
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The charges of the
Concept introduction: Strong ligands produce high crystal field splitting and weak ligands produce small crystal field splitting. High spin complex ions have low crystal field splitting.
To determine: The charges of the
(a)
Answer to Problem 22.49QP
Solution
The charge on
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The manganese minerals pyrolusite,
The charge on
There is
Substitute the value of number of atoms of manganese and oxygen atoms and charge on the compound in the above equation.
Therefore, the charge on
Manganese is present in two oxidation states
The charge on
There is
Substitute the value of number of atoms of manganese and oxygen atoms and charge on the compound in the above equation.
The charge on
There are
Substitute the value of number of atoms of manganese and oxygen atoms and charge on the compound in the above equation.
Therefore, charge on
(b)
To determine: The compound in which there could be high spin and low spin
(b)
Answer to Problem 22.49QP
Solution
The compound in which there could be high spin and low spin
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The charge on
The electronic configuration of
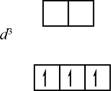
Figure 1
There is only high spin state in
The charge on
The electronic configuration of
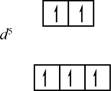
Figure 2
Three electrons will occupy the lower energy orbital (
In case of low spin state, pairing of electrons takes place. The distribution of electrons is as follows:
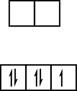
Figure 3
All electrons will occupy the lower energy orbital (
Therefore, the compound in which there could be high spin and low spin
Conclusion
The compound in which there could be high spin and low spin
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Chemistry: The Science in Context (Fifth Edition)
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





