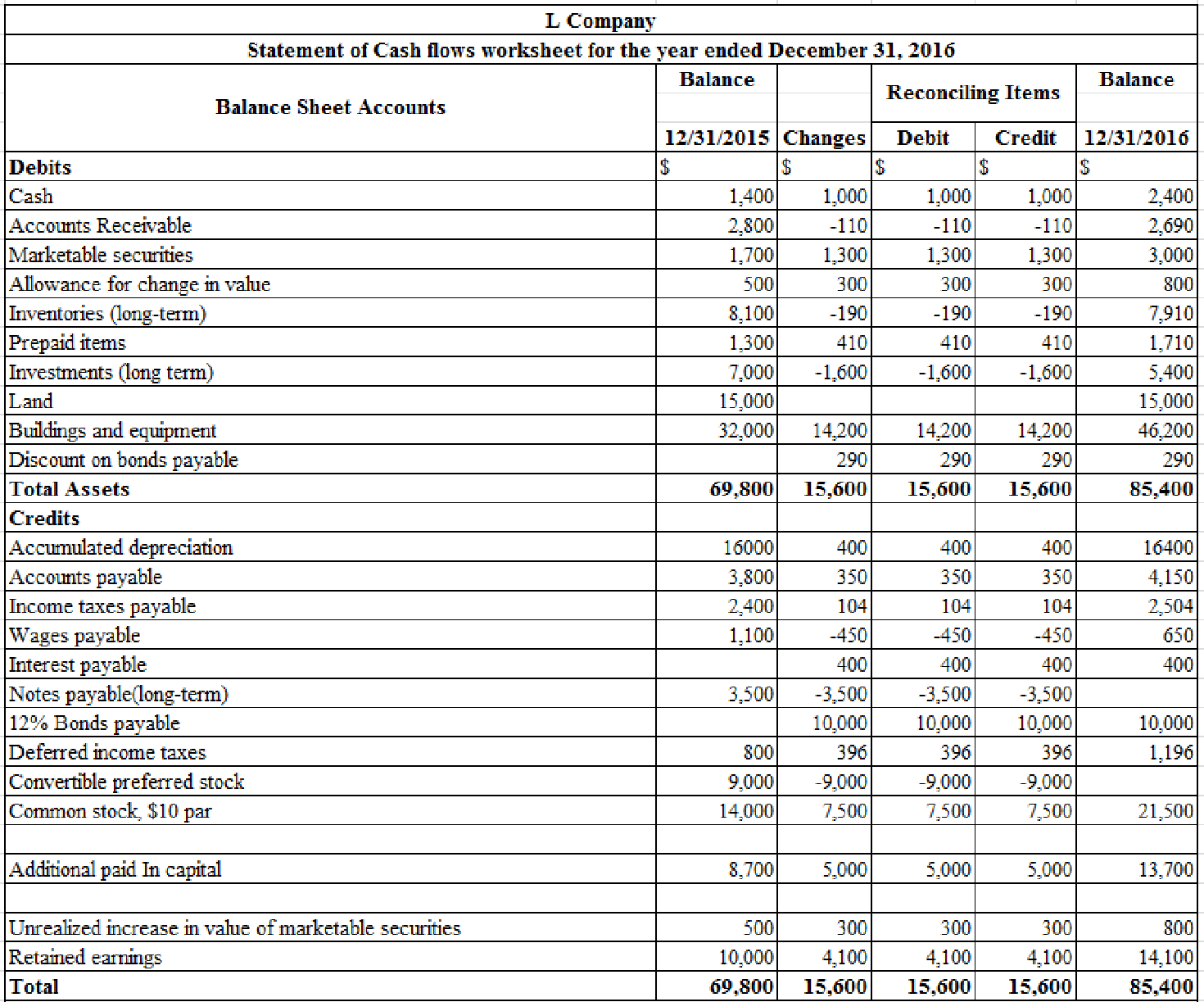
Table (1)
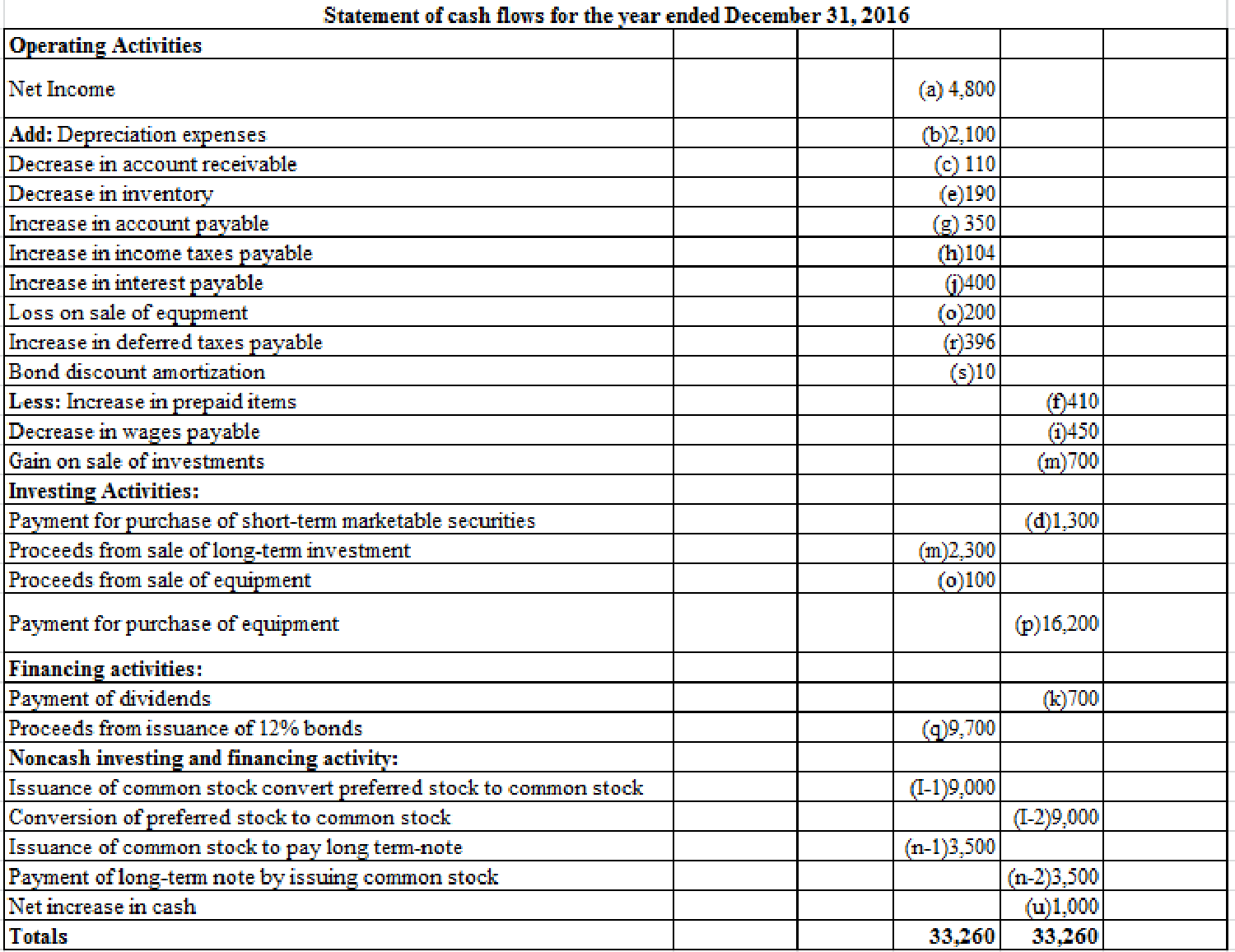
Table (2)
Notes:
- a. Depreciation for the year ended is $2,100
- b. Calculate accounts receivable.
- c. Calculate the marketable securities.
- d. Calculate the decrease in inventories.
- e. Calculate the prepaid items.
- f. Calculate the increase in accounts payable.
- g. Calculate the income taxes payable.
- h. Calculate the wages payable.
j. Interest payable for the year ended is $400.
k. Calculate the retained earnings.
l-1. Calculate the issuance of common stock to preferred stock.
1-2. Conversion of preferred stock to common stock is $9,000.
m. Calculate the proceeds from sale of long-term investments
n-1. Calculate the Issuance of common stock to pay long-term note.
n-2. Long- term notes payable is $3,500.
o. Calculate the sale of building and equipment.
- Cost of the equipment is $2,000.
- Loss on sale of equipment is $200.
- Proceeds from sale of equipment are $100.
p. Calculate the payment for purchase of equipment.
q. Calculate the proceeds from issuance of bonds.
r. Calculate the increase in deferred tax.
s. Calculate the bond discount amortization.
t. Calculate the allowance for change in value.
u. Calculate net increase in cash.
2.
Prepare the statement of cash flows of L Company for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the statement of cash flows of L Company for the year ended December 31, 2016.
| L Company | ||
| Statement of cash flows for the year 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Operating Activities: | ||
| Net income | 4,800 | |
| Adjustment for non-cash income items: | ||
| Add: Depreciation expenses | 2,100 | |
| Bound discount amortization | 10 | |
| Loss on sale of equipment | 200 | |
| Increase in deferred taxes payable | 396 | |
| Less: Gain on sale of equipment | (700) | |
| Adjustments for cash flow effects from working capital items: | ||
| Decrease in accounts receivable | 110 | |
| Decrease in inventories | 190 | |
| Increase in prepaid items | (410) | |
| Increase in accounts payable | 350 | |
| Decrease in wages payable | (450) | |
| Increase in income taxes payable | 104 | |
| Increase in interest payable | 400 | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 7,100 | |
| Investing Activities: | ||
| Payment for purchase of short-term marketable securities | (1,300) | |
| Proceeds from sale of long-term investments | 2,300 | |
| Proceeds from sale of equipment | 100 | |
| Payment for purchase of equipment | (16,200) | |
| Net cash used for investing activities | (15,100) | |
| Financing Activities: | ||
| Proceeds from issuance of 12% bonds | 9,700 | |
| Payment of dividends | (700) | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 9,000 | |
| Net increase in cash( schedule 1) | 1,000 | |
| Cash on January 1, 2016 | 1,400 | |
| Cash on December 31,2016 | 2,400 | |
| Schedule 1: Investing and Financial Activities Not Affecting Cash | ||
| Financing Activities: | ||
| Conversion of preferred stock to common stock | (9,000) | |
| Issuance of common stock to convert preferred stock | 9,000 | |
| Payment of long-term note by issuing common stock | (3,500) | |
| Issuance of common stock to pay long- term note | 3,500 | |
Table (3)
3.
Determine the difference in cash flow from operation to sales ratio and profit margin ratio of L Company for the year 2016.
Explanation of Solution
Cash flow to sales ratio: The cash flow to sales ratio reveals the ability of a business to generate cash flow in proportion to its sales volume. It is calculated by dividing operating cash flows by net sales.
Formula for Formula for to sales ratio:
Profit margin ratio: The profit margin ratio, also called the return on sales ratio or gross profit ratio, is a profitability ratio that measures the amount of net income earned with each dollar of sales generated by comparing the net income and net sales of a company.
Formula for Formula for to profit margin ratio
The primary reason for the difference is depreciation expenses ($2,100), which was deducted to determine the net income, which did not involve an operating cash outflow.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting and Analysis
- Common stock transactions on the statement of cash flows Jones Industries received 600,000 from issuing shares of its common stock and 400,000 from issuing bonds. During the year, Jones Industries also paid dividends of 60,000. How are the effects of these transactions reported on the statement of cash flows?arrow_forwardTidwell Company experienced the following during 20X1: a. Sold preferred stock for 480,000. b. Declared dividends of 150,000 payable on March 1, 20X2. c. Borrowed 575,000 from a bank on a 2-year note. d. Purchased 80,000 of its own common stock to hold as treasury stock. e. Repaid 5-year bonds issued for 400,000 that mature and are due in December. Required: Prepare the net cash from financing activities section of the statement of cash flows.arrow_forwardStatement of Cash Flows The following are Mueller Companys cash flow activities: a. Net income, 68,000 b. Increase in accounts receivable, 4,400 c. Receipt from sale of common stock, 12,300 d. Depreciation expense, 11,300 e. Dividends paid, 24,500 f. Payment for purchase of building, 65,000 g. Bond discount amortization, 2,700 h. Receipt from sale of long-term investments at cost, 10,600 i. Payment for purchase of equipment, 8,000 j. Receipt from sale of preferred stock, 20,000 k. Increase in income taxes payable, 3,500 l. Payment for purchase of land, 9,700 m. Decrease in accounts payable, 2,900 n. Increase in inventories, 10,300 o. Beginning cash balance, 18,000 Required: Prepare Mueller Company's statement of cash flows.arrow_forward
- Comprehensive: Balance Sheet from Statement of Cash Flows Mills Company prepared the following balance sheet at the beginning of 2019: Additional information related to the statement of cash flows: 1. The long-term bonds have a face value of 6,000 and were issued on December 31, 2019. 2. The building was purchased on December 30, 2019. 3. The land was sold at its original cost. 4. The common stock which was sold totaled 300 shares and had a par value of 10 per share. Required: Next Level Prepare a classified balance sheet for Mills as of December 31, 2019. (Hint. Review the information on the statement of cash flows and the balances in the beginning balance sheet accounts to determine the impact on the ending balance sheet accounts.)arrow_forwardSolpoder Corporation has the following comparative financial statements: Dividends of 17,100 were paid. No equipment was purchased or retired during the current year. Required: Prepare a statement of cash flows using the direct method.arrow_forwardEXPANDED STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS Financial statements for McGinnis Company as well as additional information relevant to cash flows during the period are given below and on the next page. Additional information: 1. Office equipment was sold in 20-2 for 35,000. Additional information on the office equipment sold is provided below. 2. Depreciation expense for the year was 70,000. 3. The following purchases were made for cash: 4. Declared and paid cash dividends of 40,000. 5. Issued 10,000 shares of 10 par common stock for 22 per share. 6. Acquired additional office equipment by issuing a note payable for 8,000. REQUIRED Prepare a statement of cash flows explaining the change in cash and cash equivalents for the year ended December 31, 20-2.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub





